|
19th Century BC
The 19th century BC was the century that lasted from 1900 BC to 1801 BC. Events * 1900 BC: Transition from Early Helladic III to Middle Helladic culture in Greece. * c. 1900 BC: Minoan Old Palace (Protopalatial) period starts in Crete. * c. 1900 BC: Fall of last Sumerian dynasty. * c. 1900 BC: Late Harappan phase of the Indus Valley civilization begins * c. 1900 BC: The Mokaya along the Pacific coast of present-day Chiapas, Mexico were preparing cacao beverages. * c. 1900 BC: Port of Lothal is abandoned. * Hittite empire in Hattusa, Anatolia. * c. 1897 BC: Senwosret II (Twelfth Dynasty) started to rule. He built Kahun near his pyramide tomb complex at el-Lahun. * c. 1895 BC–1878 BC: "Pectoral of Senwosret II", from the tomb of princess Sithathoryunet at el-Lahun was made. Twelfth Dynasty. It is now in the Metropolitan Museum of Art, New York. * c. 1880 BC: Pharaoh Senwosret II starts to rule (other date is 1897 BC). * 1878 BC: Senwosret II (Twelfth Dynasty) died. * c. 1878 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
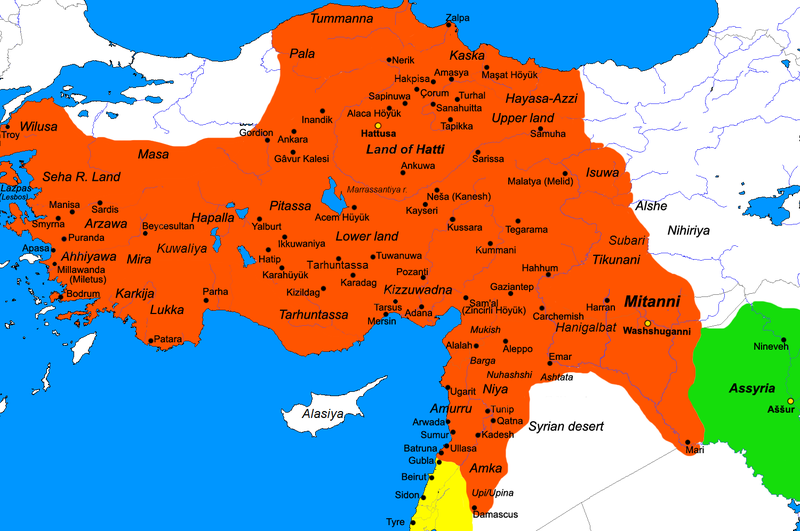
Hattusa
Hattusa (also Ḫattuša or Hattusas ; Hittite: URU''Ḫa-at-tu-ša'', Turkish: Hattuşaş , Hattic: Hattush) was the capital of the Hittite Empire in the late Bronze Age. Its ruins lie near modern Boğazkale, Turkey, within the great loop of the Kızılırmak River (Hittite: ''Marashantiya''; Greek: '' Halys''). Hattusa was added to the UNESCO World Heritage Site list in 1986. Surroundings The landscape surrounding the city included rich agricultural fields and hill lands for pasture as well as woods. Smaller woods are still found outside the city, but in ancient times, they were far more widespread. This meant the inhabitants had an excellent supply of timber when building their houses and other structures. The fields provided the people with a subsistence crop of wheat, barley and lentils. Flax was also harvested, but their primary source for clothing was sheep wool. They also hunted deer in the forest, but this was probably only a luxury reserved for the nobility. Dome ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Senusret III
Khakaure Senusret III (also written as Senwosret III or the hellenised form, Sesostris III) was a pharaoh of Egypt. He ruled from 1878 BC to 1839 BC during a time of great power and prosperity, and was the fifth king of the Twelfth Dynasty of the Middle Kingdom. He was a great pharaoh of the Twelfth Dynasty and is considered to be, perhaps, the most powerful Egyptian ruler of the dynasty. Consequently, he is regarded as one of the sources for the legend about Sesostris. His military campaigns gave rise to an era of peace and economic prosperity that reduced the power of regional rulers and led to a revival in craftwork, trade, and urban development."''The Pyramids: Their Archeology and History''", Miroslav Verner, Translated by Steven Rendall,p386-387 & p416-421, Atlantic, Senusret III was among the few Egyptian kings who were deified and honored with a cult during their own lifetime. Family Senusret III was the son of Senusret II and Khenemetneferhedjet I, also called Khene ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Senwosret III
Khakaure Senusret III (also written as Senwosret III or the hellenised form, Sesostris III) was a pharaoh of Egypt. He ruled from 1878 BC to 1839 BC during a time of great power and prosperity, and was the fifth king of the Twelfth Dynasty of the Middle Kingdom. He was a great pharaoh of the Twelfth Dynasty and is considered to be, perhaps, the most powerful Egyptian ruler of the dynasty. Consequently, he is regarded as one of the sources for the legend about Sesostris. His military campaigns gave rise to an era of peace and economic prosperity that reduced the power of regional rulers and led to a revival in craftwork, trade, and urban development."''The Pyramids: Their Archeology and History''", Miroslav Verner, Translated by Steven Rendall,p386-387 & p416-421, Atlantic, Senusret III was among the few Egyptian kings who were deified and honored with a cult during their own lifetime. Family Senusret III was the son of Senusret II and Khenemetneferhedjet I, also called Khene ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pharaoh
Pharaoh (, ; Egyptian: ''pr ꜥꜣ''; cop, , Pǝrro; Biblical Hebrew: ''Parʿō'') is the vernacular term often used by modern authors for the kings of ancient Egypt who ruled as monarchs from the First Dynasty (c. 3150 BC) until the annexation of Egypt by the Roman Empire in 30 BC. However, regardless of gender, "king" was the term used most frequently by the ancient Egyptians for their monarchs through the middle of the Eighteenth Dynasty during the New Kingdom. The term "pharaoh" was not used contemporaneously for a ruler until a possible reference to Merneptah, c. 1210 BC during the Nineteenth Dynasty, nor consistently used until the decline and instability that began with the Twenty-Fifth Dynasty. In the early dynasties, ancient Egyptian kings had as many as three titles: the Horus, the Sedge and Bee ( ''nswt-bjtj''), and the Two Ladies or Nebty ( ''nbtj'') name. The Golden Horus and the nomen and prenomen titles were added later. In Egyptian society, religio ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
New York City
New York, often called New York City or NYC, is the List of United States cities by population, most populous city in the United States. With a 2020 population of 8,804,190 distributed over , New York City is also the List of United States cities by population density, most densely populated major city in the United States, and is more than twice as populous as second-place Los Angeles. New York City lies at the southern tip of New York (state), New York State, and constitutes the geographical and demographic center of both the Northeast megalopolis and the New York metropolitan area, the largest metropolitan area in the world by urban area, urban landmass. With over 20.1 million people in its metropolitan statistical area and 23.5 million in its combined statistical area as of 2020, New York is one of the world's most populous Megacity, megacities, and over 58 million people live within of the city. New York City is a global city, global Culture of New ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Metropolitan Museum Of Art
The Metropolitan Museum of Art of New York City, colloquially "the Met", is the largest art museum in the Americas. Its permanent collection contains over two million works, divided among 17 curatorial departments. The main building at 1000 Fifth Avenue, along the Museum Mile on the eastern edge of Central Park on Manhattan's Upper East Side, is by area one of the world's largest art museums. The first portion of the approximately building was built in 1880. A much smaller second location, The Cloisters at Fort Tryon Park in Upper Manhattan, contains an extensive collection of art, architecture, and artifacts from medieval Europe. The Metropolitan Museum of Art was founded in 1870 with its mission to bring art and art education to the American people. The museum's permanent collection consists of works of art from classical antiquity and ancient Egypt, paintings, and sculptures from nearly all the European masters, and an extensive collection of American and modern ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sithathoryunet
Sithathoriunet (her name means “daughter of Hathor of Dendera”) was an Ancient Egyptian ''king's daughter'' of the 12th Dynasty, mainly known from her burial at El-Lahun in which a treasure trove of jewellery was found., p.99 She was possibly a daughter of Senusret II since her burial site was found next to the pyramid of this king. If so, this would make her one of five known children and one of three daughters of Senusret II—the other children were Senusret III, Senusretseneb, Itakayt and Nofret. Sithathoriunet was buried in the Kahun pyramid complex. She must have died while Amenemhat III was pharaoh, since objects with his name were found in her tomb. Her name and titles survived on her canopic jars and on an alabaster vessel found in her tomb. The tomb was excavated in 1914 by Flinders Petrie and Guy Brunton. It had previously been robbed in antiquity but a niche in the burial site escaped the looters' attention. In this niche were found remains of several boxes ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Princess
Princess is a regal rank and the feminine equivalent of prince (from Latin ''princeps'', meaning principal citizen). Most often, the term has been used for the consort of a prince, or for the daughter of a king or prince. Princess as a substantive title Some princesses are reigning monarchs of principalities. There have been fewer instances of reigning princesses than reigning princes, as most principalities excluded women from inheriting the throne. Examples of princesses regnant have included Constance of Antioch, princess regnant of Antioch in the 12th century. Since the President of France, an office for which women are eligible, is ''ex-officio'' a Co-Prince of Andorra, then Andorra could theoretically be jointly ruled by a princess. Princess as a courtesy title Descendants of monarchs For many centuries, the title "princess" was not regularly used for a monarch's daughter, who, in English, might simply be called "Lady". Old English had no female equivalent of "prince ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pectoral (Ancient Egypt)
The pectorals of ancient Egypt were a form of jewelry, often represented as a brooch. These were mostly worn by richer people and the pharaoh. One type is attached with a nah necklace, meant to be suspended from the neck but to lie upon the breast. Statuary from the Old Kingdom onwards shows this form. A later form was attached as a brooch, with the thematic, iconographic function and statement outweighing its actual use as a piece of jewellery for adornment. The thematic statements were typically about the pharaoh or statements of ancient Egyptian mythology and culture. They are usually of gold with cloisonné inlays of gemstones. Ancient Egyptian definition of pectoral The many determinatives for ''pectoral'' are not portrayed in the Gardiner's Sign List. However, one of the 10 words for 'pectoral', or 'collar' uses the Usekh collar determinative, S11, the ''"collar necklace"'' S11. However a similar hieroglyph for the verb "to collar", "to net" shows the relationship betwe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
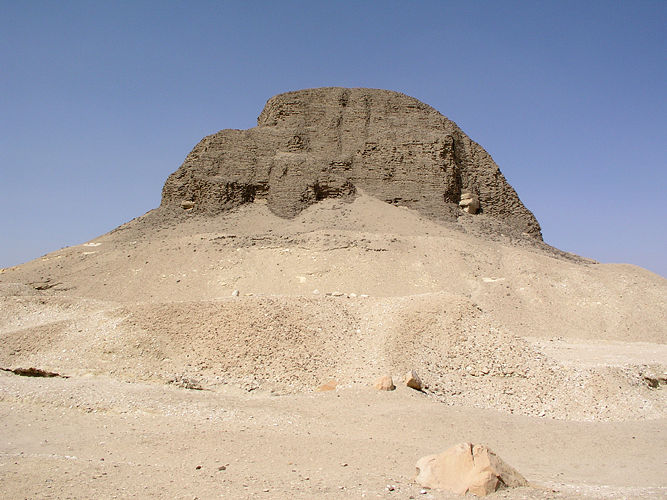
El-Lahun
El Lahun ( ar, اللاهون ''El Lāhūn,'' alt. Illahun, Lahun, or Kahun (the latter being a neologism coined by archaeologist William Matthew Flinders Petrie) is a workmen's village in Faiyum, Egypt. El Lahun is associated with the Pyramid of Senusret II ( gr, Sesostris II), which is located near the modern town, and is often called the Pyramid of Lahun. The ancient name of the site was ''rꜣ-ḥn.t'', literally, "Mouth (or Opening) of the Canal"). It was known as Ptolemais Hormos () in Ptolemaic Egypt. Overview Like the other Twelfth Dynasty pyramids in the Faiyum, the Pyramid of Lahun is made of mudbrick, but here the core of the pyramid consists of a network of stone walls that were infilled by mudbrick. This approach was probably intended to ensure the stability of the brick structure. Unusually, despite a Pyramid Temple on the east side, the entrance to the pyramid is on the south. The archaeologist Flinders Petrie nevertheless spent considerable time searching for it ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
El-Lahun
El Lahun ( ar, اللاهون ''El Lāhūn,'' alt. Illahun, Lahun, or Kahun (the latter being a neologism coined by archaeologist William Matthew Flinders Petrie) is a workmen's village in Faiyum, Egypt. El Lahun is associated with the Pyramid of Senusret II ( gr, Sesostris II), which is located near the modern town, and is often called the Pyramid of Lahun. The ancient name of the site was ''rꜣ-ḥn.t'', literally, "Mouth (or Opening) of the Canal"). It was known as Ptolemais Hormos () in Ptolemaic Egypt. Overview Like the other Twelfth Dynasty pyramids in the Faiyum, the Pyramid of Lahun is made of mudbrick, but here the core of the pyramid consists of a network of stone walls that were infilled by mudbrick. This approach was probably intended to ensure the stability of the brick structure. Unusually, despite a Pyramid Temple on the east side, the entrance to the pyramid is on the south. The archaeologist Flinders Petrie nevertheless spent considerable time searching for it ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |