|
1998 Mionica Earthquake
In the late evening of 29 September 1998, a 5.5 magnitude earthquake occurred near the town of Mionica in western Central Serbia. The epicentral area was near the village of Brežđe, where it had a maximum intensity of VIII on the Mercalli intensity scale. It was felt in Central Serbia, Vidin (Bulgaria), Sarajevo (Bosnia) and parts of Croatia, Hungary and Greece. One person died from a heart attack and 17 were injured. Some 60 schools (mostly in villages) were damaged. See also * List of earthquakes in 1998 *2010 Serbia earthquake The 2010 Serbia earthquake (also referred to as the Kraljevo earthquake) occurred on 3 November in central Serbia just several kilometers from Kraljevo. The earthquake had a of 5.5 and a maximum Mercalli intensity of VI (''Strong''). The shock w ... References {{DEFAULTSORT:1998 Mionica Earthquake Brijezde earthquake Earthquakes in Europe Earthquakes in Serbia Mionica Earthquake, 1998 Earthquake ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Moment Magnitude Scale
The moment magnitude scale (MMS; denoted explicitly with or Mw, and generally implied with use of a single M for magnitude) is a measure of an earthquake's magnitude ("size" or strength) based on its seismic moment. It was defined in a 1979 paper by Thomas C. Hanks and Hiroo Kanamori. Similar to the local magnitude scale, local magnitude/Richter scale () defined by Charles Francis Richter in 1935, it uses a logarithmic scale; small earthquakes have approximately the same magnitudes on both scales. Despite the difference, news media often says "Richter scale" when referring to the moment magnitude scale. Moment magnitude () is considered the authoritative magnitude scale for ranking earthquakes by size. It is more directly related to the energy of an earthquake than other scales, and does not saturate—that is, it does not underestimate magnitudes as other scales do in certain conditions. It has become the standard scale used by seismological authorities like the U.S. Geological ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
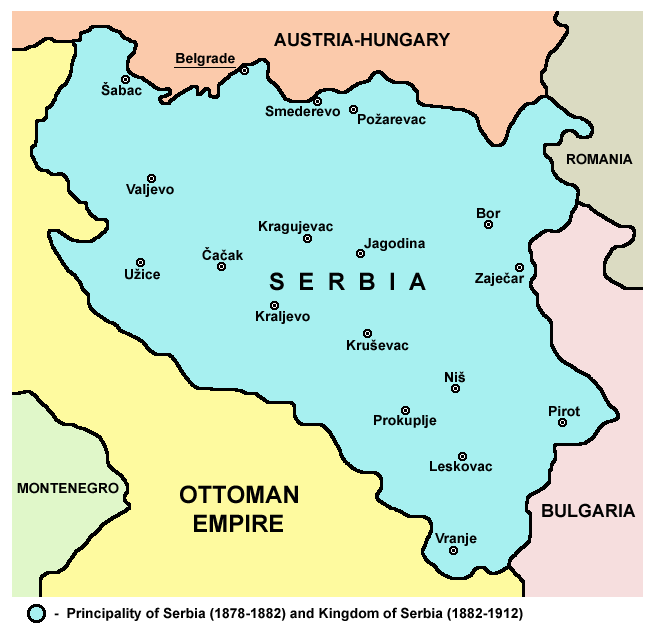
Serbia
Serbia (, ; Serbian language, Serbian: , , ), officially the Republic of Serbia (Serbian language, Serbian: , , ), is a landlocked country in Southeast Europe, Southeastern and Central Europe, situated at the crossroads of the Pannonian Basin and the Balkans. It shares land borders with Hungary to the north, Romania to the northeast, Bulgaria to the southeast, North Macedonia to the south, Croatia and Bosnia and Herzegovina to the west, and Montenegro to the southwest, and claims a border with Albania through the Political status of Kosovo, disputed territory of Kosovo. Serbia without Kosovo has about 6.7 million inhabitants, about 8.4 million if Kosvo is included. Its capital Belgrade is also the List of cities in Serbia, largest city. Continuously inhabited since the Paleolithic Age, the territory of modern-day Serbia faced Slavs#Migrations, Slavic migrations in the 6th century, establishing several regional Principality of Serbia (early medieval), states in the early Mid ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Moment Magnitude Scale
The moment magnitude scale (MMS; denoted explicitly with or Mw, and generally implied with use of a single M for magnitude) is a measure of an earthquake's magnitude ("size" or strength) based on its seismic moment. It was defined in a 1979 paper by Thomas C. Hanks and Hiroo Kanamori. Similar to the local magnitude scale, local magnitude/Richter scale () defined by Charles Francis Richter in 1935, it uses a logarithmic scale; small earthquakes have approximately the same magnitudes on both scales. Despite the difference, news media often says "Richter scale" when referring to the moment magnitude scale. Moment magnitude () is considered the authoritative magnitude scale for ranking earthquakes by size. It is more directly related to the energy of an earthquake than other scales, and does not saturate—that is, it does not underestimate magnitudes as other scales do in certain conditions. It has become the standard scale used by seismological authorities like the U.S. Geological ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Earthquake
An earthquake (also known as a quake, tremor or temblor) is the shaking of the surface of the Earth resulting from a sudden release of energy in the Earth's lithosphere that creates seismic waves. Earthquakes can range in intensity, from those that are so weak that they cannot be felt, to those violent enough to propel objects and people into the air, damage critical infrastructure, and wreak destruction across entire cities. The seismic activity of an area is the frequency, type, and size of earthquakes experienced over a particular time period. The seismicity at a particular location in the Earth is the average rate of seismic energy release per unit volume. The word ''tremor'' is also used for Episodic tremor and slip, non-earthquake seismic rumbling. At the Earth's surface, earthquakes manifest themselves by shaking and displacing or disrupting the ground. When the epicenter of a large earthquake is located offshore, the seabed may be displaced sufficiently to cause ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mionica
Mionica ( sr-cyr, Мионица, ) is a town and municipality located in the Kolubara District of western Serbia. , the population of the town is 1,571, while population of the municipality is 14,263 inhabitants. Geography The township of Mionica is located from Belgrade, the capital of Serbia. With an area of , it is bordering the Maljen and Suvobor mountains to the South and has access to the Kolubara river, Sava region and the Panonian plain to the North. While the Serbs make up for a large majority of the population, the Roma make up a significant minority, while there are smaller populations of ethnic Montenegrins, Croats, Hungarians, Macedonians, Slovenians, Germans and Albanians. Demographics According to the 2011 census results, the municipality of Mionica has 14,335 inhabitants. Ethnic groups The ethnic composition of the municipality: Economy Mionica's economy is predominantly agricultural. Its primary activities are the fruit orchards and raising cattle. The muni ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Central Serbia
Central Serbia ( sr, централна Србија / centralna Srbija), also referred to as Serbia proper ( sr, link=no, ужа Србија / uža Srbija), is the region of Serbia lying outside the autonomous province of Vojvodina to the north and the disputed territory of Kosovo to the south. Central Serbia is a term of convenience, not an administrative division of Serbia as such, and does not have any form of separate administration. Broadly speaking, Central Serbia is the historical core of modern Serbia, which emerged from the Serbian Revolution (1804–17) and subsequent wars against the Ottoman Empire. In the following century, Serbia gradually expanded south, acquiring South Serbia, Kosovo, Sandžak and Vardar Macedonia, and in 1918 – following the unification and annexation of Montenegro and unification of Austro-Hungarian areas left of the Danube and Sava (Vojvodina) – it merged with other South Slavic territories into the Kingdom of Yugoslavia. The current b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Brežđe
Brežđe ( sr, Брежђе) is a village in the Mionica municipality, Kolubara District in Serbia. Šalitrena Cave Šalitrena Cave ( sr, Шалитрена пећина, Šalitrena pećina) is located in the village area, in the gorge of the Ribnica river. The name means " Saltpeter Cave" in Serbian. It is the richest Paleolithic find of the central and west Balkan Peninsula, a valuable source on the material culture and spiritual life of the Paleolithic humans. The cave is also the only Gravettian find in the west Balkans and one of the richest and most important finds of the Upper Paleolithic in the Southeast Europe. A technological and typological analysis of the discovered materials, numerous stone artifacts and fauna remnants, and the subsequent accelerator mass spectrometry method, established that the cave was already inhabited in the Middle Paleolithic, 38,000 years ago. Materials discovered in the chronologically younger layers belong to the major Upper Pale ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Seismic Scales
Seismic magnitude scales are used to describe the overall strength or "size" of an earthquake. These are distinguished from seismic intensity scales that categorize the intensity or severity of ground shaking (quaking) caused by an earthquake at a given location. Magnitudes are usually determined from measurements of an earthquake's seismic waves as recorded on a seismogram. Magnitude scales vary on what aspect of the seismic waves are measured and how they are measured. Different magnitude scales are necessary because of differences in earthquakes, the information available, and the purposes for which the magnitudes are used. Earthquake magnitude and ground-shaking intensity The Earth's crust is stressed by tectonic forces. When this stress becomes great enough to rupture the crust, or to overcome the friction that prevents one block of crust from slipping past another, energy is released, some of it in the form of various kinds of seismic waves that cause ground-shaking, o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mercalli Intensity Scale
The Modified Mercalli intensity scale (MM, MMI, or MCS), developed from Giuseppe Mercalli's Mercalli intensity scale of 1902, is a seismic intensity scale used for measuring the intensity of shaking produced by an earthquake. It measures the effects of an earthquake at a given location, distinguished from the earthquake's inherent force or strength as measured by seismic magnitude scales (such as the "" magnitude usually reported for an earthquake). While shaking is caused by the seismic energy released by an earthquake, earthquakes differ in how much of their energy is radiated as seismic waves. Deeper earthquakes also have less interaction with the surface, and their energy is spread out across a larger volume. Shaking intensity is localized, generally diminishing with distance from the earthquake's epicenter, but can be amplified in sedimentary basins and certain kinds of unconsolidated soils. Intensity scales empirically categorize the intensity of shaking based on the effect ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
List Of Earthquakes In 1998
This is a list of earthquakes in 1998. Only earthquakes of magnitude 6 or above are included, unless they result in damage or casualties, or are notable for some other reason. All dates are listed according to UTC time. Maximum intensities are indicated on the Modified Mercalli intensity scale, and all data are sourced from the United States Geological Survey. By death toll At least 10 dead. By magnitude By month January February March April May June July August September October November December See also * * Lists of 20th-century earthquakes * Lists of earthquakes by year References {{DEFAULTSORT:Earthquakes in 1998 1998 1998 1998 was designated as the ''International Year of the Ocean''. Events January * January 6 – The '' Lunar Prospector'' spacecraft is launched into orbit around the Moon, and later finds evidence for frozen water, in soil in permanently ... 1998 earthquakes 1998-related lists ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
2010 Serbia Earthquake
The 2010 Serbia earthquake (also referred to as the Kraljevo earthquake) occurred on 3 November in central Serbia just several kilometers from Kraljevo. The earthquake had a of 5.5 and a maximum Mercalli intensity of VI (''Strong''). The shock was felt across the country, including the capital Belgrade, and in neighboring countries. Two people were killed and over 100 suffered light injuries. There were 5,967 structures that sustained some damage, 1,551 declared unsafe for use and require repairment, and 138 were damaged beyond repair. There were more than 350 aftershocks, including a magnitude 4.3 earthquake on November 4. Background The earthquake had magnitude of 5.3 and took place at 01:56 local time (00:56 UTC). The epicenter of the earthquake was located ten kilometers north of Kraljevo near the village of Vitanovac. Following the earthquake electricity, phone lines and water supply were interrupted in Kraljevo region. Emergency situation was declared throughout the reg ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
1998 Earthquakes
1998 was designated as the ''International Year of the Ocean''. Events January * January 6 – The ''Lunar Prospector'' spacecraft is launched into orbit around the Moon, and later finds evidence for frozen water, in soil in permanently shadowed craters near the Moon's poles. * January 11 – Over 100 people are killed in the Sidi-Hamed massacre in Algeria. * January 12 – Nineteen European nations agree to forbid human cloning. * January 17 – The ''Drudge Report'' breaks the story about U.S. President Bill Clinton's alleged affair with Monica Lewinsky, which will lead to the House of Representatives' impeachment of him. February * February 3 – Cavalese cable car disaster: A United States military pilot causes the deaths of 20 people near Trento, Italy, when his low-flying EA-6B Prowler severs the cable of a cable-car. * February 4 – The 5.9 Afghanistan earthquake shakes the Takhar Province with a maximum Mercalli intensity of VII (''Very strong''). With up to 4, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |