|
1997 United Kingdom Budget
The 1997 United Kingdom budget (sometimes referred to as the People's budget and officially titled ''Equipping Britain for our Long-Term Future'') was delivered by Gordon Brown, the Chancellor of the Exchequer, to the House of Commons on 2 July 1997. It was the first budget to be presented by Brown during his tenure as Chancellor, and the first Labour budget to be presented since April 1979. The 1997 budget marked a significant change of direction in economic policy following Labour's election win in May 1997. Among the measures announced were a five-year plan to reduce the budget deficit, a £5.2bn windfall tax on recently privatised utilities which was to fund Labour's planned Welfare to Work scheme, and a reduction in VAT on fuel. The budget was welcomed by business, which viewed it as fiscally responsible, but it was greeted less warmly by the UK's utility providers. Background The budget was to be the first presented by a Labour Government since April 1979. Gordon Brown an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
List Of MPs Elected In The 1997 United Kingdom General Election
This is a list of Members of Parliament (MPs) elected to the House of Commons at the 1997 general election, held on 1 May. The list is arranged by constituency. New MPs elected since the general election are noted at the bottom of the page. During the 1997–2001 Parliament, Betty Boothroyd and Michael Martin served as Speaker, Tony Blair served as Prime Minister, and John Major and William Hague served as Leader of the Opposition. Dissolution of Parliament was on 14 May 2001. Sub-lists * List of MPs for constituencies in Scotland (1997–2001) * List of MPs for constituencies in Wales (1997–2001) Composition These representative diagrams show the composition of the parties in the 1997 general election. Note: The Scottish National Party and Plaid Cymru sit together as a party group, while Sinn Féin has not taken its seats. This is not the official seating plan of the House of Commons, which has five rows of benches on each side, with the government party to the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Budget Box
Red boxes, or sometimes ministerial boxes, are a type of despatch box produced by Barrow Hepburn & Gale or Wickwar & Co and are used by ministers in the British government and the British monarch to carry government documents. Similar in appearance to a briefcase, they are primarily used to hold and transport official ministerial papers. Red boxes are one modern form of despatch boxes, which have been in government use for centuries. Despatch boxes of a very different design remain in use in the chamber of the lower house of the British and Australian parliaments. Those boxes hold religious books for swearing-in new members of the chamber, but are also used as lecterns by front bench members. Ministerial boxes According to HM Treasury: Historical and famous red boxes The boxes are used by ministers on a daily basis while in government and thus become an important memory of their time in office, with many opting to buy and keep their red boxes. Many boxes owned and used by fa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vehicle Excise Duty
Vehicle Excise Duty (VED; also known as "vehicle tax", "car tax", and more controversially as "road tax", and formerly as a "tax disc") is an annual tax that is levied as an excise duty and which must be paid for most types of powered vehicles which are to be used (or parked) on public roads in the United Kingdom. Registered vehicles that are not being used or parked on public roads and which have been taxed since 31 January 1998, must be covered by a Statutory Off Road Notification (SORN) to avoid VED. In 2016, VED generated approximately £6 billion for the Exchequer. A vehicle tax was first introduced in Britain in 1888. In 1920, an excise duty was introduced that was specifically applied to motor vehicles; initially it was hypothecated (ring-fenced or earmarked) for road construction and paid directly into a special Road Fund. After 1937, this reservation of vehicle revenue for roads was ended, and instead the revenue was paid into the Consolidated Fund – the general pot of m ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Individual Savings Account
An individual savings account (ISA; ) is a class of retail investment arrangement available to residents of the United Kingdom. First introduced in 1999, the accounts have favourable tax status. Payments into the account are made from after-tax income, then the account is exempt from income tax and capital gains tax on the investment returns, and no tax is payable on money withdrawn from the scheme. Cash and a broad range of investments can be held within the arrangement, and there is no restriction on when or how much money can be withdrawn. Since 2017, there have been four types of account: cash ISA, stocks & shares ISA, innovative finance ISA (IFISA) and lifetime ISA (LISA). Each taxpayer has an annual investment limit (£20,000 since ) which can be split among the four types as desired. Additionally, children under 18 may hold a junior ISA, with a different annual limit. Until the lifetime ISA was introduced in 2017, ISAs were not a specific retirement investment, but any type ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
National Lottery (United Kingdom)
The National Lottery is the state-franchising, franchised national lottery established in 1994 in the United Kingdom. It is regulated by the Gambling Commission, and is currently operated by Camelot Group, to which the licence was granted in 1994, 2001 and again in 2007, but will be operated by Allwyn Entertainment Ltd from 2024. Prizes are paid as a lump sum (with the exception of the Set For Life which is paid over a set period) and are tax-free. Of all money spent on National Lottery games, around 53% goes to the prize fund and 25% to "good causes" as set out by UK Parliament, Parliament (though some of this is considered by some to be a form of "stealth tax" levied to support the National Lottery Community Fund, a fund constituted to support public spending). 12% goes to the UK Government as lottery duty, 4% to retailers as commission, and a total of 5% to operator Camelot, with 4% to cover operating costs and 1% as profit. From introduction in November 1994 until April 20 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mortgage Interest Relief At Source
Mortgage interest relief at source, or MIRAS, was a scheme introduced in the United Kingdom from 1983 in a bid to encourage home ownership; it allowed borrowers tax relief for interest payments on their mortgage. Previously tax had to be reclaimed from HMRC In the 1983 Budget Geoffrey Howe raised the tax allowance from £25,000 to £30,000. Unmarried couples with joint mortgages could pool their allowances to £60,000, a provision known as Multiple Mortgage Tax Relief. This remained in place until the 1988 Budget, when Nigel Lawson ended the option to pool allowances from August 1988. Lawson later publicly expressed regret at not having implemented the change with effect from the time of the budget, as it is generally accepted that the rush to beat the deadline fuelled a sharp increase in house prices. MIRAS was completely abolished in April 2000 by Gordon Brown, who argued it had become a middle class perk. Receiving MIRAS was one of the justifications given by mortgage adviser ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Stamp Duty In The United Kingdom
Stamp duty in the United Kingdom is a form of tax charged on legal instruments (written documents), and historically required a physical stamp to be attached to or impressed upon the document in question. The more modern versions of the tax no longer require a physical stamp. History of UK stamp duties Stamp duty was first introduced in England on 28 June 1694, during the reign of William III and Mary II, under "An act for granting to their Majesties several duties upon vellum, parchment and paper, for four years, towards carrying on the war against France". Dagnall, H. (1994) ''Creating a Good Impression: three hundred years of The Stamp Office and stamp duties.'' London: HMSO, p. 3. In the 1702/03 financial year 3,932,933 stamps were embossed in England for a total value of £91,206.10s.4d. Stamp duty was so successful that it continues to this day through a series of Stamp Acts. Similar duties have been levied in the Netherlands, France and elsewhere. During the 18th a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gas Levy Act 1981
The Gas Levy Act 1981 (c. 3) is an Act of the Parliament of the United Kingdom which imposed on the British Gas Corporation a levy in respect of purchased natural gas. Background In May 1980 the Government announced that it intended to impose a levy on the British Gas Corporation on gas purchased from the United Kingdom continental shelf (UKCS) and sold to the corporation under contracts which were not subject to petroleum revenue tax. Virtually all the gas that came onshore from the UKCS was sold to the British Gas Corporation by the producers under long-term contracts signed before the oil crisis of 1973–74 and 1979–80 and the subsequent increase in prices. As a consequence, the prices paid for gas from these fields reflected the prices and the escalation clauses agreed in an era of cheap energy. The average basic cost to British Gas of all its gas purchases in 1980–81 was about 8p a therm. The price paid by producers for new supplies or renegotiated contracts were mo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Personal Equity Plan
A personal equity plan (PEP) was a form of tax-privileged investment account in the United Kingdom, available between 1986 and 1999. History The plans were introduced by Nigel Lawson in the 1986 budget to encourage equity ownership among the wider population. PEPs were allowed to contain collective investments such as unit trusts. The ''single company PEP'', which was allowed to contain shares of a single company, was introduced in 1992. PEPs were superseded by individual savings accounts in 1999, and remaining accounts were converted to individual savings accounts in 2008. Types and privileges Growth in a PEP was free from capital gains tax within the fund and on encashment. Income was free from income tax. There were two types of PEP: the "general PEP" with an annual allowance of £6,000 and the "single company PEP" with an annual allowance of £3,000. Investments in a general PEP were limited to qualifying collective investments. Qualifying investments had at least half of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
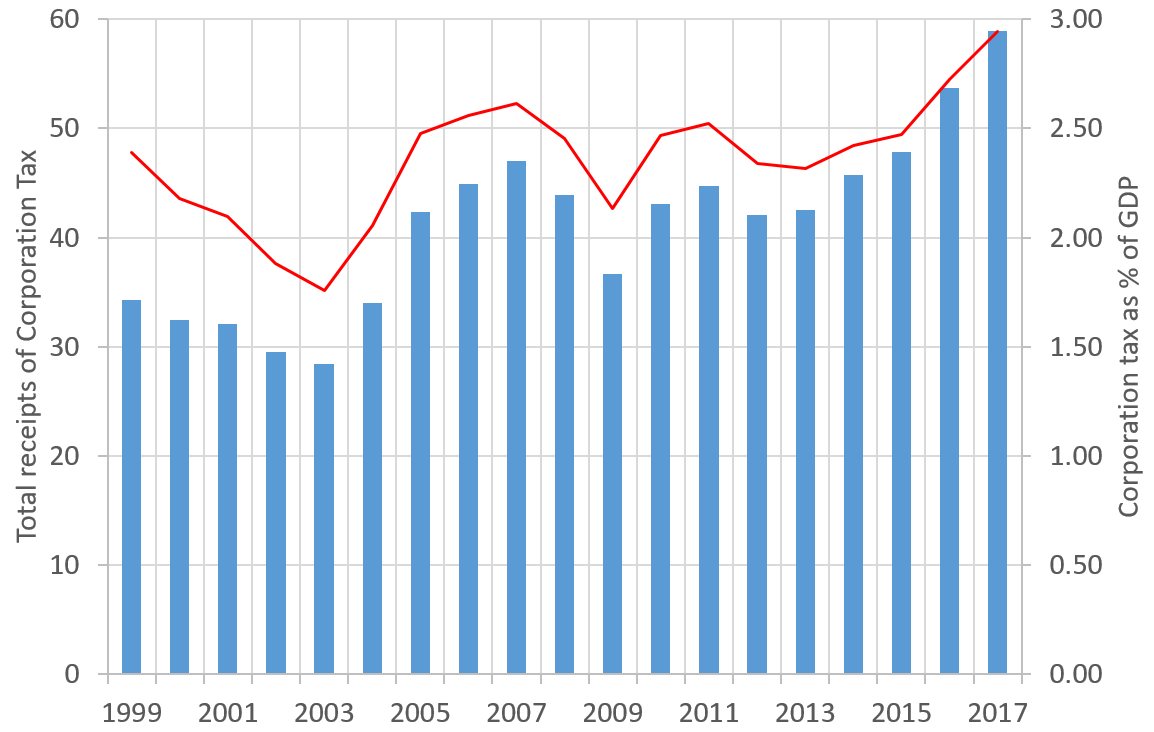
United Kingdom Corporation Tax
: ''Throughout this article, the term "pound" and the £ symbol refer to the Pound sterling.'' Corporation tax in the United Kingdom is a corporate tax levied in on the profits made by UK-resident companies and on the profits of entities registered overseas with permanent establishments in the UK. Until 1 April 1965, companies were taxed at the same income tax rates as individual taxpayers, with an additional profits tax levied on companies. Finance Act 1965 replaced this structure for companies and associations with a single corporate tax, which took its basic structure and rules from the income tax system. Since 1997, the UK's Tax Law Rewrite ProjectTax Law Rewrite , |
Gross Domestic Product
Gross domestic product (GDP) is a money, monetary Measurement in economics, measure of the market value of all the final goods and services produced and sold (not resold) in a specific time period by countries. Due to its complex and subjective nature this measure is often revised before being considered a reliable indicator. List of countries by GDP (nominal) per capita, GDP (nominal) per capita does not, however, reflect differences in the cost of living and the inflation, inflation rates of the countries; therefore, using a basis of List of countries by GDP (PPP) per capita, GDP per capita at purchasing power parity (PPP) may be more useful when comparing standard of living, living standards between nations, while nominal GDP is more useful comparing national economies on the international market. Total GDP can also be broken down into the contribution of each industry or sector of the economy. The ratio of GDP to the total population of the region is the GDP per capita, p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Prime Minister's Questions
Prime Minister's Questions (PMQs, officially known as Questions to the Prime Minister, while colloquially known as Prime Minister's Question Time) is a constitutional convention in the United Kingdom, currently held as a single session every Wednesday at noon when the House of Commons is sitting, during which the prime minister answers questions from members of Parliament (MPs).The Institute for Government has described PMQs as 'the most distinctive and internationally famous feature of British politics.' History Although prime ministers have answered questions in parliament for centuries, until the 1880s, questions to the prime minister were treated the same as questions to other ministers of the Crown: asked without notice, on days when ministers were available, in whatever order MPs rose to ask them. In 1881 fixed time-limits for questions were introduced and questions to the prime minister were moved to the last slot of the day as a courtesy to the 72-year-old prime minis ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |

.jpg)