|
1993–94 South-West Indian Ocean Cyclone Season
The 1993–94 South-West Indian Ocean cyclone season was the most active season in the basin since the start of reliable satellite coverage in 1967, until the record was surpassed 25 years later in the 2018–19 South-West Indian Ocean cyclone season. Activity lasted from mid-November, when Moderate Tropical Storm Alexina formed, until mid-April, when Tropical Cyclone Odille became extratropical cyclone, extratropical. Four tropical cyclones – Daisy, Cyclone Geralda, Geralda, Litanne, and Cyclone Nadia, Nadia – struck eastern Madagascar, of which Geralda was the costliest and deadliest. With gusts as strong as accompanied by heavy rainfall, Geralda destroyed more than 40,000 homes and left 356,000 people homeless. Geralda killed 231 people and caused more than $10 million in damage. Cyclone Nadia was the second deadliest cyclone, having killed 12 people in northern Madagascar and later severely damaging portions of northeastern Mozambique, killing abou ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cyclone Geralda
Intense Tropical Cyclone Geralda was a powerful tropical cyclone that caused catastrophic damage in Madagascar in late January 1994, among the strongest to hit the country. It was also the most intense tropical cyclone Tropical cyclones in 1994, worldwide in 1994. Cyclone Geralda originated from an area of low pressure over the Indian Ocean on 25 January. Over the following few days, the depression underwent gradual intensification, reaching its peak intensity with ten-minute sustained winds of on 31 January. It eventually made landfall near Toamasina, Madagascar after weakening from its peak intensity, and substantially weakened within hours of moving onshore. By 5 February, Geralda had degenerated into a Tropical cyclone scales#South-West Indian Ocean, land depression, and became extratropical three days later. Geralda's remnants dissipated on 12 February. Geralda was the second cyclone in as many months to strike eastern Madagascar, after 1993–94 South-West Indian Ocean cy ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Regional Specialised Meteorological Centre
A Regional Specialized Meteorological Centre (RSMC) is responsible for the distribution of information, advisories, and warnings regarding the specific program they have a part of, agreed by consensus at the World Meteorological Organization as part of the World Weather Watch. Environmental emergency response programme As a result of the poor communications between countries following the Chernobyl disaster in the Spring of 1986, the World Meteorological Organization (WMO) was requested by the International Atomic Energy Agency (IAEA) and other international organizations to arrange for early warning messages about nuclear accidents to be transmitted over the Global Telecommunications System (GTS). In addition some WMO member countries that lacked extensive forecasting capability requested that specialized pollutant transport and dispersion forecasts be provided during these emergencies. As a result, during 1989 Meteo-France (MF), Environment Canada (EC) and the United Kingdom ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
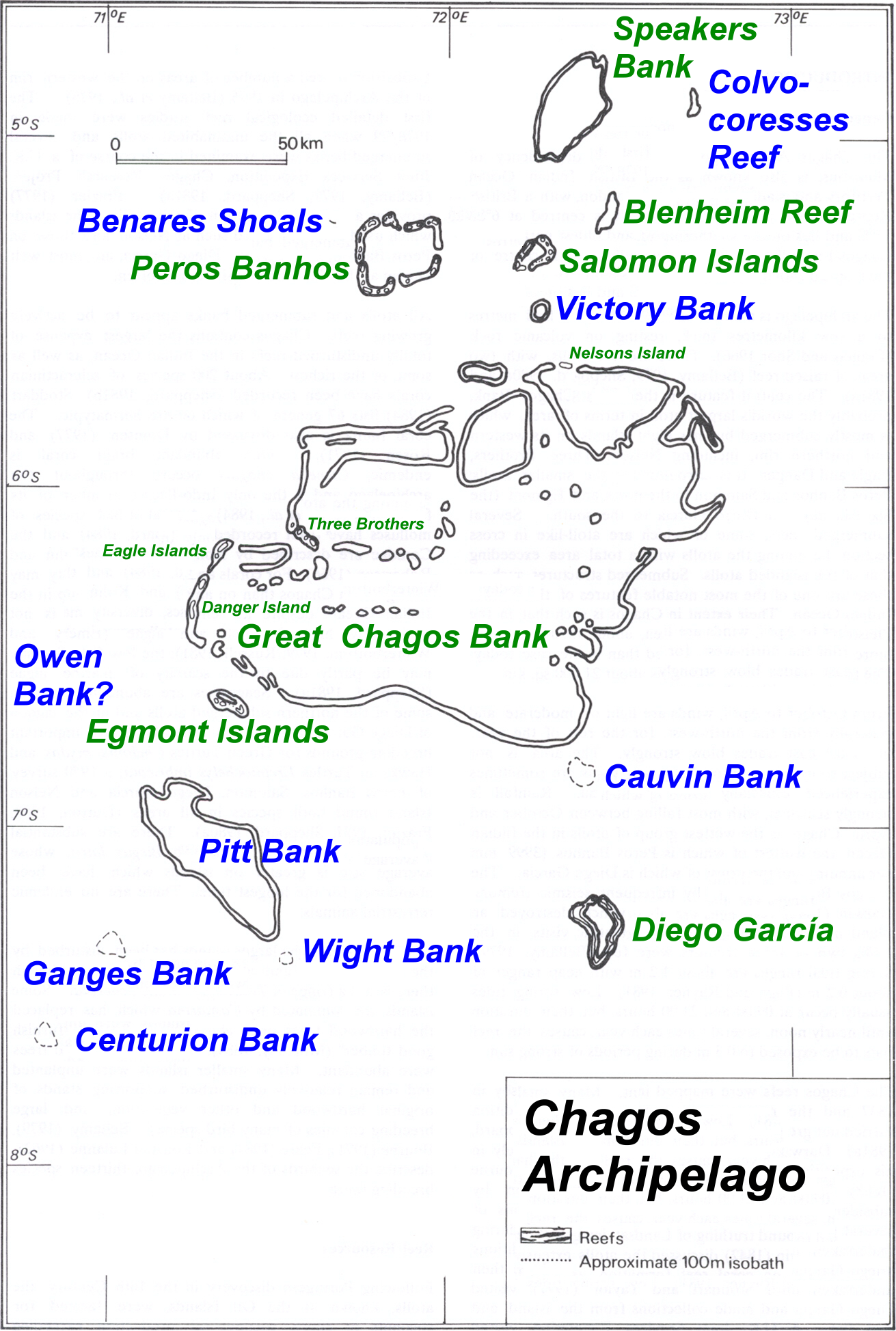
Chagos Archipelago
The Chagos Archipelago (, ) or Chagos Islands (formerly , and later the Oil Islands) is a group of seven atolls comprising more than 60 islands in the Indian Ocean about south of the Maldives archipelago. This chain of islands is the southernmost archipelago of the Chagos–Laccadive Ridge, a long submarine mountain range in the Indian Ocean. In its north are the Salomon Islands, Nelsons Island and Peros Banhos; towards its south-west are the Three Brothers, Chagos, Three Brothers, Eagle Islands, Egmont Islands and Danger Island, Great Chagos Bank, Danger Island; southeast of these is Diego Garcia, by far the largest island. All are low-lying atolls, save for a few extremely small instances, set around lagoons. From 1715 to 1810, the Chagos Islands were part of France's List of French possessions and colonies, Indian Ocean possessions, administered through Isle de France (Mauritius), Isle de Francewhich was a French colonial empire, colony of France (later renamed as Mauritius). ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Convection (meteorology)
Atmospheric convection is the vertical transport of heat and moisture in the atmosphere. It occurs when warmer, less dense air rises, while cooler, denser air sinks. This process is driven by Air parcel, parcel-environment instability, meaning that a "parcel" of air is warmer and less dense than the surrounding environment at the same altitude. This difference in temperature and density (and sometimes humidity) causes the parcel to rise, a process known as buoyancy. This rising air, along with the compensating sinking air, leads to mixing, which in turn expands the height of the planetary boundary layer (PBL), the lowest part of the atmosphere directly influenced by the Earth's surface. This expansion contributes to increased Wind, winds, cumulus cloud development, and decreased surface Dew point, dew points (the temperature below which condensation occurs). Convection plays a crucial role in weather patterns, influencing cloud formation, wind, and the development of Thunderstor ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Low-pressure Area
In meteorology, a low-pressure area (LPA), low area or low is a region where the atmospheric pressure is lower than that of surrounding locations. It is the opposite of a high-pressure area. Low-pressure areas are commonly associated with inclement weather (such as cloudy, windy, with possible rain or storms), while high-pressure areas are associated with lighter winds and clear skies. Winds circle anti-clockwise around lows in the northern hemisphere, and clockwise in the southern hemisphere, due to opposing Coriolis forces. Low-pressure systems form under areas of wind divergence that occur in the upper levels of the atmosphere (aloft). The formation process of a low-pressure area is known as cyclogenesis. In meteorology, atmospheric divergence aloft occurs in two kinds of places: * The first is in the area on the east side of upper troughs, which form half of a Rossby wave within the Westerlies (a trough with large wavelength that extends through the troposphere). * A ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
2001–02 South-West Indian Ocean Cyclone Season
The 2001–02 South-West Indian Ocean cyclone season had the earliest named storm since 1992. Many storms formed in the north-east portion of the basin, and several more originated around Australia. The basin is defined as the waters of the Indian Ocean west of longitude 90°E to the coast of Africa and south of the equator. Eleven tropical storms formed, compared to an average of nine. Tropical systems were present during 73 days, which was significantly higher than the average of 58 for this basin. Tropical cyclones in this basin are monitored by the Regional Specialized Meteorological Center (RSMC) in Réunion. The season started on November 1, 2001, and ended on April 30, 2002; for Mauritius and the Seychelles, the season continued until May 15. These dates conventionally delimit the period of each year when most tropical cyclones form in the basin; however, storms formed both before and after the designated season. The first storm was Andre, which eme ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Monsoon Trough
The monsoon trough is a convergence zone between the wind patterns of the southern and northern hemispheres. It is a portion of the Intertropical Convergence Zone in the Western Pacific,Bin WangThe Asian Monsoon.Retrieved 2008-05-03. and is depicted by a line on a weather map showing the locations of minimum sea level pressure. Westerly monsoon winds lie in its equatorward portion while easterly trade winds exist poleward of the trough. Right along its axis, heavy rains can be found which usher in the peak of a location's respective rainy season. The monsoon trough plays a role in creating many of the world's rainforests. The term ''monsoon trough'' is most commonly used in monsoonal regions of the Western Pacific such as Asia and Australia. The migration of the ITCZ/monsoon trough into a landmass heralds the beginning of the annual rainy season during summer months. Depressions and tropical cyclones often form in the vicinity of the monsoon trough, with each capable of produc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
El Niño
EL, El or el may refer to: Arts and entertainment Fictional entities * El, a character from the manga series ''Shugo Chara!'' by Peach-Pit * Eleven (''Stranger Things'') (El), a fictional character in the TV series ''Stranger Things'' * El, family name of Kal-El (Superman) and his father Jor-El in the Superman dynasty * E.L. Faldt, character in the road comedy film '' Road Trip'' Music * Él Records, an independent record label from the UK founded by Mike Alway * ''Él ''(Lucerito album), a 1982 album by Lucerito * "Él", Spanish song by Rubén Blades from the album '' Caminando'' * "Él" (Lucía song), the Spanish entry performed by Lucía in the Eurovision Song Contest 1982 Other media * ''Él'', 1926 autobiographical novel by Mercedes Pinto * ''Él'' (film), a 1953 film by Luis Buñuel based on the 1926 novel * ''Él'' (visual novel), a 1991 Japanese adult visual novel * EL TV, an Azerbaijani regional television channel Companies and organizations * Estée Lauder Co ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Longitude
Longitude (, ) is a geographic coordinate that specifies the east- west position of a point on the surface of the Earth, or another celestial body. It is an angular measurement, usually expressed in degrees and denoted by the Greek letter lambda (λ). Meridians are imaginary semicircular lines running from pole to pole that connect points with the same longitude. The prime meridian defines 0° longitude; by convention the International Reference Meridian for the Earth passes near the Royal Observatory in Greenwich, south-east London on the island of Great Britain. Positive longitudes are east of the prime meridian, and negative ones are west. Because of the Earth's rotation, there is a close connection between longitude and time measurement. Scientifically precise local time varies with longitude: a difference of 15° longitude corresponds to a one-hour difference in local time, due to the differing position in relation to the Sun. Comparing local time to an absol ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
World Meteorological Organization
The World Meteorological Organization (WMO) is a List of specialized agencies of the United Nations, specialized agency of the United Nations responsible for promoting international cooperation on atmospheric science, climatology, hydrology and geophysics. The WMO originated from the International Meteorological Organization (IMO), a nongovernmental organization founded in 1873 as a forum for exchanging weather data and research. Proposals to reform the status and structure of the IMO culminated in the World Meteorological Convention of 1947, which formally established the World Meteorological Organization. The Convention entered into force on 23 March 1950, and the following year the WMO began operations as an intergovernmental organization within the UN system. The WMO is made up of 193 countries and territories, and facilitates the "free and unrestricted" exchange of data, information, and research between the respective meteorological and hydrological institutions of its m ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Météo-France
Météo-France is the official French meteorological administration, also offering services to Andorra and Monaco. It has the powers of the state and can exercise them in relation to meteorology. Météo-France is in charge of observing, studying, and forecasting weather and monitoring snowpack. The organization also issues weather warnings for the Metropole and the overseas territories. Météo-France is also in charge of recording and predicting the climate. Organisation The organisation was established by decree in June 1993 and is a department of the Ministry of Transportation. It is headquartered in Paris but many domestic operations have been decentralised to Toulouse. Its budget of around €300 million is funded by state grants, aeronautic royalties and sale of commercial services. Météo-France has a particularly strong international presence, and is the French representative at the World Meteorological Organization. The organisation is a leading member of EUM ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tropical Cyclone Scales
Tropical cyclones are ranked on one of five tropical cyclone intensity scales, according to their maximum sustained winds and which tropical cyclone basins they are located in. Only a few classifications are used officially by the meteorological agencies monitoring the tropical cyclones, but other scales also exist, such as accumulated cyclone energy, the Power Dissipation Index, the Integrated Kinetic Energy Index, and the Hurricane Severity Index. Tropical cyclones that develop in the Northern Hemisphere are classified by the warning centres on one of three intensity scales. Tropical cyclones or subtropical cyclones that exist within the North Atlantic Ocean or the North-eastern Pacific Ocean are classified as either tropical depressions or tropical storms. Should a system intensify further and become a hurricane, then it will be classified on the Saffir–Simpson hurricane wind scale, and is based on the estimated maximum sustained winds over a 1-minute period. In the W ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |