|
1990 Bohol Sea Earthquake
The 1990 Bohol earthquake occurred on February 8, 1990 at 15:15:32 (UTC +8) which had a magnitude of 6.8 . The earthquake had a moderate depth of 25.9 km (16 mi). Most of the damage was observed in the province of Bohol. A tsunami hit the southeastern coastline of Bohol and the island of Camiguin. There were 6 deaths, over 200 injuries and an estimated ₱157 million ( $7 million) in total damage reported. Twenty-three years later, a much more devastating 7.2 Mw under the same fault system would strike the island killing 222 individuals. Tectonic Setting The Philippines is usually prone to earthquakes due to its location within the Pacific Ring of Fire, where most of the world's seismological events occur. The Bohol Sea is home to segments of the Philippine Fault System, a system of fault line extending from the Northwestern province of Ilocos Sur, transversing through Quezon province, Masbate Island and the Eastern Visayas region, and ending at the end of Davao Gulf. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bohol
Bohol (), officially the Province of Bohol ( ceb, Lalawigan sa Bohol; tl, Lalawigan ng Bohol), is an island province of the Philippines located in the Central Visayas Regions of the Philippines, region, consisting of the island itself and 75 minor surrounding islands. Its capital is Tagbilaran. With a land area of and a coastline long, Bohol is the List of islands of the Philippines#List of islands by size, tenth largest island of the Philippines.The Island-Province of Bohol Retrieved November 15, 2006. The province of Bohol is a first-class province divided into 3 Legislative districts of Bohol, congressional districts, comprising 1 Cities of the Philippines, component city and 47 Philippine municipality, municipalities. It has 1,109 barangays. The province is ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Eastern Visayas
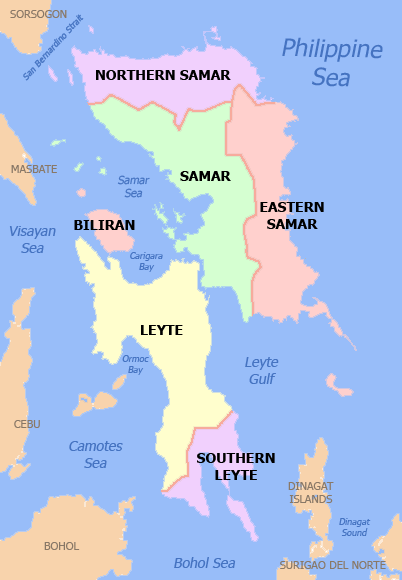
Eastern Visayas ( war, Sinirangan Kabisay-an; ceb, Sidlakang Kabisay-an; tl, Silangang Kabisayaan or ''Silangang Visayas'') is an administrative region in the Philippines, designated as Region VIII. It consists of three main islands, Samar, Leyte and Biliran. The region has six provinces, one independent city and one highly urbanized city namely, Biliran, Leyte, Northern Samar, Samar, Eastern Samar, Southern Leyte, Ormoc and Tacloban. The highly urbanized city of Tacloban is the sole regional center. These provinces and cities occupy the easternmost islands of the Visayas group of islands. Eastern Visayas faces the Philippine Sea to the east. The region's most famous landmark is the San Juanico Bridge, which links the provinces of Samar and Leyte. As of 2020, the Eastern Visayas region has a population of 4,547,150 inhabitants, making it the third most populous region in the Visayas. Etymology The current name of the region was derived from its location in the easternmost p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
1990 Earthquakes ...
This is a list of earthquakes in 1990. Only earthquakes of magnitude 6 or above are included, unless they result in damage and/or casualties, or are notable for some other reason. All dates are listed according to UTC time. By death toll By magnitude Listed are earthquakes with at least 7.0 magnitude. By month January February March April May June July August September October November December See also * * Lists of 20th-century earthquakes * Lists of earthquakes by year References {{Earthquakes by year 1990 1990 1990 File:1990 Events Collage.png, From left, clockwise: The 1990 FIFA World Cup is played in Italy; The Human Genome Project is launched; Voyager I takes the famous Pale Blue Dot image- speaking on the fragility of Humankind, humanity on Earth, Astroph ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
List Of Earthquakes In The Philippines
The Philippines lies along the Pacific Ring of Fire, which causes the country to have frequent seismic and volcanic activity. Many earthquakes of smaller magnitude occur very regularly due to the meeting of major tectonic plates in the region. The largest was the 1918 Celebes Sea earthquake with . Spanish period Earthquakes recorded from the 17th to 19th century: 17th century 18th century 19th century American period and post–World War II (1900-1999) 20th century Mid to Late 20th century 21st century Largest earthquakes by year The largest or most notable Philippine earthquakes per year since 2001. As for the repeated entries, Moro Gulf near the Cotabato Trench is a seismically active area (the location of the devastating 1918 Celebes Sea earthquake and 1976 Moro Gulf earthquake). Meanwhile, Samar and Davao Region are near the northern and southern portions of the Philippine Trench, respectively. 2001–present As the Philippines is subjec ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
List Of Earthquakes In 1990
This is a list of earthquakes in 1990. Only earthquakes of magnitude 6 or above are included, unless they result in damage and/or casualties, or are notable for some other reason. All dates are listed according to UTC time. By death toll By magnitude Listed are earthquakes with at least 7.0 magnitude. By month January February March April May June July August September October November December See also * * Lists of 20th-century earthquakes * :Lists of earthquakes by year, Lists of earthquakes by year References {{Earthquakes by year 1990 earthquakes, 1990 Lists of 20th-century earthquakes, 1990 Lists of earthquakes by year, 1990 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mud Volcano
A mud volcano or mud dome is a landform created by the eruption of mud or slurries, water and gases. Several geological processes may cause the formation of mud volcanoes. Mud volcanoes are not true igneous volcanoes as they do not produce lava and are not necessarily driven by magmatic activity. Mud volcanoes may range in size from merely 1 or 2 meters high and 1 or 2 meters wide, to 700 meters high and 10 kilometers wide. Smaller mud exudations are sometimes referred to as mud-pots. The mud produced by mud volcanoes is mostly formed as hot water, which has been heated deep below the Earth's surface, begins to mix and blend with subterranean mineral deposits, thus creating the mud slurry exudate. This material is then forced upwards through a geological fault or fissure due to local subterranean pressure imbalances. Mud volcanoes are associated with subduction zones and about 1100 have been identified on or near land. The temperature of any given active mud volcano generally r ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fissure
A fissure is a long, narrow crack opening along the surface of Earth. The term is derived from the Latin word , which means 'cleft' or 'crack'. Fissures emerge in Earth's crust, on ice sheets and glaciers, and on volcanoes. Ground fissure A , also called an , is a long, narrow crack or linear opening in the Earth's crust. Ground fissures can form naturally, such as from tectonic faulting and earthquakes, or as a consequence of human activity, such as oil mining and groundwater pumping. Once formed, ground fissures can be extended and eroded by torrential rain. They can be hazardous to people and livestock living on the affected surfaces and damaging to property and infrastructure, such as roads, underground pipes, canals, and dams. In circumstances where there is the extensive withdrawal of groundwater, the earth above the water table can subside causing fissures to form at the surface. This typically occurs at the floor of arid valleys having rock formations and compacte ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Landslide
Landslides, also known as landslips, are several forms of mass wasting that may include a wide range of ground movements, such as rockfalls, deep-seated grade (slope), slope failures, mudflows, and debris flows. Landslides occur in a variety of environments, characterized by either steep or gentle slope gradients, from mountain ranges to coastal cliffs or even underwater, in which case they are called submarine landslides. Gravity is the primary driving force for a landslide to occur, but there are other factors affecting slope stability that produce specific conditions that make a slope prone to failure. In many cases, the landslide is triggered by a specific event (such as a heavy rainfall, an earthquake, a slope cut to build a road, and many others), although this is not always identifiable. Causes Landslides occur when the slope (or a portion of it) undergoes some processes that change its condition from stable to unstable. This is essentially due to a decrease in the She ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Anda, Bohol
Anda, officially the Municipality of Anda ( ceb, Munisipyo sa Anda; tgl, Bayan ng Anda), is a 5th class municipality in the province of Bohol, Philippines. According to the 2015 census, it has a population of 16,462 people. In 2006, the Anda red hermatite print petroglyphs of Bohol were included in the tentative list of the Philippines for UNESCO World Heritage Site under the name of ''Petroglyphs and Petrographs of the Philippines'', which also includes the Singnapan charcoal-drawn petrographs of southern Palawan, Angono Petroglyphs of Rizal province, Alab petroglyphs of Mountain province, and charcoal-drawn Penablanca petrographs of Cagayan. Etymology The decree in 1875 on the separation of Quinale from Guindulman did not explain why the name "Anda" was chosen. It was presumed that the name referred to Governor General Simón de Anda y Salazar who was Governor General of the Philippines from 1769 to 1770. Simon de Anda was a member of the Royal Audiencia in the Philippin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Duero, Bohol
Duero, officially the Municipality of Duero ( ceb, Munisipyo sa Duero; tgl, Bayan ng Duero), is a 4th class municipality in the province of Bohol, Philippines. According to the 2020 census, it has a population of 18,861 people. It may have been named after the Douro (Duero) in the Iberian peninsula. Roman Catholicism was introduced to the town in 1860 by a Spanish priest. Duero was established as a municipality two years later, in 1862, and a convent was constructed in 1868. The town of Duero, Bohol celebrates its fiesta on December 8, to honor the town patron Immaculate Conception. Geography Barangays Duero comprises 21 barangays: Climate Demographics Economy Gallery Duero Bohol 3.JPG, Duero town hall Duero Bohol 1.JPG, Public market duerochurch.jpg, Church References External links * Philippine Standard Geographic Code The Philippines (; fil, Pilipinas, links=no), officially the Republic of the Philippines ( fil, Republi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jagna
Jagna, officially the Municipality of Jagna ( ceb, Munisipalidad sa Jagna; tgl, Bayan ng Jagna), is a 3rd class municipality in the province of Bohol, Philippines. According to the 2020 census, it has a population of 35,832 people. Jagna is located on the southern coast of Bohol. It is one of the commercial trading centers of the province with daily market and port operations. Of interest to visitors is the town church built during the Spanish era, with its ceiling frescoes and baroque architecture. A waterfall and a spring reservoir can be found on the highlands, accessible by road travel north. A marine sanctuary zone has been set up by the local government just off the shore. A double reef is protected inside the sanctuary zone and marked off by buoys to restrict access from fishers. Like Tagbilaran, Jagna is a port town. Ferries travel daily to and from other islands. Routes to Mindanao are available via Cagayan de Oro and Butuan. The island of Camiguin is visible from Jag ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rossi–Forel Scale
The Rossi–Forel scale was one of the first seismic scales to represent earthquake intensities. Developed by Michele Stefano de Rossi, Michele Stefano Conte de Rossi of Italy and François-Alphonse Forel of Switzerland during the late 19th century, it was used commonly for about two decades until the introduction of the Mercalli intensity scale in 1902. The Rossi–Forel scale and/or its modifications is still used in some countries, such as the Philippines until 1996 when it was replaced by the PHIVOLCS Earthquake Intensity Scale. Scale The 1873 version of the Rossi–Forel scale had 10 intensity levels: See also *Richter magnitude scale *Seismic intensity scales *Seismic magnitude scales Bibliography * Seismic intensity scales {{Seismology-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |