|
1987–88 South-West Indian Ocean Cyclone Season
The 1987–88 South-West Indian Ocean cyclone season was a moderately active cyclone season, with nine named storms. Four of the storms attained tropical cyclone status, which is the equivalent of a minimal hurricane with 10 minute sustained winds of at least . The seasonal activity was evenly dispersed, officially beginning on December 9 when the Météo-France office (MFR) on Réunion started tracking Tropical Storm Ariny. The storm crossed 90° E from the adjacent Australian basin, one of two storms in the season to do so along with Cyclone Ezenina. There were also two storms tracked unofficially by the Joint Typhoon Warning Center (JTWC) in November. Cyclone Filao was the most notable storm of the season, originating in late February off northern Madagascar. It ultimately struck Mozambique on March 1, where it killed about 100 people and left $10 million in damage (1988 USD). In January, both tropical storms Calidera and Doaza crossed M ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
1985–86 South-West Indian Ocean Cyclone Season
The 1985–86 South-West Indian Ocean cyclone season was the first in which the Météo-France office (MFR) on Réunion tracked cyclones as far east as 90° E in Indian Ocean, south of the equator. Previously, the agency's area of responsibility was limited to 80° E. It was an active season with twelve named storms, of which five strengthened into tropical cyclone with 10 minute sustained winds of at least . The first named storm was Tropical Storm Alifredy, which originated in the Mozambique Channel in late December and moved across Madagascar. However, the unofficial Joint Typhoon Warning Center (JTWC) tracked a short-lived storm in September. Most of the activity occurred in 1986, with four storms in January, three of which briefly existed simultaneously on January 10. The first of these three, Tropical Storm Berobia, struck eastern Mozambique. Tropical Storm Costa was a series of three tropical depressions within the same broader system that persisted ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dvorak Technique
The Dvorak technique (developed between 1969 and 1984 by Vernon Dvorak) is a widely used system to estimate tropical cyclone intensity (which includes tropical depression, tropical storm, and hurricane/typhoon/intense tropical cyclone intensities) based solely on visible and infrared Weather satellite, satellite images. Within the Dvorak satellite strength estimate for tropical cyclones, there are several Pattern recognition, visual patterns that a cyclone may take on which define the upper and lower bounds on its intensity. The primary patterns used are curved rainband, band pattern (T1.0-T4.5), Wind shear#Effects on tropical cyclones, shear pattern (T1.5–T3.5), central dense overcast (CDO) pattern (T2.5–T5.0), central cold cover (CCC) pattern, banding eye pattern (T4.0–T4.5), and Eye (cyclone), eye pattern (T4.5–T8.0). Both the central dense overcast and embedded eye pattern use the size of the CDO. The CDO pattern intensities start at T2.5, equivalent to minimal trop ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Convection (meteorology)
Atmospheric convection is the vertical transport of heat and moisture in the atmosphere. It occurs when warmer, less dense air rises, while cooler, denser air sinks. This process is driven by Air parcel, parcel-environment instability, meaning that a "parcel" of air is warmer and less dense than the surrounding environment at the same altitude. This difference in temperature and density (and sometimes humidity) causes the parcel to rise, a process known as buoyancy. This rising air, along with the compensating sinking air, leads to mixing, which in turn expands the height of the planetary boundary layer (PBL), the lowest part of the atmosphere directly influenced by the Earth's surface. This expansion contributes to increased Wind, winds, cumulus cloud development, and decreased surface Dew point, dew points (the temperature below which condensation occurs). Convection plays a crucial role in weather patterns, influencing cloud formation, wind, and the development of Thunderstor ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
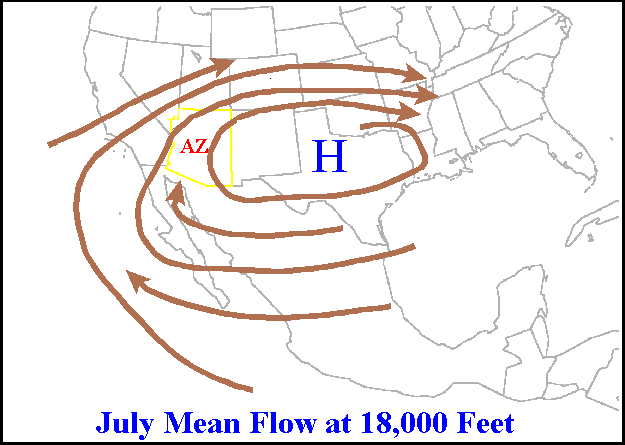
Ridge (meteorology)
In meteorology a ridge or barometric ridge is an elongated area of relatively high atmospheric pressure compared to the surrounding environment, without being a closed circulation. It is associated with an area of maximum anticyclonic curvature of wind flow. The ridge originates in the center of an anticyclone and sandwiched between two low-pressure areas, and the locus of the maximum curvature is called the ''ridge line''. This phenomenon is the opposite of a trough. Description Ridges can be represented in two ways: * On surface weather maps, the pressure isobars form contours where the maximum pressure is found along the axis of the ridge. * In upper-air maps, geopotential height isohypses form similar contours where the maximum defines the ridge. Related weather Given the direction of the winds around an anticyclonic circulation and the fact that weather systems move from west to east: *ahead of an upper-ridge, the airflow that comes from the polar regions and bri ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bureau Of Meteorology
The Bureau of Meteorology (BOM or BoM) is an executive agency of the Government of Australia, Australian Government that is responsible for providing Weather forecasting, weather forecasts and Meteorology, meteorological services to Australia and neighbouring countries. It was established in 1906 under the Meteorology Act (Cth), and brought together the States and territories of Australia, state meteorological services that existed before then. The states officially transferred their weather recording responsibilities to the Bureau of Meteorology on 1 January 1908. History The Bureau of Meteorology was established on 1 January 1908 following the passage of the ''Meteorology Act 1906''. Prior to Federation of Australia, Federation in 1901, each colony had had its own meteorological service, with all but two colonies also having a subsection devoted to astronomy. In August 1905, federal home affairs minister Littleton Groom surveyed state governments for their willingness to cede ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Intertropical Convergence Zone
The Intertropical Convergence Zone (ITCZ , or ICZ), known by sailors as the doldrums or the calms because of its monotonous windless weather, is the area where the northeast and the southeast trade winds converge. It encircles Earth near the thermal equator though its specific position varies seasonally. When it lies near the geographic equator, it is called the near-equatorial trough. Where the ITCZ is drawn into and merges with a monsoon, monsoonal circulation, it is sometimes referred to as a ''monsoon trough'' (a usage that is more common in Australia and parts of Asia). Meteorology The ITCZ was originally identified from the 1920s to the 1940s as the ''Intertropical Front'' (''ITF''), but after the recognition in the 1940s and the 1950s of the significance of convergence zone, wind field convergence in tropics, tropical weather production, the term ''Intertropical Convergence Zone'' (''ITCZ'') was then applied. The ITCZ appears as a band of clouds, usually thunderstorms, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Quirimbas National Park
The Quirimbas National Park (QNP)(''Hifadhi ya Taifa ya Kirimba'', in Swahili) is a protected area in the Cabo Delgado Province of Mozambique, encompassing the southern part of the Quirimbas Islands, as well as a significant mainland area. The mainland region of Taratibua contain various inselbergs. Location The park was established in June 2002. It stretches for along the northeast coast of Mozambique, and contains the southernmost 11 of the Quirimbas islands. The park has a tropical climate with a rainy season from December to April and a drier but cooler season from May to September. Daytime temperatures vary from around to depending on the time of year. Water temperatures are from to . Accommodations for tourists range from basic beach-front cottages to luxurious villas. Islands include Ibo Island, Mefunvo Island, Matemo Island, Quirimba Island, Quisiva island, Quilálea Island, Sencar Island and Rolas Island. Ecology The park protects of coastal forest, mangroves ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tropical Storm Five (5B) (1987)
The 1987 North Indian Ocean cyclone season was at the time, the most active cyclone season on record, taking the record from 1975 until it was beaten out 5 years later. The season has no official bounds but cyclones tend to form between April and December. These dates conventionally delimit the period of each year when most tropical cyclones form in the northern Indian Ocean. There are two main seas in the North Indian Ocean—the Bay of Bengal to the east of the Indian subcontinent and the Arabian Sea to the west of India. The official Regional Specialized Meteorological Centre in this basin is the India Meteorological Department (IMD), while the Joint Typhoon Warning Center (JTWC) releases unofficial advisories. An average of five tropical cyclones form in the North Indian Ocean every season with peaks in May and November. Cyclones occurring between the meridians 45°E and 100°E are included in the season by the IMD. Systems Very Severe Cyclonic Storm One (01B) Tropica ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sumatra
Sumatra () is one of the Sunda Islands of western Indonesia. It is the largest island that is fully within Indonesian territory, as well as the list of islands by area, sixth-largest island in the world at 482,286.55 km2 (182,812 mi.2), including adjacent islands such as the Simeulue Island, Simeulue, Nias Island, Nias, Mentawai Islands, Mentawai, Enggano Island, Enggano, Riau Islands, Bangka Belitung and Krakatoa archipelago. Sumatra is an elongated landmass spanning a diagonal northwest–southeast axis. The Indian Ocean borders the northwest, west, and southwest coasts of Sumatra, with the island chain of Simeulue, Nias, Mentawai Islands, Mentawai, and Enggano off the western coast. In the northeast, the narrow Strait of Malacca separates the island from the Malay Peninsula, which is an extension of the Eurasian continent. In the southeast, the narrow Sunda Strait, containing the Krakatoa archipelago, separates Sumatra from Java. The northern tip of Sumatra is near ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Diego Garcia
Diego Garcia is the largest island of the Chagos Archipelago. It has been used as a joint UK–U.S. military base since the 1970s, following the expulsion of the Chagossians by the UK government. The Chagos Islands are set to become a former British Overseas Territories, British overseas territory — a treaty to transfer sovereignty from the UK to Mauritius was signed on 22 May 2025, with a provision that the military base at the island would remain under British control for at least 99 years. Located just south of the equator in the central Indian Ocean, Diego Garcia lies east of Tanzania, east-southeast of Somalia, south of the Maldives, southwest of India, west-southwest of Sumatra, northwest of Australia, and northeast of Mauritius#Mauritius_Island, Mauritius Island. Diego Garcia is part of the Chagos–Laccadive Ridge, Chagos-Laccadive Ridge, an underwater mountain range that includes the Lakshadweep, the Maldives, and the other 60 small islands of the Chagos Archi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
United States Air Force
The United States Air Force (USAF) is the Air force, air service branch of the United States Department of Defense. It is one of the six United States Armed Forces and one of the eight uniformed services of the United States. Tracing its origins to 1 August 1907, as a part of the United States Army Signal Corps, the USAF was established by transfer of personnel from the Army Air Forces with the enactment of the National Security Act of 1947. It is the second youngest branch of the United States Armed Forces and the fourth in United States order of precedence, order of precedence. The United States Air Force articulates its core missions as air supremacy, intelligence, surveillance, target acquisition, and reconnaissance, global integrated intelligence, surveillance and reconnaissance, airlift, rapid global mobility, Strategic bombing, global strike, and command and control. The United States Department of the Air Force, Department of the Air Force, which serves as the USAF's ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
United States Navy
The United States Navy (USN) is the naval warfare, maritime military branch, service branch of the United States Department of Defense. It is the world's most powerful navy with the largest Displacement (ship), displacement, at 4.5 million tons in 2021. It has the world's largest aircraft carrier fleet, with List of aircraft carriers in service, eleven in service, one undergoing trials, two new carriers under construction, and six other carriers planned as of 2024. With 336,978 personnel on active duty and 101,583 in the Ready Reserve, the U.S. Navy is the third largest of the United States military service branches in terms of personnel. It has 299 deployable combat vessels and about 4,012 operational aircraft as of 18 July 2023. The U.S. Navy is one of six United States Armed Forces, armed forces of the United States and one of eight uniformed services of the United States. The United States Navy traces its origins to the Continental Navy, which was established during ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |