|
1986–88 French Nuclear Tests
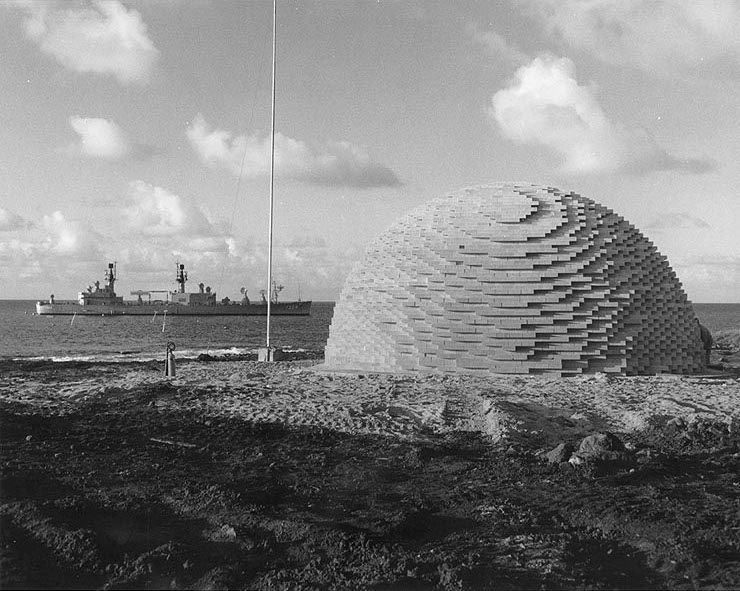
The 1986–1988 French nuclear tests were a group of 24 nuclear tests conducted between 1986 and 1988. These tests followed the '' 1983–1985 French nuclear tests'' series and preceded the '' 1989–1991 French nuclear tests'' series. References {{DEFAULTSORT:1986-88 French nuclear tests French nuclear weapons testing 1986 in French Polynesia 1987 in France 1988 in France ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
1983–85 French Nuclear Tests
The France's 1983–1985 nuclear test series was a group of 25 nuclear tests conducted in 1983–1985. These tests followed the '' 1981–1982 French nuclear tests'' series and preceded the '' 1986–1988 French nuclear tests'' series. References {{DEFAULTSORT:1983-85 French nuclear tests French nuclear weapons testing 1983 in French Polynesia 1984 in France 1985 in France ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nuclear Test
Nuclear weapons tests are experiments carried out to determine nuclear weapons' effectiveness, yield, and explosive capability. Testing nuclear weapons offers practical information about how the weapons function, how detonations are affected by different conditions, and how personnel, structures, and equipment are affected when subjected to nuclear explosions. However, nuclear testing has often been used as an indicator of scientific and military strength. Many tests have been overtly political in their intention; most nuclear weapons states publicly declared their nuclear status through a nuclear test. The first nuclear device was detonated as a test by the United States at the Trinity site in New Mexico on July 16, 1945, with a yield approximately equivalent to 20 kilotons of TNT. The first thermonuclear weapon technology test of an engineered device, codenamed "Ivy Mike", was tested at the Enewetak Atoll in the Marshall Islands on November 1, 1952 (local date), also by the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Universal Time
Universal Time (UT or UT1) is a time standard based on Earth's rotation. While originally it was mean solar time at 0° longitude, precise measurements of the Sun are difficult. Therefore, UT1 is computed from a measure of the Earth's angle with respect to the International Celestial Reference Frame (ICRF), called the Earth Rotation Angle (ERA, which serves as a modern replacement for Greenwich Mean Sidereal Time). UT1 is the same everywhere on Earth. UT1 is required to follow the relationship :ERA = 2π(0.7790572732640 + 1.00273781191135448'' · Tu'') radians where ''Tu'' = ( Julian UT1 date - 2451545.0). History Prior to the introduction of standard time, each municipality throughout the clock-using world set its official clock, if it had one, according to the local position of the Sun (see solar time). This served adequately until the introduction of rail travel in Britain, which made it possible to travel fast enough over long distances to require continuous ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Time Zone
A time zone is an area which observes a uniform standard time for legal, Commerce, commercial and social purposes. Time zones tend to follow the boundaries between Country, countries and their Administrative division, subdivisions instead of strictly following longitude, because it is convenient for areas in frequent communication to keep the same time. All time zones are defined as offsets from Coordinated Universal Time (UTC), ranging from UTC−12:00 to UTC+14:00. The UTC offset, offsets are usually a whole number of hours, but a few zones are offset by an additional 30 or 45 minutes, such as in Indian Standard Time, India, Time in Australia, South Australia and Nepal Time, Nepal. Some areas of higher latitude use daylight saving time for about half of the year, typically by adding one hour to local time during spring (season), spring and summer. List of UTC offsets In the table below, the locations that use daylight saving time (DST) are listed in their UTC offse ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tz Database
The tz database is a collaborative compilation of information about the world's time zones, primarily intended for use with computer programs and operating systems. Paul Eggert is its current editor and maintainer, with the organizational backing of ICANN. The tz database is also known as tzdata, the zoneinfo database or IANA time zone database, and occasionally as the Olson database, referring to the founding contributor, Arthur David Olson. Its uniform naming convention for time zones, such as ''America/New_York'' and ''Europe/Paris'', was designed by Paul Eggert. The database attempts to record historical time zones and all civil changes since 1970, the Unix time epoch. It also includes transitions such as daylight saving time, and also records leap seconds. The database, as well as some reference source code, is in the public domain. New editions of the database and code are published as changes warrant, usually several times per year. Data structure File formats The t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
List Of Nuclear Test Sites
This article contains a list of nuclear weapon explosion sites used across the world. It includes nuclear test sites, nuclear combat sites, launch sites for rockets forming part of a nuclear test, and peaceful nuclear test (PNE) sites. There are a few non-nuclear sites included, such as the Degelen Omega chemical blast sites, which are intimately involved with nuclear testing. Listed with each is an approximate location and coordinate link for viewing through GeoHack, and each site is linked to a Wikipedia page on the locality or the nuclear event(s) that occurred there. References See also * List of Milestone nuclear explosions * List of nuclear and radiation accidents and incidents * List of nuclear weapons tests * Worldwide nuclear testing counts and summary Nuclear weapons testing is the act of experimentally and deliberately firing one or more nuclear devices in a controlled manner pursuant to a military, scientific or technological goal. This has been done on ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Elevation
The elevation of a geographic location is its height above or below a fixed reference point, most commonly a reference geoid, a mathematical model of the Earth's sea level as an equipotential gravitational surface (see Geodetic datum § Vertical datum). The term ''elevation'' is mainly used when referring to points on the Earth's surface, while ''altitude'' or ''geopotential height'' is used for points above the surface, such as an aircraft in flight or a spacecraft in orbit, and '' depth'' is used for points below the surface. Elevation is not to be confused with the distance from the center of the Earth. Due to the equatorial bulge, the summits of Mount Everest and Chimborazo have, respectively, the largest elevation and the largest geocentric distance. Aviation In aviation the term elevation or aerodrome elevation is defined by the ICAO as the highest point of the landing area. It is often measured in feet and can be found in approach charts of the aerodrome. It is n ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Partial Nuclear Test Ban Treaty
The Partial Test Ban Treaty (PTBT) is the abbreviated name of the 1963 Treaty Banning Nuclear Weapon Tests in the Atmosphere, in Outer Space and Under Water, which prohibited all test detonations of nuclear weapons except for those conducted underground. It is also abbreviated as the Limited Test Ban Treaty (LTBT) and Nuclear Test Ban Treaty (NTBT), though the latter may also refer to the Comprehensive Nuclear-Test-Ban Treaty (CTBT), which succeeded the PTBT for ratifying parties. Negotiations initially focused on a comprehensive ban, but that was abandoned because of technical questions surrounding the detection of underground tests and Soviet concerns over the intrusiveness of proposed verification methods. The impetus for the test ban was provided by rising public anxiety over the magnitude of nuclear tests, particularly tests of new thermonuclear weapons (hydrogen bombs), and the resulting nuclear fallout. A test ban was also seen as a means of slowing nuclear proliferati ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
List Of Nuclear Weapons
This is a list of nuclear weapons listed according to country of origin, and then by type within the states. United States US nuclear weapons of all types – bombs, warheads, shells, and others – are numbered in the same sequence starting with the Mark 1 and () ending with the W-91 (which was canceled prior to introduction into service). All designs which were formally intended to be weapons at some point received a number designation. Pure test units which were experiments (and not intended to be weapons) are not numbered in this sequence. Early weapons were very large and could only be used as free fall bombs. These were known by "Mark" designators, like the Mark 4 which was a development of the Fat Man weapon. As weapons became more sophisticated they also became much smaller and lighter, allowing them to be used in many roles. At this time the weapons began to receive designations based on their role; bombs were given the prefix "B", while the same warhead used in other r ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nuclear Weapon Yield
The explosive yield of a nuclear weapon is the amount of energy released when that particular nuclear weapon is detonated, usually expressed as a TNT equivalent (the standardized equivalent mass of trinitrotoluene which, if detonated, would produce the same energy discharge), either in kilotonnes (kt—thousands of tonnes of TNT), in megatonnes (Mt—millions of tonnes of TNT), or sometimes in terajoules (TJ). An explosive yield of one terajoule is equal to . Because the accuracy of any measurement of the energy released by TNT has always been problematic, the conventional definition is that one kilotonne of TNT is held simply to be equivalent to 1012 calories. The yield-to-weight ratio is the amount of weapon yield compared to the mass of the weapon. The practical maximum yield-to-weight ratio for fusion weapons (thermonuclear weapons) has been estimated to six megatonnes of TNT per tonne of bomb mass (25 TJ/kg). Yields of 5.2 megatonnes/tonne and higher have been reported ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
TNT Equivalent
TNT equivalent is a convention for expressing energy, typically used to describe the energy released in an explosion. The is a unit of energy defined by that convention to be , which is the approximate energy released in the detonation of a metric ton (1,000 kilograms) of TNT. In other words, for each gram of TNT exploded, (or 4184 joules) of energy is released. This convention intends to compare the destructiveness of an event with that of conventional explosive materials, of which TNT is a typical example, although other conventional explosives such as dynamite contain more energy. Kiloton and megaton The "kiloton (of TNT)" is a unit of energy equal to 4.184 terajoules (). The "megaton (of TNT)" is a unit of energy equal to 4.184 petajoules (). The kiloton and megaton of TNT have traditionally been used to describe the energy output, and hence the destructive power, of a nuclear weapon. The TNT equivalent appears in various nuclear weapon control treaties, and has b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |