|
1983–84 Isthmian League
The 1983–84 season was the 69th season of the Isthmian League, an English football competition. Harrow Borough were champions, winning their first Isthmian League title. There was no promotion from the Isthmian League to the Alliance Premier League till 1985. Windsor & Eton finished first in Division One achieving the second promotion in a row. Corinthian-Casuals were excluded from the league after new groundsharing ruled were introduced. At the end of the season Division Two was split into two sections after 19 clubs, mainly from the Athenian League joined Division Two. Thus, the Athenian League was finally absorbed by Isthmian League. Premier Division The Premier Division consisted of 22 clubs, including 20 clubs from the previous season and two new clubs, promoted from Division One: * Harlow Town *Worthing Also, at the end of the previous season Leytonstone & Ilford changed name into Leytonstone/Ilford. At the end of the season Staines Town were demoted to Division One due ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Isthmian League
The Isthmian League () is a regional Association football, football league covering Greater London, East of England, East and South East England, featuring mostly semi-professional clubs. Founded in 1905 by amateur clubs in the London area, the league now consists of 88 teams in four divisions: the Premier Division above its three feeder divisions, the North, South Central and South East divisions. Together with the Southern Football League, Southern League and the Northern Premier League, it forms the seventh and eighth levels of the English football league system. It has various regional feeder leagues and the league as a whole is a feeder league mainly to the National League South. History Before the Isthmian League was formed, there were no leagues in which amateur football clubs could compete, only knock-out cup competitions. Therefore, a meeting took place between representatives of Casuals F.C., Casuals, Civil Service F.C., Civil Service, Clapton F.C., Clapton, Ealing A ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Wokingham Town F
Wokingham ( ) is a market town and civil parish in Berkshire, England. It is the main administrative centre of the wider Borough of Wokingham. At the 2021 census the parish had a population of 38,284 and the wider built-up area had a population of 50,325. History Wokingham means 'Wocca's people's home'. Wocca was apparently a Saxon chieftain who may also have owned lands at Wokefield in Berkshire and Woking in Surrey. In Victorian times, the name became corrupted to ''Oakingham'', and consequently the acorn with oak leaves is the town's heraldic charge, granted in the 19th century. Geologically, Wokingham sits at the northern end of the Bagshot Formation, overlying London clay, suggesting a prehistorical origin as a marine estuary. The courts of Windsor Forest were held at Wokingham and the town had the right to hold a market from 1219. The Bishop of Salisbury was largely responsible for the growth of the town during this period. He set out roads and plots making them ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Church Road (football Stadium)
Church Road was a 4,500-capacity football stadium Hayes, England – the home ground of Hayes, and latterly Hayes & Yeading United, following the two clubs' merger in 2007. BBC Sport, 28 March 2011 History After initially playing at Botwell Common, Hayes F.C. (then known as Botwell Mission) moved to the ground in Church Road. The site was originally named Cox's Meadow and later Townfield. It officially opened with a Whites vs Stripes trial match on 26 August 1920.Pyramid Passion During th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Champion Hill
Champion Hill is a association football, football stadium in East Dulwich in the London Borough of Southwark. It is the home ground of Dulwich Hamlet F.C., Dulwich Hamlet. History Dulwich Hamlet began playing at the ground in 1912. 'The Hill' was formerly one of the largest amateur grounds in England, with attendances often reaching 20,000 and beyond. Currently, it holds the record for the highest attendance at a league match outside of the English Football League at 16,254 for a 1931 Isthmian League match between Dulwich Hamlet and Nunhead F.C., Nunhead. The ground was also used for football at the 1948 Summer Olympics, staging a game between Mexico and South Korea. When Dulwich Hamlet suffered financial problems, much of the land they owned was sold for development of a Sainsbury's supermarket. As a result, a new stadium was built on the site of the old Champion Hill stadium, and the Sainsbury's supermarket was built on what had been the training pitch before the 1980s. The ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hayes Lane
Hayes Lane, currently known as the Copperjax Community Stadium for sponsorship reasons, is a association football, football Football-specific stadium, stadium in Bromley, Greater London, England. Located between Bromley town centre and Hayes, Bromley, Hayes, it is the home of Bromley F.C., Bromley Football Club and London City Lionesses. The current capacity of the ground is 5,000, of which 1,300 is seated and 2,500 covered.Mike Williams & Tony Williams (2013) ''Non-League Club Directory 2013: 35th Edition'' TW Publications, p273 History Bromley F.C. moved to Hayes Lane in 1938 from their previous ground, also on the same road.Bromley Pyramid Passion It initially featured a 2,500-seat stand on one side of the pitch, with the remainder of the pitch surrounded by banking. The ground was opened by Stanley Rous on 3 September 193 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tooting & Mitcham United F
Tooting is a district in South London, forming part of the London Borough of Wandsworth. It is located south south-west of Charing Cross. History Tooting has been settled since pre-Saxon times. The name is of Anglo-Saxon origin but the meaning is disputed. It could mean ''the people of Tota'', in which context Tota may have been a local Anglo-Saxon chieftain. Alternatively it could be derived from an old meaning of the verb ''to tout'', to look out. There may have been a watchtower here on the road to London and hence ''the people of the look-out post.'' The Romans built a road, which was later named Stane Street by the English, from London (Londinium) to Chichester (Noviomagus Regnorum), and which passed through Tooting. Tooting High Street is built on this road. In Saxon times, Tooting and Streatham (then Toting-cum-Stretham) was given to the Abbey of Chertsey. Later, Suene (Sweyn), believed to be a Viking, may have been given all or part of the land. In 933, King Æ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Carshalton Athletic F
Carshalton ( ) is a town, with a historic village centre, in south London, England, within the London Borough of Sutton. It is situated around southwest of Charing Cross and around east by north of Sutton town centre, in the valley of the River Wandle, one of the sources of which is Carshalton Ponds in the south of the village. Prior to the creation of Greater London in 1965, Carshalton was in the administrative county of Surrey. Carshalton consists of a number of neighbourhoods. The main focal point, Carshalton Village, is visually scenic and picturesque. At its centre it has two adjoining ponds, which are overlooked by the Grade II listed All Saints Church on the south side and the Victorian Grove Park on the north side. The Grade II listed Honeywood Museum sits on the west side, a few yards from the water. There are a number of other listed buildings, as well as three conservation areas, including one in the village. In addition to Honeywood Museum, there are several othe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Walthamstow Avenue F
Walthamstow ( or ) is a town within the London Borough of Waltham Forest in east London. The town borders Chingford to the north, Snaresbrook and South Woodford to the east, Leyton and Leytonstone to the south, and Tottenham to the west. At the 2011 census, Walthamstow had a population of approximately 109,424 and is around north-east of Central London. Occupying most of the town's east-to-west High Street, Walthamstow Market is the longest outdoor market in Europe. East of the town centre is Walthamstow Village, the oldest part of Walthamstow, and the location of St. Mary's Church, Walthamstow, St Mary's Church, the town's parish church. To the north of the town is the former Walthamstow Stadium, which was considered an Cockney, East End landmark. The William Morris Gallery in Forest Road, a museum that was once the family home of William Morris, is a Grade II* listed building. The town is served by five railway stations, including Walthamstow Central station, Walthamstow ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
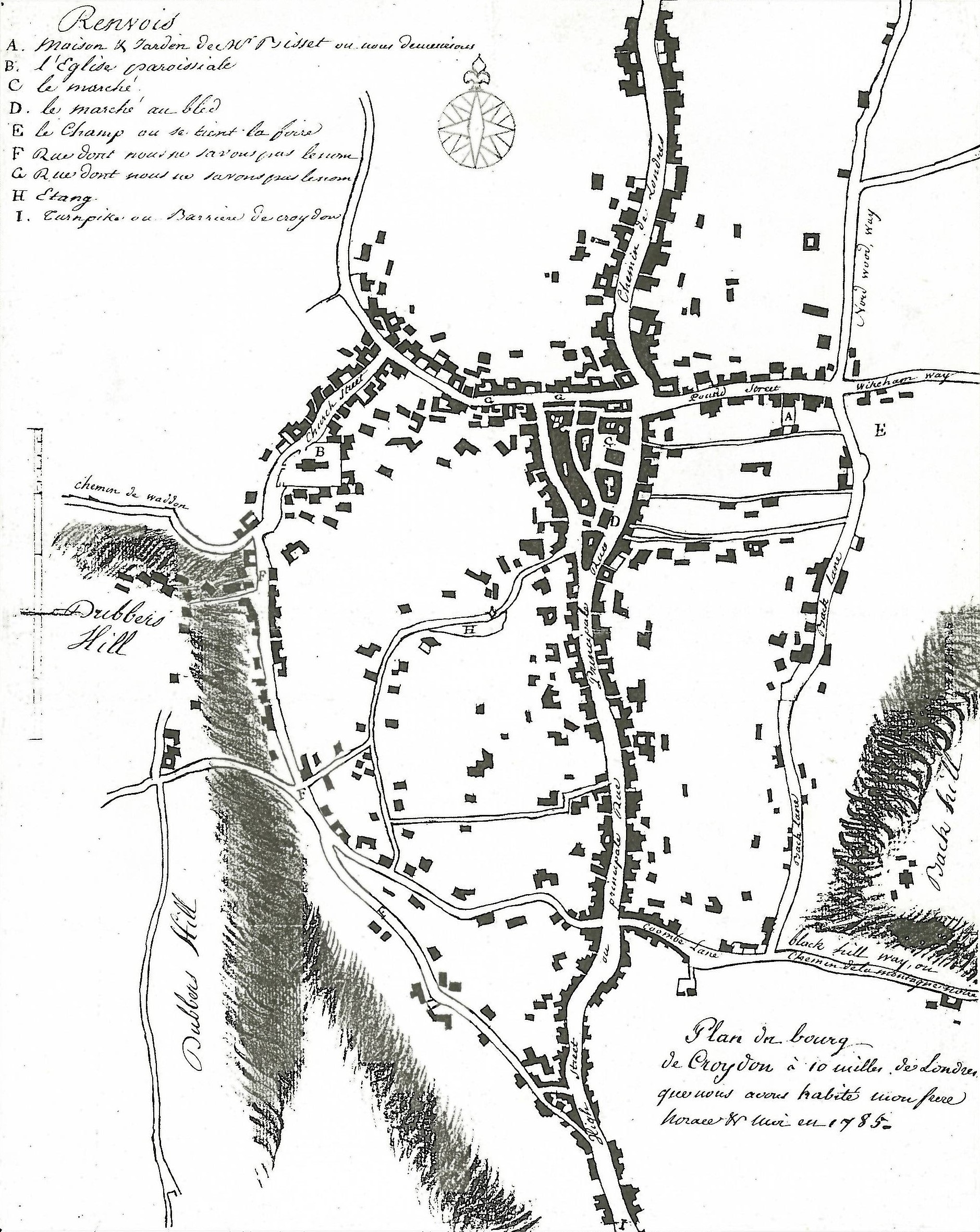
Croydon F
Croydon is a large town in South London, England, south of Charing Cross. Part of the London Borough of Croydon, a local government district of Greater London; it is one of the largest commercial districts in Greater London, with an extensive shopping area. The entire town had a population of 192,064 as of 2011, whilst the wider borough had a population of 384,837. Historically an ancient parish in the Wallington Hundred of Surrey, at the time of the Norman conquest of England Croydon had a church, a mill, and around 365 inhabitants, as recorded in the Domesday Book of 1086. Croydon expanded in the Middle Ages as a market town and a centre for charcoal production, leather tanning and brewing, with the brewing industry in particular remaining strong for hundreds of years. The Surrey Iron Railway from Croydon to Wandsworth opened in 1803 and was an early public railway. Later 19th century railway building facilitated Croydon's growth as a commuter town for London. By the early 2 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Barking F
Barking may refer to: Places * Barking, London, a town in East London, England ** London Borough of Barking, 1965–1980 ** Municipal Borough of Barking, 1931–1965 ** Barking (UK Parliament constituency) ** Barking (electoral division), Greater London Council * Barking, Suffolk, a village and civil parish in the Mid Suffolk district of Suffolk, England Arts and entertainment * ''Barking'' (album), by Underworld * "Barking" (song), by Ramz * ''Barking'' (TV series), a 1998 British sketch comedy show * '' Barking!'', a 2004 British children's series Other uses * Bark (sound) A bark is a sound most often produced by dogs. Other animals that make this noise include, but are not limited to, wolves, coyotes, foxes, seals, frogs and owls. "Bark" is also a verb that describes the sound of many canids. Definition ..., the sound dogs and some other animals make * Barking Rugby Football Club, an English rugby union club in Barking, London See also * Barking Lodge, a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Billericay Town F
Billericay ( ) is a town and civil parish in the Borough of Basildon in Essex, England. It lies within the London Basin, east of the City of London. The town was founded in the 13th century by the Abbot of West Ham, in his Manor of Great Burstead. During the Peasants’ Revolt of 1381, the Essex rebels were defeated in a battle with Richard II's forces in the Battle of Billericay. In 1620 four local people were on board the Mayflower as it sailed to Massachusetts, to establish the first English settlement in what would become the north of the United States. The town has long taken a pride in this connection, and many businesses and other organisations use the name ''Mayflower'', with the Town Council and other local organisations using it as their emblem. Toponym The origin of the name Billericay is unclear. It was first recorded as "Byllyrica" in 1291.PH Reaney-Place Names of Essex- English Place name Society - V12 The urban settlement, which was within the manor and par ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bognor Regis Town F
Bognor Regis (), also known as Bognor, is a town and seaside resort in West Sussex on the south coast of England, south-west of London, west of Brighton, south-east of Chichester and east of Portsmouth. Other nearby towns include Littlehampton east-north-east and Selsey to the south-west. The nearby villages of Felpham, and Aldwick are now suburbs of Bognor Regis, along with those of North and South Bersted. The population of the Bognor Regis built-up area, including Felpham and Aldwick, was 63,855 at the 2011 census. A seaside resort was developed by Sir Richard Hotham in the late 18th century on what was a sand and gravel, undeveloped coastline. It has been claimed that Hotham and his new resort are portrayed in Jane Austen's unfinished novel '' Sanditon''. The resort grew slowly in the first half of the 19th century but grew rapidly following the coming of the railway in 1864. In 1929 King George V spent three months in the area recuperating, and later that year the t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |