|
1953 In Spaceflight
The year 1953 saw the rockoon join the stable of sounding rockets capable of reaching beyond the boundary of space (as defined by the World Air Sports Federation). Employed by both the University of Iowa and the Naval Research Laboratory, 22 total were launched from the decks of the and the this year. All branches of the United States military continued their program of Aerobee sounding rocket launches, a total of 23 were launched throughout 1953. The Soviet Union launched no sounding rockets in 1953; however, the Soviet Union did conduct several series of missile test launches. Both the United States and the Union of Soviet Socialist Republics continued their development of ballistic missiles: the United States Air Force with its Atlas ICBM, the United States Army with its Redstone SRBM, the Soviet OKB-1 with its R-5 IRBM, and Soviet Factory 586 with its R-12 IRBM. None entered active service during 1953. The first meeting of the Comité Speciale de l'Année Géophy ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Deacon (rocket)
Deacon is the designation of an American sounding rocket. The Deacon was launched 90 times from 1947 to 1957 from Wallops Island, and it also was the rocket portion of the first rockoons, launched 1952 to 1956. The Deacon has a maximum flight height of 20 kilometers and a pay load ability of 17 kilograms. The takeoff thrust of the Deacon amounts to 27 kN, the takeoff weight In science and engineering, the weight of an object is the force acting on the object due to gravity. Some standard textbooks define weight as a vector quantity, the gravitational force acting on the object. Others define weight as a scalar qua ... 93 kg, the diameter 0.16 m and the length 3.28 m. Triple Deacon The Triple Deacon was a single stage member of the Deacon family that used three Deacon booster motors. Five launches from NASA's Wallops Flight Facility occurred in 1953 - 1954. See also * 1.9KS2150 References Deacon-Rocket {{Cajun rockets 1953 in spaceflight Sounding rockets of the United ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
OKB-1
PAO S. P. Korolev Rocket and Space Corporation Energia (russian: Ракетно-космическая корпорация «Энергия» им. С. П. Королёва, Raketno-kosmicheskaya korporatsiya "Energiya" im. S. P. Korolyova), also known as RSC Energia (, RKK "Energiya"), is a Russian manufacturer of spacecraft and space station components. The company is the prime developer and contractor of the Russian crewed spaceflight program; it also owns a majority of Sea Launch. Its name is derived from Sergei Korolev, the first chief of its design bureau, and the Russian word for energy. Overview Energia is the largest company of the Russian space industry and one of its key players. It is responsible for all operations involving human spaceflight and is the lead developer of the Soyuz and Progress spacecraft, and the lead developer of the Russian end of the International Space Station (ISS). In the mid-2000s, the company employed 22,000–30,000 people. The ente ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Skyhook Balloon
Skyhook balloons were high-altitude balloons developed by Otto C. Winzen and General Mills, Inc. They were used by the United States Navy Office of Naval Research (ONR) in the late 1940s and 1950s for atmospheric research, especially for constant-level meteorological observations at very high altitudes. Instruments like the Cherenkov detector were first used on Skyhook balloons. Project Skyhook In the late 1940s, Project Skyhook was conceived of as a means by which plastic balloons could be used to transmit or send instruments into the stratosphere to conduct research. This project carried forward work from an earlier project, Helios, that General Mills and Jean Piccard initiated to use arrays of giant plastic balloons to carry humans aloft. Balloons, long used for collecting meteorological data, now offered the opportunity of collecting highly specialized information and photographs. The first Skyhook balloon was launched on September 25, 1947. The balloon was developed by ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
1952 In Spaceflight
In 1952, several branches of the United States' military, often in partnership with civilian organizations, continued their programs of sounding rocket research beyond the boundary of space (as defined by the World Air Sports Federation) using the Aerobee rocket. The University of Iowa launched its first series of rockoon flights, demonstrating the validity of the balloon-launched rocket, a comparatively inexpensive way to explore the upper atmosphere. The launch of Viking 9 at the end of the year to an altitude of , by the Naval Research Laboratory team under the management of Milton Rosen, represented the pinnacle of contemporary operational rocket design. The same year, groundwork was laid for the launch of the first artificial satellite when, in October, the General Assembly of the International Council of Scientific Unions (ICSU) scheduled the International Geophysical Year for 1957–58. This scientific endeavor would involve 67 nations in a global investigation of ph ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
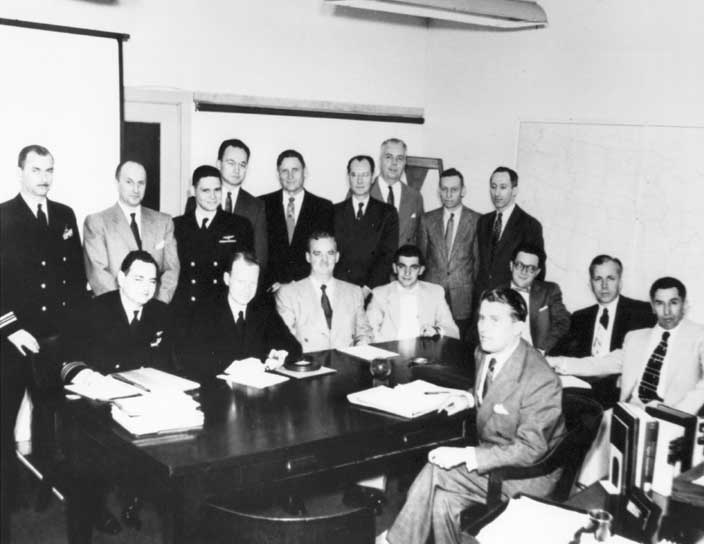
Milton Rosen
Milton William Rosen (July 25, 1915 – December 30, 2014) was a United States Navy engineer and project manager in the US space program between the end of World War II and the early days of the Apollo Program. He led development of the Viking and Vanguard rockets, and was influential in the critical decisions early in NASA's history that led to the definition of the Saturn rockets, which were central to the eventual success of the American Moon landing program. He died of prostate cancer in 2014. Early life Rosen was born in Philadelphia and earned a BS degree in Electrical Engineering from the University of Pennsylvania in 1937. In 1940, he began work at the Naval Research Laboratory, and during World War II, he worked on missile guidance systems. Viking rocket program After the end of WWII, Rosen worked at the US Naval Research Laboratory (NRL), where he was involved in the definition of alternative designs for high-altitude sounding rockets, both for scientific research on t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Glenn L
Glenn may refer to: Name or surname * Glenn (name) * John Glenn, U.S. astronaut Cultivars * Glenn (mango) * a 6-row barley variety Places In the United States: * Glenn, California * Glenn County, California * Glenn, Georgia, a settlement in Heard County * Glenn, Illinois * Glenn, Michigan * Glenn, Missouri * University, Orange County, North Carolina, formerly called Glenn * Glenn Highway in Alaska Organizations *Glenn Research Center, a NASA center in Cleveland, Ohio See also * New Glenn New Glenn is a heavy-lift orbital launch vehicle in development by Blue Origin. Named after NASA astronaut John Glenn, design work on the vehicle began in 2012. Illustrations of the vehicle, and the high-level specifications, were initial ..., a heavy-lift orbital launch vehicle * * * Glen, a valley * Glen (other) {{disambiguation, geo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
New Mexico
) , population_demonym = New Mexican ( es, Neomexicano, Neomejicano, Nuevo Mexicano) , seat = Santa Fe , LargestCity = Albuquerque , LargestMetro = Tiguex , OfficialLang = None , Languages = English, Spanish ( New Mexican), Navajo, Keres, Zuni , Governor = , Lieutenant Governor = , Legislature = New Mexico Legislature , Upperhouse = Senate , Lowerhouse = House of Representatives , Judiciary = New Mexico Supreme Court , Senators = * * , Representative = * * * , postal_code = NM , TradAbbreviation = N.M., N.Mex. , area_rank = 5th , area_total_sq_mi = 121,591 , area_total_km2 = 314,915 , area_land_sq_mi = 121,298 , area_land_km2 = 314,161 , area_water_sq_mi = 292 , area_water_km2 = 757 , area_water_percent = 0.24 , population_as_of = 2020 , population_rank = 36th , 2010Pop = 2,117,522 , population_density_rank = 45th , 2000DensityUS = 17.2 , 2000Density = 6.62 , MedianHouseholdIncome = $51,945 , IncomeRank = 45th , AdmittanceOrder = ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
White Sands Missile Range
White Sands Missile Range (WSMR) is a United States Army military testing area and firing range located in the US state of New Mexico. The range was originally established as the White Sands Proving Ground on 9July 1945. White Sands National Park is located within the range. Significant events *The first atomic bomb (code named Trinity) was test detonated at Trinity Site near the northern boundary of the range on 16 July 1945, seven days after the White Sands Proving Ground was established. *After the conclusion of World War II, 100 long-range German V-2 rockets that were captured by U.S. military troops were brought to WSMR. Of these, 67 were test-fired between 1946 and 1951 from the White Sands V-2 Launching Site. (This was followed by the testing of American rockets, which continues to this day, along with testing other technologies.) *NASA's Space Shuttle Columbia landed on the Northrop Strip at WSMR on 30 March 1982 as the conclusion to mission STS-3. This was the only ti ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
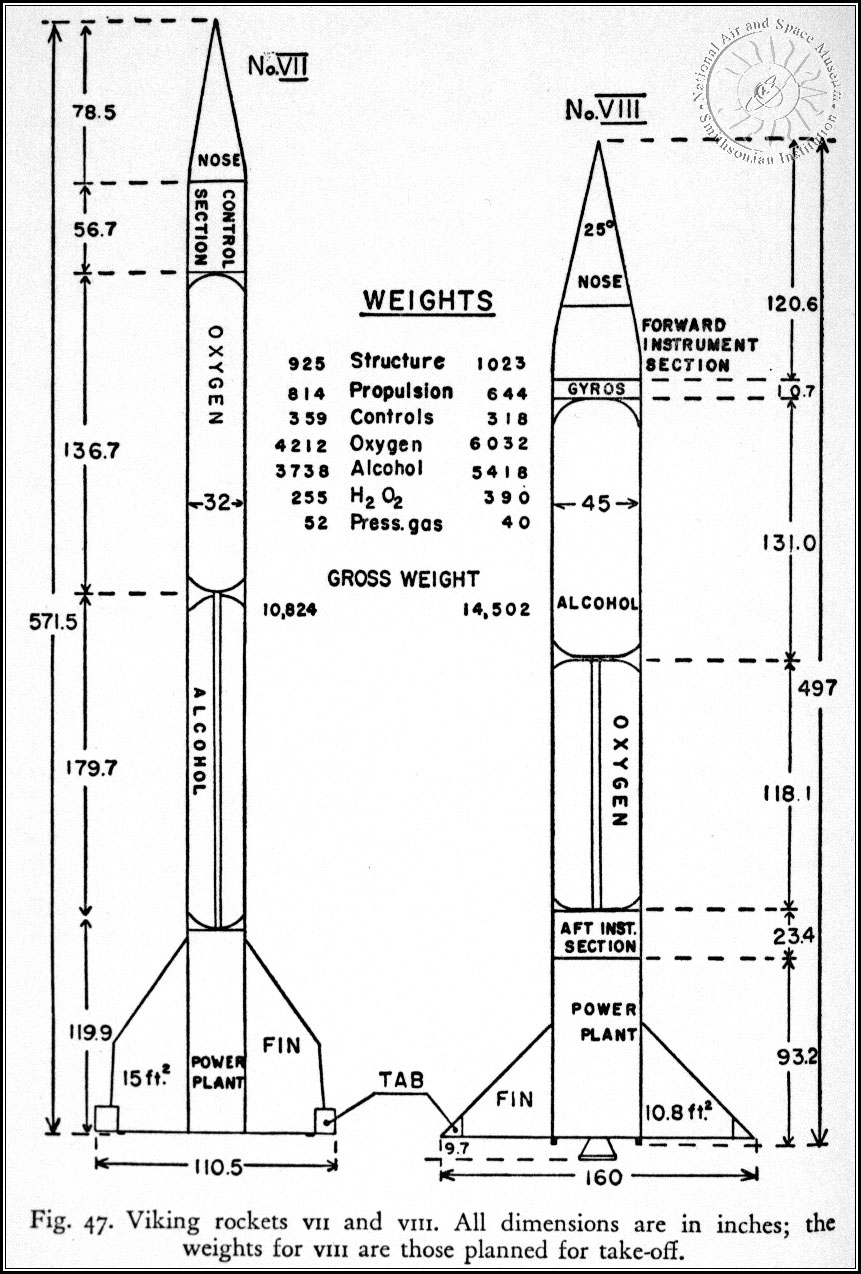
Viking (rocket)
Viking was series of twelve sounding rockets designed and built by the Glenn L. Martin Company under the direction of the U.S. Naval Research Laboratory (NRL). Designed to supersede the German V-2, the Viking was the most advanced large, liquid-fueled rocket developed in the United States in the late 1940s, returning valuable scientific data from the edge of space between 1949 and 1955. Viking 4, launched in 1950, was the first sounding rocket to be launched from the deck of a ship. After twelve flights, the Viking was adapted into the first stage for the Vanguard rocket, which launched America's second satellite into orbit in 1958. Origins After World War II, the United States experimented with captured German V-2 rockets as part of the Hermes program. Based on these experiments the U.S. issued a contract 21 August 1946 to the Glenn L. Martin Company for a series of ten large liquid-fueled rockets. The intent was to provide an independent U.S. capability in rocketry, to co ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Viking 10
Viking was series of twelve sounding rockets designed and built by the Glenn L. Martin Company under the direction of the U.S. Naval Research Laboratory (NRL). Designed to supersede the German V-2, the Viking was the most advanced large, liquid-fueled rocket developed in the United States in the late 1940s, returning valuable scientific data from the edge of space between 1949 and 1955. Viking 4, launched in 1950, was the first sounding rocket to be launched from the deck of a ship. After twelve flights, the Viking was adapted into the first stage for the Vanguard rocket, which launched America's second satellite into orbit in 1958. Origins After World War II, the United States experimented with captured German V-2 rockets as part of the Hermes program. Based on these experiments the U.S. issued a contract 21 August 1946 to the Glenn L. Martin Company for a series of ten large liquid-fueled rockets. The intent was to provide an independent U.S. capability in rocketry, to co ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
International Geophysical Year
The International Geophysical Year (IGY; french: Année géophysique internationale) was an international scientific project that lasted from 1 July 1957 to 31 December 1958. It marked the end of a long period during the Cold War when scientific interchange between East and West had been seriously interrupted. Sixty-seven countries participated in IGY projects, although one notable exception was the mainland People's Republic of China, which was protesting against the participation of the Republic of China (Taiwan). East and West agreed to nominate the Belgian Marcel Nicolet as secretary general of the associated international organization. The IGY encompassed eleven Earth sciences: aurora and airglow, cosmic rays, geomagnetism, gravity, ionospheric physics, longitude and latitude determinations (precision mapping), meteorology, oceanography, seismology, and solar activity. The timing of the IGY was particularly suited for studying some of these phenomena, since it covered th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
International Council Of Scientific Unions
The International Council for Science (ICSU, after its former name, International Council of Scientific Unions) was an international non-governmental organization devoted to international cooperation in the advancement of science. Its members were national scientific bodies and international scientific unions. In July 2018, the ICSU merged with the International Social Science Council (ISSC) to form the International Science Council (ISC). In 2017, the ICSU comprised 122 multi-disciplinary National Scientific Members, Associates and Observers representing 142 countries and 31 international, disciplinary Scientific Unions. ICSU also had 22 Scientific Associates. In July 2018, ICSU merged with the International Social Science Council (ISSC) to form the International Science Council (ISC) at a constituent general assembly in Paris. Mission and principles The ICSU's mission was to strengthen international science for the benefit of society. To do this, the ICSU mobilized the know ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |




_in_1950.jpg)