|
1940 Pacific Typhoon Season
The 1940 Pacific typhoon season marked an interruption in meteorological records in both the Philippines and Hong Kong due to the start of World War II. There were 43 reported tropical cyclones, including 27 that attained typhoon status. The first storm was observed in February, and the first typhoon formed two months later, killing three people along Mindanao. Several storms formed in June and July, including reports of a typhoon in the newspapers that killed 52 in South Korea, and another typhoon reported in newspapers that killed one person on Samar after dropping heavy rainfall. The strongest typhoon of the season originated in July and attained a minimum pressure of , as reported by a ship northeast of the Philippines. On August 18, a typhoon moved near or over northeastern Luzon, killing nine people. In early September, a typhoon passed through the Bonin Islands south of Japan and later moved near Kyushu; heavy rainfall caused a reservoir to collapse in Ĺ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
1938 Pacific Typhoon Season
The 1938 Pacific typhoon season featured 31 storms. Data from this period was extremely sparse, so intensity is not available for these systems. The only agency that tracked these typhoons is the International Best Track Archive for Climate Stewardship (IBRrACS), which has compiled a database of all known tropical cyclones since 1851. Systems January–May The first storm of the season formed on January 11, west of the Philippines. It moved northwestward, and made landfall on Luzon late on January 12 before dissipating the next day. It caused no known deaths or damage. IBTRACS gives a storm of unknown intensity, from April 5 to April 12. It did not affect land. IBTRACS gives a storm of unknown intensity, from April 29 to May 4. It affected the Philippines, and neared China. IBTRACS gives a storm of unknown intensity, from May 9 to May 16. It affected the Philippines. June and July IBTRACS gives a storm of unknown intensity, from June 21 to July 3. It affected Japan. IBTRAC ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Wake Island
Wake Island ( mh, Ānen Kio, translation=island of the Sida fallax, kio flower; also known as Wake Atoll) is a coral atoll in the western Pacific Ocean in the northeastern area of the Micronesia subregion, east of Guam, west of Honolulu, southeast of Tokyo and north of Majuro. The island is an Territories of the United States, unorganized, unincorporated territories of the United States, unincorporated territory belonging to (but not a part of) the United States that is also claimed by the Marshall Islands, Republic of the Marshall Islands. Wake Island is one of the most isolated islands in the world. The nearest inhabited island is Utirik Atoll in the Marshall Islands, to the southeast. The United States took possession of Wake Island in 1899. One of 14 U.S. insular areas, Wake Island is administered by the United States Air Force under an agreement with the United States Department of the Interior, U.S. Department of the Interior. The center of activity on the atoll is at ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cebu
Cebu (; ceb, Sugbo), officially the Province of Cebu ( ceb, Lalawigan sa Sugbo; tl, Lalawigan ng Cebu; hil, Kapuroan sang Sugbo), is a province of the Philippines located in the Central Visayas region, and consists of a main island and 167 surrounding islands and islets. Its capital and largest city is Cebu City, nicknamed "the Queen City of the South", the oldest city and first capital of the Philippines, which is politically independent from the provincial government. The Cebu Metropolitan Area or Metro Cebu is the second largest metropolitan area in the Philippines (after Metro Manila) with Cebu City as the main center of commerce, trade, education and industry in the Visayas. Being one of the most developed provinces in the Philippines, in a decade it has transformed into a global hub for business processing services, tourism, shipping, furniture-making, and heavy industry. Mactan–Cebu International Airport, located on Mactan Island, is the second busiest ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Negros (island)
Negros is the fourth largest and third most populous island in the Philippines, with a total land area of . Negros is one of the many islands of the Visayas, in the central part of the country. The predominant inhabitants of the island region are mainly called '' Negrenses'' (locally ''Negrosanons''). As of 2020 census, the total population of Negros is 4,656,945 people. From May 29, 2015 to August 9, 2017, the whole island was governed as an administrative region officially named the Negros Island Region, which comprised the highly urbanized city of Bacolod and the provinces of Negros Occidental and Negros Oriental, along with its corresponding outlying islands and islets within a total regional area of . It was created on May 29, 2015 by virtue of ''Executive Order No. 183'' issued by Benigno Aquino III, who was the president at that time. On August 9, 2017, President Rodrigo Duterte signed the Executive Order No. 38 dissolving the Negros Island Region. History Precolo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hinatuan, Surigao Del Sur
Hinatuan is a second class municipality in the province of Surigao del Sur, Philippines. According to the 2020 census, it has a population of 43,841 people. Hinatuan is approximately 44 kilometers (27 miles) north of Bislig, a component city in the same province. History Pre-Spanish Era The history of Hinatuan in the annals of historical heritage can be traced back from the time of the Spaniards in this part of Mindanao. The intermingling of tribes such as the Manobos, the Mansakas, Subanons and the Mandayas through assimilation and amalgamation leads to the final unification of a group of people who settled in the old town site known as Da-an Lungsod. Being the first and the earliest settlement, it was later identified as part of the province of Caraga under the administration of the politico - militar of Encomienda Bislig. The name Hinatuan, originally derived from the word "''Hatud''" and later called "''Hatudan''" was handed down from generation to generation throu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Landfall (meteorology)
Landfall is the event of a storm moving over land after being over water. More broadly, and in relation to human travel, it refers to 'the first land that is reached or seen at the end of a journey across the sea or through the air, or the fact of arriving there. Tropical cyclone A tropical cyclone is classified as making landfall when the center of the storm moves across the coast; in a relatively strong tropical cyclone, this is when the eye moves over land. This is where most of the damage occurs within a mature tropical cyclone, such as a typhoon or hurricane, as most of the damaging aspects of these systems are concentrated near the eyewall. Such effects include the peaking of the storm surge, the core of strong winds coming ashore, and heavy flooding rains. These coupled with high surf can cause major beach erosion. When a tropical cyclone makes landfall, the eye usually closes in upon itself due to negative environmental factors over land, such as friction with the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Beaufort Scale
The Beaufort scale is an empirical measure that relates wind speed to observed conditions at sea or on land. Its full name is the Beaufort wind force scale. History The scale was devised in 1805 by the Irish hydrographer Francis Beaufort (later Rear Admiral), a Royal Navy officer, while serving on . The scale that carries Beaufort's name had a long and complex evolution from the previous work of others (including Daniel Defoe the century before) to when Beaufort was Hydrographer of the Navy in the 1830s, when it was adopted officially and first used during the voyage of HMS ''Beagle'' under Captain Robert FitzRoy, who was later to set up the first Meteorological Office (Met Office) in Britain giving regular weather forecasts. In the 18th century, naval officers made regular weather observations, but there was no standard scale and so they could be very subjective – one man's "stiff breeze" might be another's "soft breeze". Beaufort succeeded in standardising the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Inch Of Mercury
Inch of mercury (inHg and ″Hg) is a non- SI unit of measurement for pressure. It is used for barometric pressure in weather reports, refrigeration and aviation in the United States. It is the pressure exerted by a column of mercury in height at the standard acceleration of gravity. Conversion to metric units depends on the temperature of mercury, and hence its density; typical conversion factors are: In older literature, an "inch of mercury" is based on the height of a column of mercury at .Barry N. Taylor, ''Guide for the Use of the International System of Units (SI),'' 1995, NIST Special Publication 811, Appendix /ref> :1 inHg60 °F = In Imperial units: 1 inHg60 °F = 0.489 771 Pounds per square inch, psi, or 2.041 771 inHg60 °F = 1 psi. Applications Aircraft and automobiles Aircraft altimeters measure the relative pressure difference between the lower ambient pressure at altitude and a calibrated reading on the ground. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bar (unit)
The bar is a metric unit of pressure, but not part of the International System of Units (SI). It is defined as exactly equal to 100,000 Pa (100 kPa), or slightly less than the current average atmospheric pressure on Earth at sea level (approximately 1.013 bar). By the barometric formula, 1 bar is roughly the atmospheric pressure on Earth at an altitude of 111 metres at 15 °C. The bar and the millibar were introduced by the Norwegian meteorologist Vilhelm Bjerknes, who was a founder of the modern practice of weather forecasting. The International System of Units, despite previously mentioning the bar, now omits any mention of it.. The bar has been legally recognised in countries of the European Union since 2004. British Standard BS 350:2004 ''Conversion Factors for Units''. The US National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST) deprecates its use except for "limited use in meteorology" and lists it as one of several units that "must not be i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Atmospheric Pressure
Atmospheric pressure, also known as barometric pressure (after the barometer), is the pressure within the atmosphere of Earth. The standard atmosphere (symbol: atm) is a unit of pressure defined as , which is equivalent to 1013.25 millibars, 760 mm Hg, 29.9212 inchesHg, or 14.696 psi.International Civil Aviation Organization. ''Manual of the ICAO Standard Atmosphere'', Doc 7488-CD, Third Edition, 1993. . The atm unit is roughly equivalent to the mean sea-level atmospheric pressure on Earth; that is, the Earth's atmospheric pressure at sea level is approximately 1 atm. In most circumstances, atmospheric pressure is closely approximated by the hydrostatic pressure caused by the weight of air above the measurement point. As elevation increases, there is less overlying atmospheric mass, so atmospheric pressure decreases with increasing elevation. Because the atmosphere is thin relative to the Earth's radius—especially the dense atmospheric layer at low altitudes—the E ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Palau
Palau,, officially the Republic of Palau and historically ''Belau'', ''Palaos'' or ''Pelew'', is an island country and microstate in the western Pacific. The nation has approximately 340 islands and connects the western chain of the Caroline Islands with parts of the Federated States of Micronesia. It has a total area of . The most populous island is Koror, home to the country's most populous city of the same name. The capital Ngerulmud is located on the nearby island of Babeldaob, in Melekeok State. Palau shares maritime boundaries with international waters to the north, the Federated States of Micronesia to the east, Indonesia to the south, and the Philippines to the northwest. The country was originally settled approximately 3,000 years ago by migrants from Maritime Southeast Asia. Palau was first drawn on a European map by the Czech missionary Paul Klein based on a description given by a group of Palauans shipwrecked on the Philippine coast on Samar. Pal ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
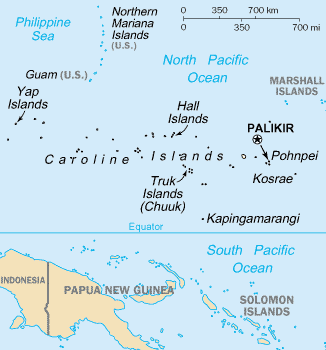
Caroline Islands
The Caroline Islands (or the Carolines) are a widely scattered archipelago of tiny islands in the western Pacific Ocean, to the north of New Guinea. Politically, they are divided between the Federated States of Micronesia (FSM) in the central and eastern parts of the group, and Palau at the extreme western end. Historically, this area was also called ''Nuevas Filipinas'' or New Philippines, because they were part of the Spanish East Indies and were governed from Manila in the Philippines. The Carolines are scattered across a distance of approximately 3,540 kilometers (2,200 miles), from the westernmost island, Tobi, in Palau, to the easternmost island, Kosrae, a state of the FSM. Description The group consists of about 500 small coral islands, east of the Philippines, in the Pacific Ocean. The distance from Yap (one of the larger Caroline islands) to Manila is . Most of the islands are made up of low, flat coral atolls, but there are some that rise high above sea leve ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |


.jpg)