|
1933 Treasure Coast Hurricane
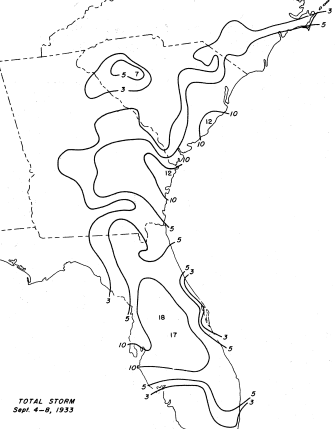
The 1933 Treasure Coast hurricane was the second-most intense tropical cyclone to strike the United States during the active 1933 Atlantic hurricane season. The eleventh tropical storm, fifth hurricane, and the third major hurricane of the season, it formed east-northeast of the Leeward Islands on August 31. The tropical storm moved rapidly west-northwestward, steadily intensifying to a hurricane. It acquired peak winds of 140 mph (220 km/h) and passed over portions of the Bahamas on September 3, including Eleuthera and Harbour Island, causing severe damage to crops, buildings, and infrastructure. Winds over affected many islands in its path, especially those that encountered its center, and many wharves were ruined. Subsequently, it weakened and made landfall at Jupiter, Florida, early on September 4 with winds of 125 mph (205 km/h). The hurricane moved across the state, passing near Tampa before moving into Georgia and dissipating. In Flor ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Surface Weather Analysis
Surface weather analysis is a special type of weather map that provides a view of weather elements over a geographical area at a specified time based on information from ground-based weather stations. Weather maps are created by plotting or tracing the values of relevant quantities such as sea level pressure, temperature, and cloud cover onto a geographical map to help find synoptic scale features such as weather fronts. The first weather maps in the 19th century were drawn well after the fact to help devise a theory on storm systems.Eric R. MillerAmerican Pioneers in Meteorology.Retrieved on 2007-04-18. After the advent of the telegraph, simultaneous surface weather observations became possible for the first time, and beginning in the late 1840s, the Smithsonian Institution became the first organization to draw real-time surface analyses. Use of surface analyses began first in the United States, spreading worldwide during the 1870s. Use of the Norwegian cyclone model for fronta ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fort Pierce, Florida
Fort Pierce is a city in and the county seat of St. Lucie County, Florida, United States. The city is part of the Treasure Coast region of Atlantic Coast Florida. It is also known as the Sunrise City, sister to San Francisco, California, the Sunset City. Per the 2020 census, the population was 47,297. History It was named after the Fort Pierce Army post which was built nearby in 1838 during the Second Seminole War. The military post had been named for Benjamin Kendrick Pierce, a career United States Army officer and the brother of President Franklin Pierce. It was the largest city on Florida's Atlantic Coast between Daytona Beach and West Palm Beach until 1970 when it was surpassed by Melbourne. Geography According to the U. S. Census Bureau, the city has a total area of 20.8 mi2 (53.8 km2), of which 14.7 square miles (38.2 km2) is land and 6.0 square miles (15.6 km2) of it (35.00%) is water. Environment Shore Protection project According to the U ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Eye (cyclone)
The eye is a region of mostly calm weather at the center of tropical cyclones. The eye of a storm is a roughly circular area, typically in diameter. It is surrounded by the ''eyewall'', a ring of towering thunderstorms where the most severe weather and highest winds occur. The cyclone's lowest barometric pressure occurs in the eye and can be as much as 15 percent lower than the pressure outside the storm. In strong tropical cyclones, the eye is characterized by light winds and clear skies, surrounded on all sides by a towering, symmetric eyewall. In weaker tropical cyclones, the eye is less well defined and can be covered by the central dense overcast, an area of high, thick clouds that show up brightly on satellite imagery. Weaker or disorganized storms may also feature an eyewall that does not completely encircle the eye or have an eye that features heavy rain. In all storms, however, the eye is the location of the storm's minimum barometric pressure—where the atmospheric pr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Coordinated Universal Time
Coordinated Universal Time or UTC is the primary time standard by which the world regulates clocks and time. It is within about one second of mean solar time (such as UT1) at 0° longitude (at the IERS Reference Meridian as the currently used prime meridian) and is not adjusted for daylight saving time. It is effectively a successor to Greenwich Mean Time (GMT). The coordination of time and frequency transmissions around the world began on 1 January 1960. UTC was first officially adopted as CCIR Recommendation 374, ''Standard-Frequency and Time-Signal Emissions'', in 1963, but the official abbreviation of UTC and the official English name of Coordinated Universal Time (along with the French equivalent) were not adopted until 1967. The system has been adjusted several times, including a brief period during which the time-coordination radio signals broadcast both UTC and "Stepped Atomic Time (SAT)" before a new UTC was adopted in 1970 and implemented in 1972. This change also a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Harbour Island, Bahamas
Harbour Island is an island and administrative district in the Bahamas and is located off the northeast coast of Eleuthera Island. It has a population of 1,762 (2010 census). - Bahamas Department of Statistics The only town on the island is , named after the governor of the Bahamas from 1786 to 1798, John Murray, 4th Earl of Dunmor ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Turks And Caicos
The Turks and Caicos Islands (abbreviated TCI; and ) are a British Overseas Territory consisting of the larger Caicos Islands and smaller Turks Islands, two groups of tropical islands in the Lucayan Archipelago of the Atlantic Ocean and northern West Indies. They are known primarily for tourism and as an offshore financial centre. The resident population in July 2021 was put at 57,196, making it the third-largest of the British overseas territories by population. The islands are southeast of Mayaguana in the Bahamas island chain and north of the island of Hispaniola (Haiti and the Dominican Republic). Grand Turk (Cockburn Town), the capital since 1766, is situated on Grand Turk Island about east-southeast of Miami, United States. They have a total land area of . The islands were inhabited for centuries by indigenous peoples. The first recorded European sighting of them was in 1512. In subsequent centuries, they were claimed by several European powers, with the British Emp ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hurricane Research Division
The Hurricane Research Division (HRD) is a section of the Atlantic Oceanographic and Meteorological Laboratory (AOML) in Miami, Florida, and is the U.S. National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration's (NOAA) focus for tropical cyclone research. The thirty member division is not a part of the National Hurricane Center but cooperates closely with them in carrying out its annual field program and in transitioning research results into operational tools for hurricane forecasters. HRD was formed from the National Hurricane Research Laboratory in 1984, when it was transferred to AOML and unified with the oceanographic laboratories. In August, 1992, the AOML/HRD facility sustained moderate damage after the passage of Hurricane Andrew across southern Dade County, Florida, however, despite significant personal disruption to the lives of almost all of its staff members, HRD reconnaissance flights continued into Andrew until it made a final landfall along the Louisiana coastline several day ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Atlantic Oceanographic And Meteorological Laboratory
The Atlantic Oceanographic and Meteorological Laboratory (AOML), a federal research laboratory, is part of the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration's (NOAA) Office of Oceanic and Atmospheric Research (OAR), located in Miami in the United States. AOML's research spans tropical cyclone and hurricanes, coastal ecosystems, oceans and human health, climate studies, global carbon systems, and ocean observations. It is one of seven NOAA Research Laboratories (RLs). AOML’s organizational structure consists of an Office of the Director and three scientific research divisions. The Office of the Director oversees the Laboratory’s scientific programs, as well as its financial, administrative, computer, outreach/education, and facility management services. Research programs are augmented by Cooperative Institutes, such as the Cooperative Institute for Marine and Atmospheric Studies (CIMAS), a joint enterprise with the University of Miami’s Rosenstiel School of Marine, Atmosphe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Atlantic Hurricane Reanalysis Project
The Atlantic hurricane reanalysis project of the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration seeks to correct and add new information about past North Atlantic hurricanes. It was started around 2000 to update HURDAT, the official hurricane database for the Atlantic Basin, which has become outdated since its creation due to various systematic errors introduced into the database over time. This effort has involved reanalyses of ship observations from the International Comprehensive Ocean-Atmosphere Data Set (ICOADS) as well as reanalyses done by other researchers over the years. It has been ongoing as of 2016, and should last another four years. Inaccuracies and omissions in existing data Errors HURDAT contains a number of errors which need to be corrected, such demonstrated by the outliers in the a pressure vs. wind speed graph of datapoints in the database (right). Some of these errors have existed since the database's creation during NASA's Apollo Program, where it was ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Atmospheric Pressure
Atmospheric pressure, also known as barometric pressure (after the barometer), is the pressure within the atmosphere of Earth. The standard atmosphere (symbol: atm) is a unit of pressure defined as , which is equivalent to 1013.25 millibars, 760mm Hg, 29.9212 inchesHg, or 14.696psi.International Civil Aviation Organization. ''Manual of the ICAO Standard Atmosphere'', Doc 7488-CD, Third Edition, 1993. . The atm unit is roughly equivalent to the mean sea-level atmospheric pressure on Earth; that is, the Earth's atmospheric pressure at sea level is approximately 1 atm. In most circumstances, atmospheric pressure is closely approximated by the hydrostatic pressure caused by the weight of air above the measurement point. As elevation increases, there is less overlying atmospheric mass, so atmospheric pressure decreases with increasing elevation. Because the atmosphere is thin relative to the Earth's radius—especially the dense atmospheric layer at low altitudes—the Earth's gravi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lesser Antilles
The Lesser Antilles ( es, link=no, Antillas Menores; french: link=no, Petites Antilles; pap, Antias Menor; nl, Kleine Antillen) are a group of islands in the Caribbean Sea. Most of them are part of a long, partially volcanic island arc between the Greater Antilles to the north-west and the continent of South America."West Indies." ''Merriam-Webster's Geographical Dictionary'', 3rd ed. 2001. () Springfield, MA: Merriam-Webster Inc., p. 1298. The islands of the Lesser Antilles form the eastern boundary of the Caribbean Sea where it meets the Atlantic Ocean. Together, the Lesser Antilles and the Greater Antilles make up the Antilles. (Somewhat confusingly, the word Caribbean is sometimes used to refer only to the Antilles, and sometimes used to refer to a much larger region.) The Lesser and Greater Antilles, together with the Lucayan Archipelago, are collectively known as the West Indies. History after European arrival The Spanish were the first Europeans to arrive on the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tropical Wave
A tropical wave (also called easterly wave, tropical easterly wave, and African easterly wave), in and around the Atlantic Ocean, is a type of atmospheric trough, an elongated area of relatively low air pressure, oriented north to south, which moves from east to west across the tropics, causing areas of cloudiness and thunderstorms. Tropical waves form in the easterly flow along the equatorial side of the subtropical ridge or belt of high air pressure which lies north and south of the Intertropical Convergence Zone (ITCZ). Tropical waves are generally carried westward by the prevailing easterly winds along the tropics and subtropics near the equator. They can lead to the formation of tropical cyclones in the north Atlantic and northeastern Pacific basins. A tropical wave study is aided by Hovmöller diagrams, a graph of meteorological data. West-moving waves can also form from the tail end of frontal zones in the subtropics and tropics, and may be referred to as easterly wa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |





.jpg)
