|
1925 Pacific Hurricane Season
The 1925 Pacific hurricane season ran through the summer and fall of 1925. Before the weather satellite, satellite age started in the 1960s, data on east Pacific hurricanes was extremely unreliable. Most east Pacific storms were of no threat to land. 1925 season was the first Pacific hurricane season that was covered in detail by Monthly Weather Review, and this season included the most intense November Pacific hurricane on record until beaten by Hurricane Kenneth (2011), Hurricane Kenneth in 2011. Systems Tropical Cyclone One A small tropical cyclone existed in the Gulf of Tehuantepec from June 3 to 6. It had gale-force winds, and its lowest reported pressure was . Hurricane Two Off the coast of Mexico, a hurricane existed from July 7 to 10. The lowest reported pressure was . Tropical Cyclone Three A tropical cyclone existed from July 17 to 22. Tropical Cyclone Four On July 31 and August 1, a tropical cyclone was encountered by a steamboat, steamer called the ''West Calera''. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
1910s Pacific Hurricane Seasons
The 1910s Pacific hurricane seasons were before the weather satellite, satellite age started in the 1960s, data on east Pacific hurricanes is extremely unreliable. For a few years, there were no reported cyclones, although many systems certainly formed. 1910 Three known tropical cyclones formed in 1910. The remnants of one of them entered southern California on September 15, bringing of rain to Santa Barbara County, California, Santa Barbara County. 1911 Eleven known tropical cyclones formed in 1911 in the eastern Pacific proper. On September 11, 1911 Atlantic hurricane season#Hurricane Four, Hurricane 4 of this year's 1911 Atlantic hurricane season, Atlantic season survived passage over Central America and emerged into the Pacific Ocean, where it dissipated on September 12. On September 29, a ship reported strong winds and a pressure of 998 Bar (unit), mbar inside a storm to the east of Hawaii. There were no other reports of this possible tropical cyclone. A "tropical hurric ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hutchinson Plantation, Hawaii
Hutchinson may refer to: Places United States * Hutchinson, Kansas * South Hutchinson, Kansas * Hutchinson, Minnesota * Hutchinson, Pennsylvania * Hutchinson, West Virginia, in Logan County * Hutchinson, Marion County, West Virginia * Hutchinson County, South Dakota * Hutchinson County, Texas * Hutchinson Island (Florida) * Hutchinson Island South, Florida * Hutchinson River, a river in New York * Hutchinson River Parkway, running through Westchester County, New York, and the Bronx * Hutchinson Township, McLeod County, Minnesota Greenland * Hutchinson Glacier South Africa * Hutchinson, Northern Cape People * Hutchinson (surname) Companies * Hutchinson SA, worldwide manufacturer of sealing solutions, insulation, fluid transfer systems and bicycle tires for all industries *Hutchinson (publisher), a publisher of books Other uses * Hutchinson Encyclopedia *, US frigate * Hutchinson's teeth, a sign of congenital syphilis * Hutchinson's ratio, concerning si ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
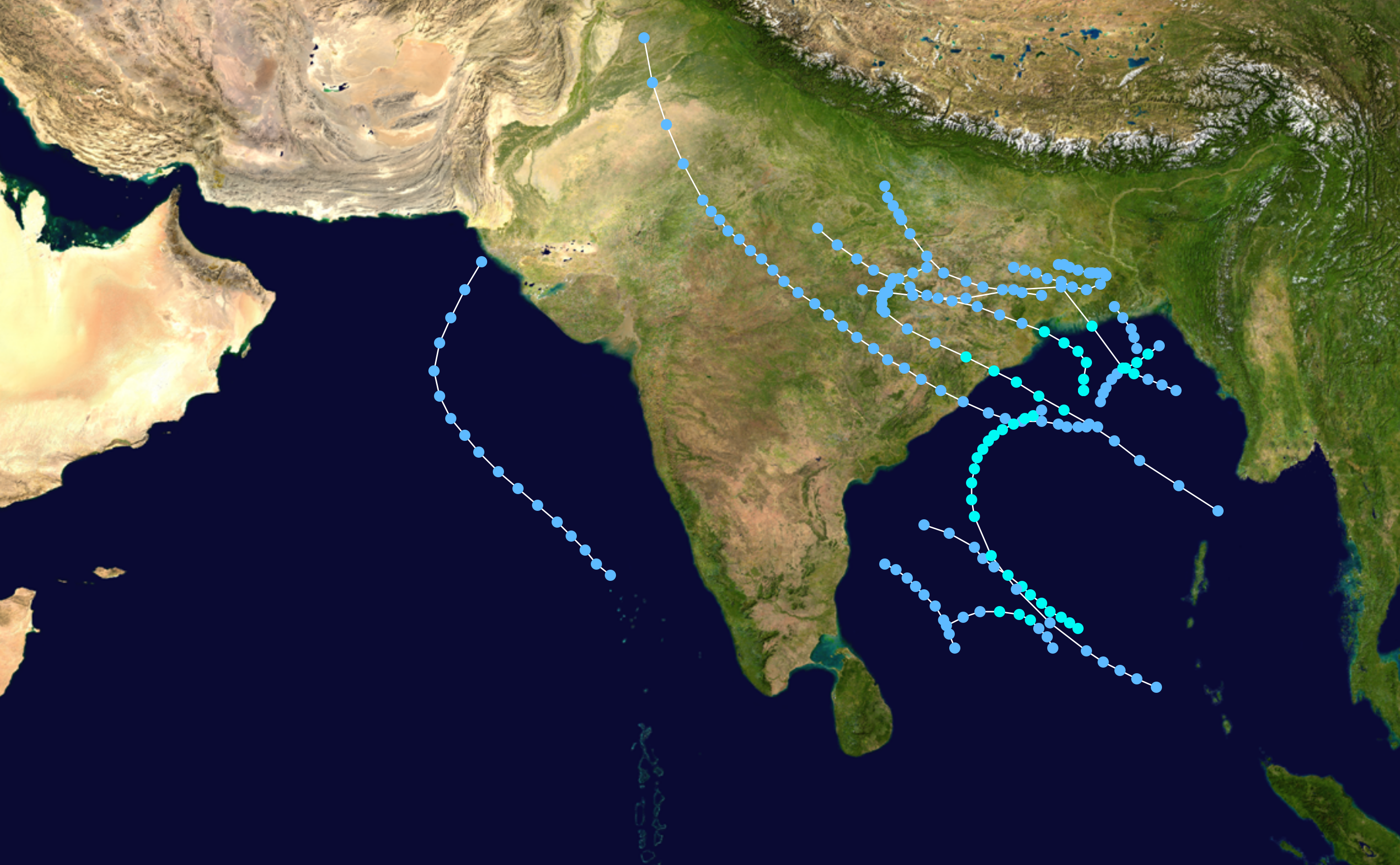
1920s North Indian Ocean Cyclone Seasons
The following is a list of North Indian Ocean tropical cyclones from 1920 to 1929. Records from before the 1970s were extremely unreliable, and storms that stayed at sea were often only reported by ship reports. 1928 *December 31, 1927 – January 5, 1928 – A depression existed over the southern Bay of Bengal. *February 29 – March 6, 1928 – A depression existed over the northeastern Arabian Sea. *March 24–28, 1928 – A cyclonic storm existed over the southern Bay of Bengal. 1927 A tropical storm struck Maharashtra 1929 There were 15 depressions and 6 cyclonic storms. See also * 1920s Australian region cyclone seasons * 1900–1940 South Pacific cyclone seasons * 1900–1950 South-West Indian Ocean cyclone seasons *Atlantic hurricane seasons: 1920, 1921, 1922, 1923, 1924, 1925, 1926, 1927, 1928, 1929 *Eastern Pacific hurricane seasons: 1920, 1921, 1922, 1923, 1924, 1925, 1926, 1927, 1928, 1929 *Western Pacific typhoon seasons: 1920, 19 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
1925 Pacific Typhoon Season
Nineteen or 19 may refer to: * 19 (number), the natural number following 18 and preceding 20 * one of the years 19 BC, AD 19, 1919, 2019 Films * 19 (film), ''19'' (film), a 2001 Japanese film * Nineteen (film), ''Nineteen'' (film), a 1987 science fiction film Music * 19 (band), a Japanese pop music duo Albums * 19 (Adele album), ''19'' (Adele album), 2008 * ''19'', a 2003 album by Alsou * ''19'', a 2006 album by Evan Yo * ''19'', a 2018 album by MHD (rapper), MHD * ''19'', one half of the double album ''63/19'' by Kool A.D. * ''Number Nineteen'', a 1971 album by American jazz pianist Mal Waldron * XIX (EP), ''XIX'' (EP), a 2019 EP by 1the9 Songs * 19 (song), "19" (song), a 1985 song by British musician Paul Hardcastle. * "Nineteen", a song by Bad4Good from the 1992 album ''Refugee (Bad4Good album), Refugee'' * "Nineteen", a song by Karma to Burn from the 2001 album ''Almost Heathen''. * Nineteen (song), "Nineteen" (song), a 2007 song by American singer Billy Ray Cyrus ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
1925 Atlantic Hurricane Season
The 1925 Atlantic hurricane season was a below-average Atlantic hurricane season during which four tropical cyclones formed. Only one of them was a hurricane. The first storm developed on August 18, and the last dissipated on December 1. The season began at a late date, more than two months after the season began. The official start of the season is generally considered to be June 1 with the end being October 31; however, the final storm of the season formed nearly a month after the official end. Due to increased activity over the following decades, the official end of the hurricane season was shifted to November 30. The final two storms of the season impacted several areas, with the final storm affecting areas from Cuba to Rhode Island. The third storm caused little or no damage along the Texas coastline with gale-force winds being recorded only along the coast. The last storm caused severe damage along the beaches of the Florida Peninsula, with damages e ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
2011 Pacific Hurricane Season
The 2011 Pacific hurricane season was a below average season in terms of named storms, although it had an above average number of hurricanes and major hurricanes. During the season, 13 tropical depressions formed along with 11 tropical storms, 10 hurricanes and 6 major hurricanes. The season officially began on May 15 in the East Pacific Ocean, and on June 1 in the Central Pacific; they ended on November 30. These dates conventionally delimit the period of each year when most tropical cyclones form in the Pacific basin. However, the formation of tropical cyclones is possible at any time of the year. Despite the decrease in storms, there were several intense and destructive hurricanes this season. Hurricane Beatriz killed four people in Southwestern Mexico. Hurricane Jova killed eight and caused $203.67 million (2011 USD) in damage to Western Mexico. Tropical Depression Twelve-E killed 30 people in Central America. Meanwhile, Kenneth became the strongest November s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
HURDAT
The Hurricane Databases (HURDAT), managed by the National Hurricane Center, are two separate databases that contain details on tropical cyclones, that have occurred within the Atlantic Ocean and Eastern Pacific Ocean since 1851 and 1949 respectively. The Eastern Pacific database was originally compiled at the NHC during 1976, to help with the initialization with two tropical cyclone forecast models. Initially tracks for the Central Pacific region and tracks for tropical depressions, that did not develop into tropical storms or hurricanes were not included within the database. Over the next few years tracks were archived best track data from the Eastern Pacific Hurricane Center (EPHC) were archived by the NHC on an annual basis. During 1982 the NHC started to include data on Central Pacific tropical storms and hurricanes within the database, before they took over the responsibility for issuing advisories during 1988. The format of the Eastern Pacific database was subsequently signif ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Barometer
A barometer is a scientific instrument that is used to measure air pressure in a certain environment. Pressure tendency can forecast short term changes in the weather. Many measurements of air pressure are used within surface weather analysis to help find surface troughs, pressure systems and frontal boundaries. Barometers and pressure altimeters (the most basic and common type of altimeter) are essentially the same instrument, but used for different purposes. An altimeter is intended to be used at different levels matching the corresponding atmospheric pressure to the altitude, while a barometer is kept at the same level and measures subtle pressure changes caused by weather and elements of weather. The average atmospheric pressure on the earth's surface varies between 940 and 1040 hPa (mbar). The average atmospheric pressure at sea level is 1013 hPa (mbar). Etymology The word ''barometer'' is derived from the Ancient Greek (), meaning "weight", and (), meaning "measure ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Puerto Vallarta
Puerto Vallarta ( or simply Vallarta) is a Mexican beach resort city situated on the Pacific Ocean's Bahía de Banderas in the Mexican state of Jalisco. Puerto Vallarta is the second largest urban agglomeration in the state after the Guadalajara Metropolitan Area. The City of Puerto Vallarta is the government seat of the Municipality of Puerto Vallarta which comprises the city as well as population centers outside of the city extending from Boca de Tomatlán to the Nayarit border (the Ameca River). The city is located at . The municipality has an area of . To the north, it borders the southwest part of the state of Nayarit. To the east, it borders the municipality of Mascota and San Sebastián del Oeste, and to the south, it borders the municipalities of Talpa de Allende and Cabo Corrientes. Puerto Vallarta is named after Ignacio Vallarta, a former governor of Jalisco. In Spanish, ''Puerto Vallarta'' is frequently shortened to "Vallarta", while English speakers call the city ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Central Pacific Hurricane Center
The Central Pacific Hurricane Center (CPHC) of the United States National Weather Service is the official body responsible for tracking and issuing tropical cyclone warnings, watches, advisories, discussions, and statements for the Central Pacific region: from the equator northward, 140°W–180°W, most significantly for Hawai‘i. It is the Regional Specialized Meteorological Center (RSMC) for tropical cyclones in this region, and in this capacity is known as RSMC Honolulu. Based in Honolulu, Hawaii, the CPHC is co-located with the National Weather Service's Honolulu forecast office on the campus of the University of Hawaii at Mānoa. The Honolulu forecast office activates the CPHC when tropical cyclones form in, or move into, the Central Pacific region. The CPHC replaced the previous forecaster, the Joint Hurricane Warning Center, starting in the 1970 season. Area of responsibility The CPHC's area of responsibility is the Central Pacific (CP) region, which is an administra ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Diamond Head, Hawaii
Diamond Head is a volcanic tuff cone on the Hawaiian island of Oahu and known to Hawaiians as Lēahi (). The Hawaiian name is most likely derived from ''lae'' (browridge, promontory) plus ''ahi'' (tuna) because the shape of the ridgeline resembles the shape of a tuna's dorsal fin. Its English name was given by British sailors in the 19th century, who named it for the calcite crystals on the adjacent beach. Geology Diamond Head is part of the system of cones, vents, and their associated eruption flows that are collectively known to geologists as the Honolulu Volcanic Series, eruptions from the Koolau Volcano that took place long after the volcano formed and had gone dormant. These eruptive events created many of Oahu's well-known landmarks, including Punchbowl Crater, Hanauma Bay, Koko Head, and Mānana Island in addition to Diamond Head. Diamond Head, like the rest of the Honolulu Volcanic Series, is much younger than the main mass of the Koolau Mountain Range. While the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |