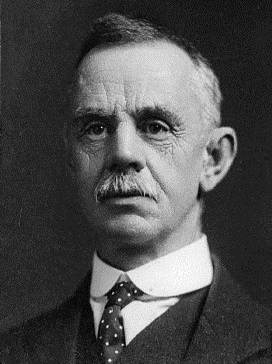|
1923 Oamaru By-election
The Oamaru by-election of 1923 was a by-election during the 21st New Zealand Parliament. The by-election was called following the invalidation of the preceding 1922 general election result due to irregularities. It was held on 1 May 1923. Background When the preliminary counts for the 1922 general election in the electorate were announced, Ernest Lee was ahead of John Andrew MacPherson by just one vote. Once the absentee votes had been counted, it was announced that MacPherson was leading by five votes, but this was subsequently increased to 25 votes. A recount was ordered, during which some irregularities came to light, and Lee asked for a judicial review. The court case was heard at the Supreme Court in Wellington by Sir Robert Stout and Justice Alexander Samuel Adams, who declared the election void and ordered the parties to pay their own expenses. Candidates Two candidates contested the seat. John Andrew MacPherson ( Liberal Party), who had taken the seat off the incumben ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Oamaru (New Zealand Electorate)
Oamaru was a parliamentary electorate in the Otago region of New Zealand, during three periods between 1866 and 1978. Population centres The previous electoral redistribution was undertaken in 1875 for the 1875–1876 election. In the six years since, New Zealand's European population had increased by 65%. In the 1881 electoral redistribution, the House of Representatives increased the number of European representatives to 91 (up from 84 since the 1875–76 election). The number of Māori electorates was held at four. The House further decided that electorates should not have more than one representative, which led to 35 new electorates being formed, and two electorates that had previously been abolished to be recreated, including Oamaru. This necessitated a major disruption to existing boundaries. Through an amendment in the Electoral Act in 1965, the number of electorates in the South Island was fixed at 25, an increase of one since the 1962 electoral redistribution. It was ac ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
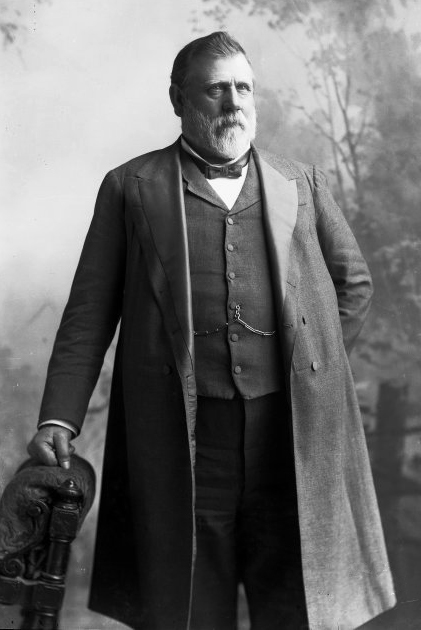
John Andrew MacPherson
John Andrew MacPherson (1856 – 21 July 1944) was a New Zealand politician of the Liberal Party and the United Party. Political career He unsuccessfully contested the electorate in the against the incumbent, Thomas Young Duncan. In the , he was one of four candidates for Oamaru and he came third. He represented the Mount Ida electorate from 1905 to 1908, when he was defeated standing for the replacement electorate of Tuapeka. In 1922 he won the Oamaru electorate from Ernest Lee. The election was declared void, but MacPherson won the subsequent by-election. Lee won the electorate back from MacPherson in the 1925 general election, but again lost it to MacPherson in the 1928 general election. MacPherson then held it until 1935, when he was defeated by Labour's Arnold Nordmeyer. In 1935, he was awarded the King George V Silver Jubilee Medal The King George V Silver Jubilee Medal is a commemorative medal, instituted to celebrate the 25th anniversary of the ac ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ernest Lee
Ernest Page Lee (27 August 1862 – 19 February 1932) was a New Zealand lawyer and politician of the Reform Party. Early life Born in 1862 in Teignmouth, England, he received his education at Cheltenham and London. Aged 18, he started learning the legal trade in a firm of solicitors in the West of England. He was submitted to the Supreme Court of Judicature in 1885. A year later, he emigrated to New Zealand. He settled in Oamaru, and was at first a clerk in a legal firm owned by Thomas William Hislop and Arthur Gethin Creagh. He founded the firm of Lee, Grave and Grave. In 1895 married Miss de Lambert. His sister, Leah Lee, was married to the French poet Jules Laforgue. Political career Lee was elected onto the Oamaru Borough council. In the , he defeated the incumbent in the Oamaru electorate, Thomas Young Duncan. He represented the electorate until 1922, when he was defeated in the 1922 election. The 1922 Oamaru election result was invalidated due to irregularities, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
By-election
A by-election, also known as a special election in the United States and the Philippines, a bye-election in Ireland, a bypoll in India, or a Zimni election (Urdu: ضمنی انتخاب, supplementary election) in Pakistan, is an election used to fill an office that has become vacant between general elections. A vacancy may arise as a result of an incumbent dying or resigning, or when the incumbent becomes ineligible to continue in office (because of a recall, election or appointment to a prohibited dual mandate, criminal conviction, or failure to maintain a minimum attendance), or when an election is invalidated by voting irregularities. In some cases a vacancy may be filled without a by-election or the office may be left vacant. Origins The procedure for filling a vacant seat in the House of Commons of England was developed during the Reformation Parliament of the 16th century by Thomas Cromwell; previously a seat had remained empty upon the death of a member. Cromwell de ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
21st New Zealand Parliament
The 21st New Zealand Parliament was a term of the New Zealand Parliament. It was elected at the 1922 general election in December of that year. 1922 general election The 1922 general election was held on Monday, 6 December in the Māori electorates and on Tuesday, 7 December in the general electorates, respectively. A total of 80 MPs were elected; 45 represented North Island electorates, 31 represented South Island electorates, and the remaining four represented Māori electorates. 700,111 voters were enrolled and the official turnout at the election was 88.7%. Sessions The 21st Parliament sat for four sessions (there were two sessions in 1923), and was prorogued on 14 October 1925. Party standings Start of Parliament End of Parliament Ministries The second Massey Ministry led by William Massey of the Reform Party had come to power in August 1919. Massey ruled until his death on 10 May 1925. Francis Bell had been acting Prime Minister during Massey's illness and to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
1922 New Zealand General Election
The 1922 New Zealand general election was held on Monday, 6 December in the Māori electorates, and on Tuesday, 7 December in the general electorates to elect a total of 80 MPs to the 21st session of the New Zealand Parliament. A total number of 700,111 (87.7%) voters turned out to vote. In one seat (Bay of Plenty) there was only one candidate. 1922 was the year residents of the Chatham Islands were enfranchised for the first time (included in Lyttelton and Western Māori electorates). Result William Massey formed a government, but with the loss in support for the Reform Party he had to negotiate for support with Independents, and with two Liberal Party members. Liberal was in decline and disorganised. Just before the 1925 election (held on 4 November), two Liberal MPs from Christchurch who had supported Massey (along with Independents Harry Atmore and Allen Bell) were appointed to the Legislative Council. They were Leonard Isitt and George Witty who were both appointed ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
High Court Of New Zealand
The High Court of New Zealand ( mi, Te Kōti Matua o Aotearoa) is the superior court of New Zealand. It has general jurisdiction and responsibility, under the Senior Courts Act 2016, as well as the High Court Rules 2016, for the administration of justice throughout New Zealand. There are 18 High Court locations throughout New Zealand, plus one stand-alone registry. The High Court was established in 1841. It was originally called the "Supreme Court of New Zealand", but the name was changed in 1980 to make way for the naming of an eventual new Supreme Court of New Zealand. The High Court is a court of first instance for serious criminal cases such as homicide, civil claims exceeding $350,000 and certain other civil cases. In its appellate function, the High Court hears appeals from the District Court, other lower courts and various tribunals. Composition and locations The High Court comprises the Chief Justice (who is head of the judiciary) and up to 55 other Judges (whic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Wellington
Wellington ( mi, Te Whanganui-a-Tara or ) is the capital city of New Zealand. It is located at the south-western tip of the North Island, between Cook Strait and the Remutaka Range. Wellington is the second-largest city in New Zealand by metro area, and is the administrative centre of the Wellington Region. It is the world's southernmost capital of a sovereign state. Wellington features a temperate maritime climate, and is the world's windiest city by average wind speed. Legends recount that Kupe discovered and explored the region in about the 10th century, with initial settlement by Māori iwi such as Rangitāne and Muaūpoko. The disruptions of the Musket Wars led to them being overwhelmed by northern iwi such as Te Āti Awa by the early 19th century. Wellington's current form was originally designed by Captain William Mein Smith, the first Surveyor General for Edward Wakefield's New Zealand Company, in 1840. The Wellington urban area, which only includes urbanised ar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Robert Stout
Sir Robert Stout (28 September 1844 – 19 July 1930) was a New Zealand politician who was the 13th premier of New Zealand on two occasions in the late 19th century, and later Chief Justice of New Zealand. He was the only person to hold both these offices. He was noted for his support of liberal causes such as women's suffrage, and for his strong belief that philosophy and theory should always triumph over political expediency. Early life Born in the town of Lerwick in Scotland's Shetland Islands, Stout retained a strong attachment to the Shetland Islands throughout his life. He received a good education and eventually qualified as a teacher. He also qualified as a surveyor in 1860. He became highly interested in politics through his extended family, which often met to discuss and debate political issues of the day. Stout was exposed to many different political philosophies during his youth. In 1863, Stout emigrated to Dunedin, New Zealand. Once there, he quickly became in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
The Evening Post (New Zealand)
''The Evening Post'' (8 February 1865 – 6 July 2002) was an afternoon metropolitan daily newspaper based in Wellington, New Zealand. It was founded in 1865 by Dublin-born printer, newspaper manager and leader-writer Henry Blundell, who brought his large family to New Zealand in 1863. With his partner from what proved to be a false-start at Havelock, David Curle, who left the partnership that July, Henry and his three sons printed with a hand-operated press and distributed Wellington's first daily newspaper, ''The Evening Post'', on 8 February 1865. Operating from 1894 as Blundell Bros Limited, his sons and their descendants continued the very successful business which dominated its circulation area. While ''The Evening Post'' was remarkable in not suffering the rapid circulation decline of evening newspapers elsewhere it was decided in 1972 to merge ownership with that of the never-as-successful politically conservative morning paper, '' The Dominion'', which belonged to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
New Zealand Liberal Party
The New Zealand Liberal Party was the first organised political party in New Zealand. It governed from 1891 until 1912. The Liberal strategy was to create a large class of small land-owning farmers who supported Liberal ideals, by buying large tracts of Māori land and selling it to small farmers on credit. The Liberal Government also established the basis of the later welfare state, with old age pensions, developed a system for settling industrial disputes, which was accepted by both employers and trade unions. In 1893 it extended voting rights to women, making New Zealand the first country in the world to enact universal adult suffrage. New Zealand gained international attention for the Liberal reforms, especially how the state regulated labour relations. It was innovating in the areas of maximum hour regulations and compulsory arbitration procedures. Under the Liberal administration the country also became the first to implement a minimum wage and to give women the right ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Reform Party (New Zealand)
The Reform Party, formally the New Zealand Political Reform League, was New Zealand's second major political party, having been founded as a conservative response to the original Liberal Party. It was in government between 1912 and 1928, and later formed a coalition with the United Party (a remnant of the Liberals), and then merged with United to form the modern National Party. Foundation The Liberal Party, founded by John Ballance and fortified by Richard Seddon, was highly dominant in New Zealand politics at the beginning of the 20th century. The conservative opposition, consisting only of independents, was disorganised and demoralised. It had no cohesive plan to counter the Liberal Party's dominance, and could not always agree on a single leader — it was described by one historian as resembling a disparate band of guerrillas, and presented no credible threat to continued Liberal Party rule. Gradually, however, the Liberals began to falter — the first blow came with ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |