|
183rd Street (NYCRR Station)
The 183rd Street station was a station on the New York Central Railroad's Harlem Line, serving the neighborhoods of Fordham, Tremont and Belmont in the Bronx, New York City. The New York, New Haven and Hartford Railroad also ran through this station but did not stop here. History Background The New York and Harlem Railroad expanded their main line across the Harlem River through Tremont into Fordham in 1841. Stations existed both in Tremont and Fordham back then, but not at 183rd Street. The New York and Harlem was bought by the New York Central and Hudson River Railroad in 1864, but did not build a station at this location until sometime between 1898 and 1901. Opening On July 1, 1901, the Metropolitan Elevated Railway (later acquired by the Interborough Rapid Transit Company) extended the Third Avenue Elevated Line to Fordham Station, bringing a rapid transit connection there. Pelham Avenue station was the northern terminus of the line until it was extended to B ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Park Avenue
Park Avenue is a wide New York City boulevard which carries north and southbound traffic in the boroughs of Manhattan and the Bronx. For most of the road's length in Manhattan, it runs parallel to Madison Avenue to the west and Lexington Avenue to the east. Park Avenue's entire length was formerly called Fourth Avenue; the title still applies to the section between Cooper Square and 14th Street. The avenue is called Union Square East between 14th and 17th Streets, and Park Avenue South between 17th and 32nd Streets. History Early years and railroad construction The entirety of Park Avenue was originally known as Fourth Avenue and carried the tracks of the New York and Harlem Railroad starting in the 1830s. The railroad originally ran through an open cut through Murray Hill, which was covered with grates and grass between 34th and 40th Street in the early 1850s. A section of this "park" was later renamed Park Avenue in 1860. Park Avenue's original southern terminus was at ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fordham (Metro-North Station)
Fordham station, also known as Fordham–East 190th Street station, is a commuter rail stop on the Metro-North Railroad's Harlem and New Haven Lines, serving Fordham Plaza in the Fordham neighborhood of the Bronx, New York City. The platforms are situated just below street level and feature two expanded side platforms that serve eight cars each, on the outer tracks. The station building sits above the tracks on the Fordham Road (East 190th Street) overpass, and still bears the name New York Central Railroad on its facade. The station is among the busiest rail stations in the Bronx. History The New York and Harlem Railroad laid tracks through Fordham as far back as 1841, and a station is known to have existed shortly afterwards. The New York and Harlem was bought by the New York Central and Hudson River Railroad in 1864. A March 17, 1848 agreement gave the New York and New Haven Railroad trackage rights over the NY&H from Williamsbridge south into New York City. NY&NH was merge ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Morrisania (NYCRR Station)
The Morrisania station was a station on the New York Central Railroad's Harlem Line, serving the community of Morrisania in the Bronx, New York City. History The station was built in 1858, but after declining ridership, which paralleled the decline of this section of the Bronx, the station was closed in 1973 along with some other stations in the Bronx as well as all stations between Dover Plains and Chatham. The station had two side platforms, and was a local station on the four-track Harlem Line. The station was located at 168th Street and Park Avenue. Originally, the station had a brick station house over the tracks on the tracks on the south side of the 168th Street bridge. Prior to the elimination of grade-crossings, the surface station had been located at 167th Street. There was no ticket agent at the station toward the end of its use. In 1964, only 40 daily commuters used the station. The New York Central Railroad was authorized to demolish the station in 1959. The s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
138th Street (NYCRR Station)
The 138th Street station was a station on the Harlem and Hudson Lines of the New York Central Railroad, serving the community of Mott Haven in the Bronx, New York City. It was the southernmost station along both branches until 1973. The New York, New Haven and Hartford Railroad also ran through this station but did not stop here. History The New York and Harlem Railroad expanded their main line across the Harlem River through Mott Haven into Williams Bridge from a bridge built in 1841. This bridge would be replaced in 1867, 1897, and 1956. A station named Mott Haven was known to exist as far back as 1858. The station was rebuilt in a much more elaborate fashion in 1886, with the construction of a Richardson Romanesque structure designed by Robert Henderson Robertson, and was hailed as "the finest and most complete way station in the country". Originally at street level, the tracks were later raised above ground level as part of a grade elimination project in order to acc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Metropolitan Transportation Authority
The Metropolitan Transportation Authority (MTA) is a public benefit corporation responsible for public transportation in the New York City metropolitan area of the U.S. state of New York. The MTA is the largest public transit authority in the United States, serving 12 counties in Downstate New York, along with two counties in southwestern Connecticut under contract to the Connecticut Department of Transportation, carrying over 11 million passengers on an average weekday systemwide, and over 850,000 vehicles on its seven toll bridges and two tunnels per weekday. History Founding In February 1965, New York Governor Nelson Rockefeller suggested that the New York State Legislature create an authority to purchase, operate, and modernize the Long Island Rail Road (LIRR). The LIRR, then a subsidiary of the Pennsylvania Railroad (PRR), had been operating under bankruptcy protection since 1949. The proposed authority would also have the power to make contracts or arrangements with ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pennsylvania Railroad
The Pennsylvania Railroad (reporting mark PRR), legal name The Pennsylvania Railroad Company also known as the "Pennsy", was an American Class I railroad that was established in 1846 and headquartered in Philadelphia, Pennsylvania. It was named for the commonwealth in which it was established. By 1882, Pennsylvania Railroad had become the largest railroad (by traffic and revenue), the largest transportation enterprise, and the largest corporation in the world. Its budget was second only to the U.S. government. Over the years, it acquired, merged with, or owned part of at least 800 other rail lines and companies. At the end of 1926, it operated of rail line;This mileage includes companies independently operated. PRR miles of all tracks, which includes first (or main), second, third, fourth, and sidings, totalled 28,040.49 at the end of 1926. in the 1920s, it carried nearly three times the traffic as other railroads of comparable length, such as the Union Pacific and Atchison, T ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
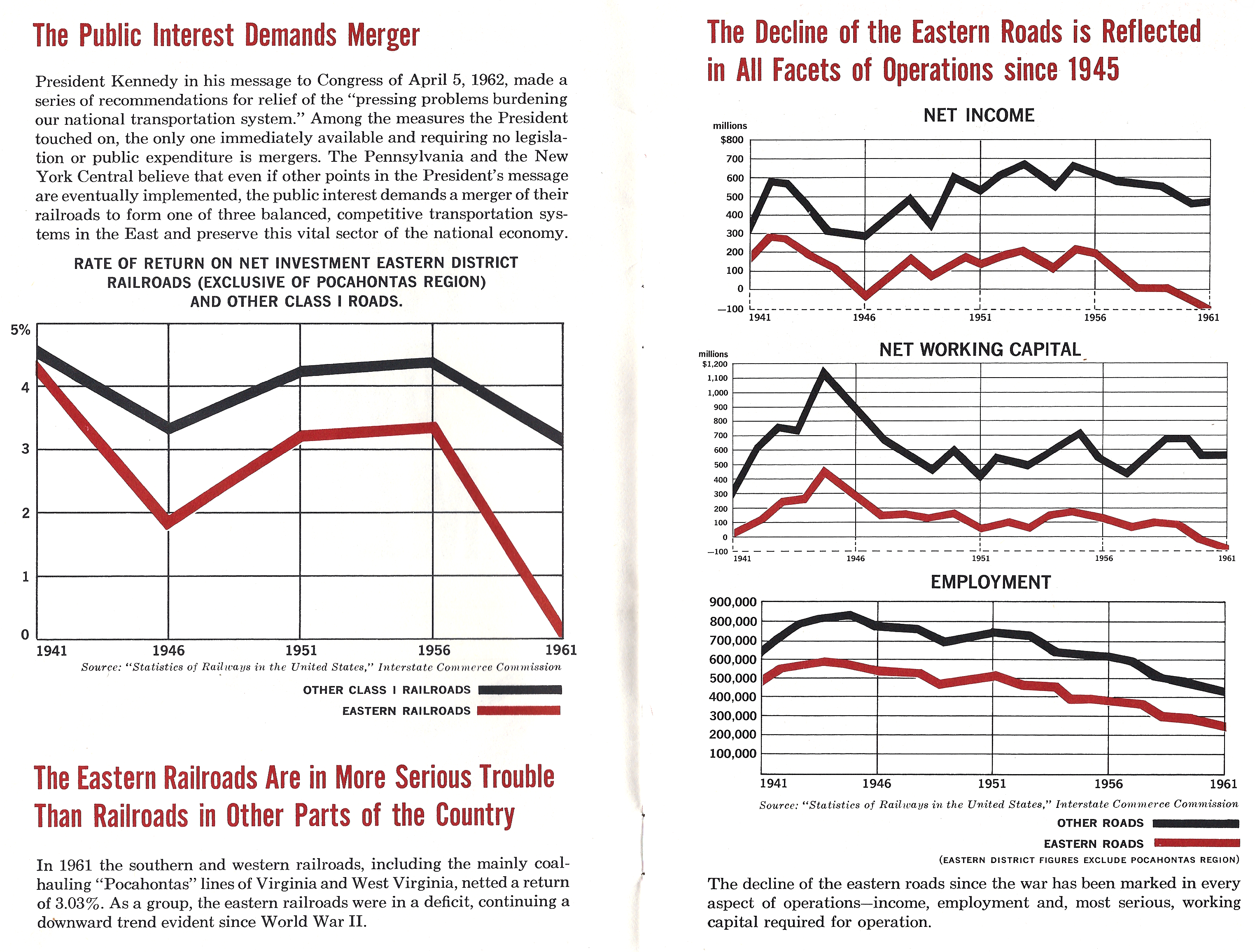
Penn Central
The Penn Central Transportation Company, commonly abbreviated to Penn Central, was an American Railroad classes, class I railroad that operated from 1968 to 1976. Penn Central combined three traditional corporate rivals (the Pennsylvania Railroad, Pennsylvania, New York Central Railroad, New York Central and the New York, New Haven and Hartford Railroad, New York, New Haven and Hartford railroads), all united by heavy service into the New York metropolitan area and (to a lesser extent) New England and Chicago. The new company failed barely two years after formation, the largest bankruptcy in U.S. history at the time. The Penn Central's railroad assets were nationalized into Conrail along with the other bankrupt northeastern roads; its real estate and insurance holdings successfully Reorganization, reorganized into American Premier Underwriters. History Pre-merger The Penn Central railroad system developed in response to challenges facing Northeast United States, northeaste ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
New York Public Service Commission
The New York Public Service Commission is the public utilities commission of the New York state government that regulates and oversees the electric, gas, water, and telecommunication industries in New York as part of the Department of Public Service. The department's regulations are compiled in title 16 of the ''New York Codes, Rules and Regulations''. The current chairman of the Commission and chief executive of the Department is Rory M. Christian. His term began on June 10, 2021 and runs through February 1, 2027. Organization The Public Service Commission consist of seven members, each appointed by the Governor of New York with the advice and consent of the New York State Senate for a term of six years or to complete an unexpired term of a member. Public Service Law § 4 A commissioner is designated as chairman by the Governor to serve in such capacity at the pleasure of the Governor or until their term as commissioner expires. No more than three commissioners may be members o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Third Avenue Railway
The Third Avenue Railway System (TARS), founded 1852, was a streetcar system serving the New York City boroughs of Manhattan and the Bronx along with lower Westchester County. For a brief period of time, TARS also operated the Steinway Lines in Long Island City.Ballard, C: "Metropolitan New York's Third Avenue Railway System", Arcadia Publishing, 2005 The conversion from streetcar to bus operation came from great pressure applied by New York City's Board of Transportation for a unified bus transportation system across the city. TARS applied for its first bus franchises in 1928. By 1948, all streetcar lines in Manhattan and The Bronx were converted to bus operation. The lines in Westchester County continued to operate, until the Yonkers city lines were shut down in 1952. Third Avenue Railway was purchased by New York City Omnibus Corporation in 1956, and transferred the remaining transit operating franchises to subsidiary Surface Transportation, Inc. Early history The origin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bronx Park Terminal (IRT Third Avenue Line)
Bronx Park Terminal was a terminal station on the demolished IRT Third Avenue Line in the Bedford Park neighborhood of the Bronx in New York City. The station was located adjacent to Bronx Park and the New York Botanical Garden at 198th Street between Webster Avenue and Southern Boulevard, in the approximate location of the modern Fordham Preparatory School. It was opened on May 21, 1902 and closed on November 14, 1951.New York's El Lines 1867-1955 Electric Railroaders Assn Dec 1956, Bulletin #25 The next southbound stop was Fordham Road – 190th Street. History The station was built as a one stop extension from Fordham Road – 190th Street (then called Pelham Avenue) to provide direct service to Bronx Park, particularly the New York Botanical Garden. It was located on a 2,200 x 50 foot tract of land on the western edge of the campus of St. John's College (now the Rose Hill campus of Fordham University), purchased from the college by the Manhattan Railway Company. This chara ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fordham Road – 190th Street (IRT Third Avenue Line)
Fordham may refer to: Education * Fordham Preparatory School, an all-male, Jesuit high school in New York City * Fordham University, a Jesuit university in New York City ** Fordham Rams, athletic teams of the above university ** Fordham University School of Law, a law school of the above university Geography * Fordham, Bronx, New York, United States ** Fordham Road, a major street in the above neighborhood ** Fordham (Metro-North station), a railway station in the above neighborhood * Fordham, Pennsylvania, an unincorporated community * Fordham, Wisconsin, United States, a ghost town * Fordham, Cambridgeshire, England * Fordham, Essex, England * Fordham, Norfolk, England Architecture * The Fordham, a skyscraper in Chicago, Illinois * Chicago Spire (originally proposed as ''Fordham Spire''), a cancelled supertall skyscraper in Chicago, Illinois Ships * HMS ''Fordham'', a Royal Navy Ham class minesweeper * , a ship which was converted into a minesweeper during World War II Oth ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
IRT Third Avenue Line
The IRT Third Avenue Line, commonly known as the Third Avenue Elevated, Third Avenue El, or Bronx El, was an elevated railway in Manhattan and the Bronx, New York City. Originally operated by the New York Elevated Railway, an independent railway company, it was acquired by the Interborough Rapid Transit Company (IRT) and eventually became part of the New York City Subway system. The first segment of the line, with service at most stations, opened from South Ferry to Grand Central Depot on August 26, 1878. Service was extended to Harlem in Manhattan on December 30. In 1881 this line already began the 24/7 service. Service in Manhattan was phased out in the early 1950s and closed completely on May 12, 1955. The remaining service in the Bronx was designated as part of the 8 route until it was discontinued on April 29, 1973. The Third Avenue El was the last elevated line to operate in Manhattan, other than the on the IRT Broadway–Seventh Avenue Line (which has elevated sectio ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
.jpeg/1200px-2013_Fordham_Metro-North_station_(cropped).jpeg)
.jpeg)
_(14575198358).jpg)
