|
1835 In Germany
Events from the year 1835 in Germany Incumbents * Kingdom of Prussia ** Monarch – Frederick William III of Prussia (16 November 1797 – 7 June 1840) * Kingdom of Bavaria ** Monarch - Ludwig I (1825–1848) * Kingdom of Saxony ** Anthony (5 May 1827 – 6 June 1836) * Kingdom of Hanover ** William IV (26 June 1830 to 1837) * Kingdom of Württemberg ** William (1816–1864) Events * 3 October – The Staedtler Company (pencil manufacturers) is founded by J. S. Staedtler in Nuremberg, Germany. * November/December – The German Federal Convention prohibits circulation of work by members of the "Young Germany" group of writers (Karl Gutzkow, Heinrich Heine, Heinrich Laube, Theodor Mundt and Ludolf Wienbarg) and the exiled poet Heinrich Heine. * 7 December – The Bavarian Ludwig Railway opens between Nuremberg and Fürth, with a train hauled by the British-built ''Der Adler'' ("''The Eagle''"), the first railway in Germany. *''unknown dates'' ** David Strauss begins publicatio ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kingdom Of Prussia
The Kingdom of Prussia (german: Königreich Preußen, ) was a German kingdom that constituted the state of Prussia between 1701 and 1918.Marriott, J. A. R., and Charles Grant Robertson. ''The Evolution of Prussia, the Making of an Empire''. Rev. ed. Oxford: Clarendon Press, 1946. It was the driving force behind the unification of Germany in 1871 and was the leading state of the German Empire until its dissolution in 1918. Although it took its name from the region called Prussia, it was based in the Margraviate of Brandenburg. Its capital was Berlin. The kings of Prussia were from the House of Hohenzollern. Brandenburg-Prussia, predecessor of the kingdom, became a military power under Frederick William, Elector of Brandenburg, known as "The Great Elector". As a kingdom, Prussia continued its rise to power, especially during the reign of Frederick II, more commonly known as Frederick the Great, who was the third son of Frederick William I.Horn, D. B. "The Youth of Frederick ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Heinrich Laube
Heinrich Laube (18 September 1806 – 1 August 1884), German dramatist, novelist and theatre-director, was born at Sprottau in Prussian Silesia. Life He studied theology at Halle and Breslau (1826–1829), and settled in Leipzig in 1832. Here he at once came into prominence with his political essays, collected under the title ''Das neue Jahrhundert'', in two parts — ''Polen'' (1833) and ''Politische Briefe'' (1833) — and with the novel ''Das junge Europa'', in three parts — ''Die Poeten'', ''Die Krieger'', ''Die Bürger'' — (1833–1837). These writings, in which, after the fashion of Heinrich Heine and Ludwig Börne, he severely criticized the political regime in Germany, together with the part he played in the literary movement known as “ Das junge Deutschland,” led to his being subjected to police surveillance and his works confiscated. On his return, in 1834, from a journey to Italy, undertaken in the company of Karl Gutzkow, Laube was expelled from Saxony and im ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Green Algae
The green algae (singular: green alga) are a group consisting of the Prasinodermophyta and its unnamed sister which contains the Chlorophyta and Charophyta/Streptophyta. The land plants (Embryophytes) have emerged deep in the Charophyte alga as sister of the Zygnematophyceae. Since the realization that the Embryophytes emerged within the green algae, some authors are starting to properly include them. The completed clade that includes both green algae and embryophytes is monophyletic and is referred to as the clade Viridiplantae and as the kingdom Plantae. The green algae include unicellular and colonial flagellates, most with two flagella per cell, as well as various colonial, coccoid and filamentous forms, and macroscopic, multicellular seaweeds. There are about 22,000 species of green algae. Many species live most of their lives as single cells, while other species form coenobia (colonies), long filaments, or highly differentiated macroscopic seaweeds. A few other organi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
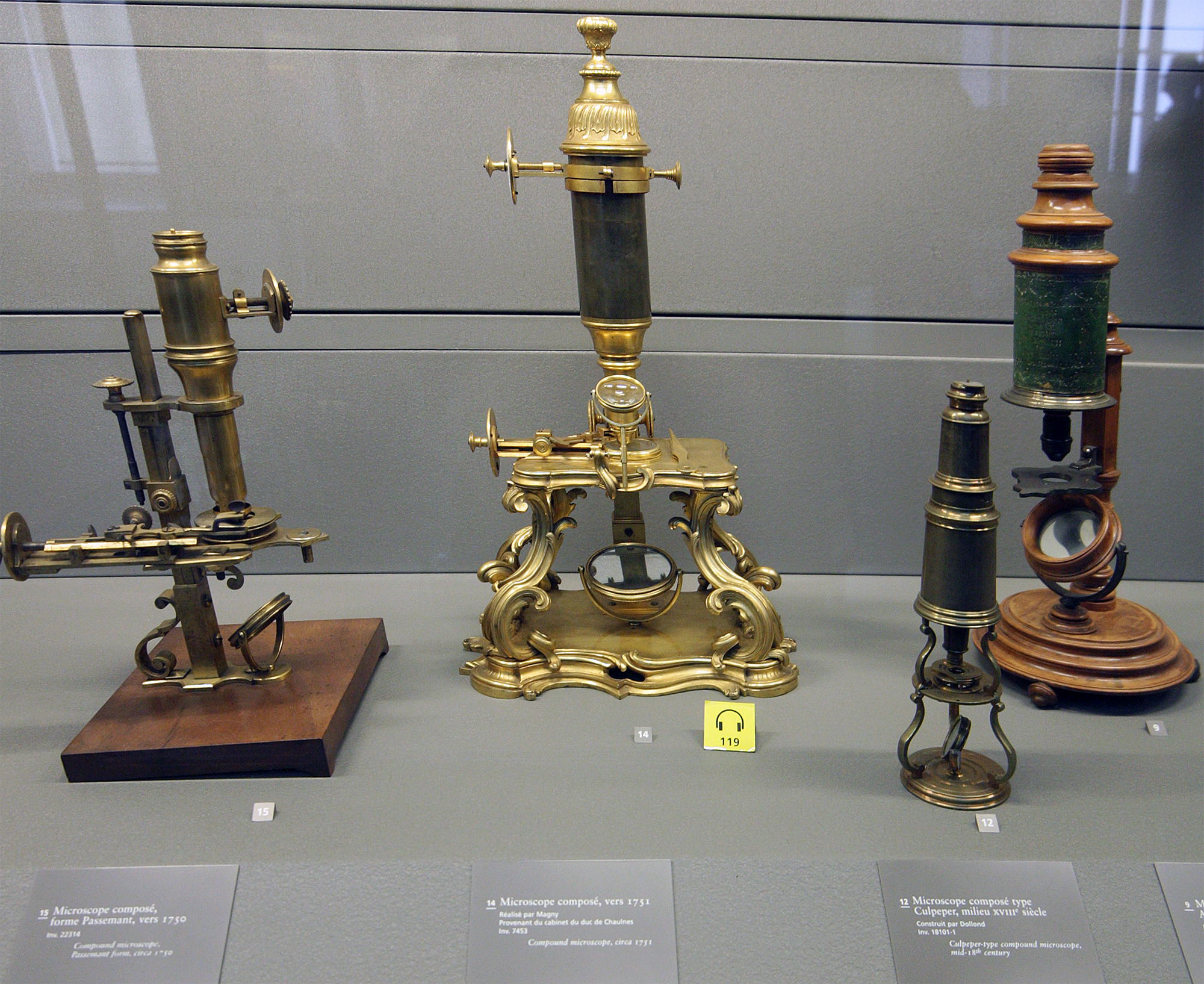
Hugo Von Mohl
Hugo von Mohl FFRS HFRSE (8 April 1805 – 1 April 1872) was a German botanist from Stuttgart. He was the first person to use the word "protoplasm". Life He was a son of the Württemberg statesman Benjamin Ferdinand von Mohl (1766–1845), the family being connected on both sides with the higher class of state officials of Württemberg. While a pupil at the gymnasium, he pursued botany and mineralogy in his leisure time, till in 1823 he entered the University of Tübingen. After graduating with distinction in medicine he went to Munich, where he met a distinguished circle of botanists, and found ample material for research. This seems to have determined his career as a botanist, and he started in 1828 those anatomical investigations which continued till his death. In 1832 he was appointed professor of botany in Tübingen, a post which he never left. Unmarried, his pleasures were in his laboratory and library, and in perfecting optical apparatus and microscopic preparations, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Microscope
A microscope () is a laboratory instrument used to examine objects that are too small to be seen by the naked eye. Microscopy is the science of investigating small objects and structures using a microscope. Microscopic means being invisible to the eye unless aided by a microscope. There are many types of microscopes, and they may be grouped in different ways. One way is to describe the method an instrument uses to interact with a sample and produce images, either by sending a beam of light or electrons through a sample in its optical path, by detecting photon emissions from a sample, or by scanning across and a short distance from the surface of a sample using a probe. The most common microscope (and the first to be invented) is the optical microscope, which uses lenses to refract visible light that passed through a thinly sectioned sample to produce an observable image. Other major types of microscopes are the fluorescence microscope, electron microscope (both the transmi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cell Division
Cell division is the process by which a parent cell (biology), cell divides into two daughter cells. Cell division usually occurs as part of a larger cell cycle in which the cell grows and replicates its chromosome(s) before dividing. In eukaryotes, there are two distinct types of cell division: a vegetative division (mitosis), producing daughter cells genetically identical to the parent cell, and a cell division that produces Haploidisation, haploid gametes for sexual reproduction (meiosis), reducing the number of chromosomes from two of each type in the diploid parent cell to one of each type in the daughter cells. In cell biology, mitosis (Help:IPA/English, /maɪˈtoʊsɪs/) is a part of the cell cycle, in which, replicated chromosomes are separated into two new Cell nucleus, nuclei. Cell division gives rise to genetically identical cells in which the total number of chromosomes is maintained. In general, mitosis (division of the nucleus) is preceded by the S stage of interph ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tübingen
Tübingen (, , Swabian: ''Dibenga'') is a traditional university city in central Baden-Württemberg, Germany. It is situated south of the state capital, Stuttgart, and developed on both sides of the Neckar and Ammer rivers. about one in three of the 90,000 people living in Tübingen is a student. As of the 2018/2019 winter semester, 27,665 students attend the Eberhard Karls University of Tübingen. The city has the lowest median age in Germany, in part due to its status as a university city. As of December 31, 2015, the average age of a citizen of Tübingen is 39.1 years. The city is known for its veganism and environmentalism. Immediately north of the city lies the Schönbuch, a densely wooded nature park. The Swabian Alb mountains rise about (beeline Tübingen City to Roßberg - 869 m) to the southeast of Tübingen. The Ammer and Steinlach rivers are tributaries of the Neckar river, which flows in an easterly direction through the city, just south of the medieval old t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
David Strauss
David Friedrich Strauss (german: link=no, Strauß ; 27 January 1808 – 8 February 1874) was a German liberal Protestant theologian and writer, who influenced Christian Europe with his portrayal of the "historical Jesus", whose divine nature he denied. His work was connected to the Tübingen School, which revolutionized study of the New Testament, early Christianity, and ancient religions. Strauss was a pioneer in the historical investigation of Jesus. Early life He was born in Ludwigsburg, near Stuttgart. At age 12 he was sent to the evangelical seminary at Blaubeuren, near Ulm, to be prepared for the study of theology. Two of the principal masters in the school were Professors Friedrich Heinrich Kern (1790–1842) and Ferdinand Christian Baur, who instilled in their pupils a deep appreciation for the ancient classics and the principles of textual criticism, which could be applied to texts in the sacred tradition as well as to classical ones. In 1825, Strauss entered the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
History Of Rail Transport In Germany
:''This article is part of the history of rail transport by country series'' The history of rail transport in Germany can be traced back to the 16th century. The earliest form of railways, wagonways, were developed in Germany in the 16th century. Modern German rail history officially began with the opening of the steam-powered Bavarian Ludwig Railway between Nuremberg and Fürth on 7 December 1835. This had been preceded by the opening of the horse-drawn Prince William Railway on 20 September 1831. The first long-distance railway was the Leipzig-Dresden railway, completed on 7 April 1839. Forerunners The forerunner of the railway in Germany, as in England, was to be found mainly in association with the mining industry. Mine carts were used below ground for transportation, initially using wooden rails, and were steered either by a guide pin between the rails or by flanges on the wheels. A wagonway operation was illustrated in Germany in 1556 by Georgius Agricola (image right) i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Adler (locomotive)
The ''Adler'' (German for "Eagle") was the first locomotive that was successfully used commercially for the rail transport of passengers and goods in Germany. The railway vehicle was designed and built in 1835 by the British railway pioneers George and Robert Stephenson in the English city of Newcastle. It was delivered to the Bavarian Ludwig Railway (''Bayerische Ludwigsbahn'') for service between Nuremberg and Fürth. It ran officially for the first time there on 7 December 1835. The ''Adler'' was a steam locomotive of the ''Patentee'' type with a wheel arrangement of 2-2-2 (Whyte notation) or 1A1 (UIC classification). The ''Adler'' was equipped with a tender of type 2 T 2. It had a sister locomotive, the ''Pfeil''. History Earlier locomotives in Germany The ''Adler'' is often cited as the very first locomotive used by a railway company on German soil, but as early as 1816 a serviceable steam locomotive was designed by the Royal Prussian Steelworks (''Königlic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
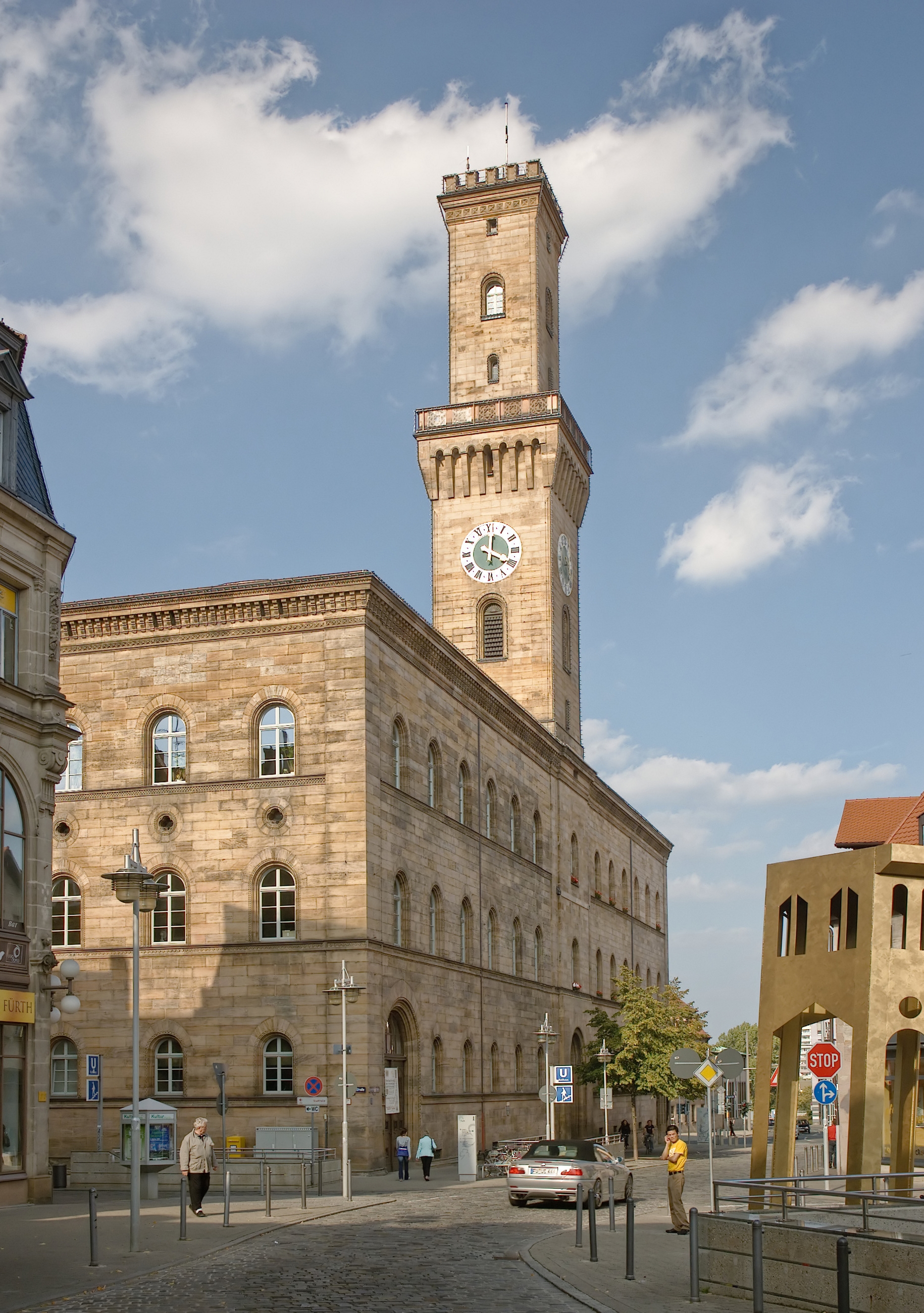
Fürth
Fürth (; East Franconian: ; yi, פיורדא, Fiurda) is a city in northern Bavaria, Germany, in the administrative division (''Regierungsbezirk'') of Middle Franconia. It is now contiguous with the larger city of Nuremberg, the centres of the two cities being only apart. Fürth is one of 23 "major centres" in Bavaria. Fürth, Nuremberg, Erlangen and some smaller towns form the "Middle Franconian Conurbation", which is one of the 11 German metropolitan regions. Fürth celebrated its thousand year anniversary in 2007, its first mention being on 1 November 1007. Geography The historic centre of the town is to the east and south of the rivers Rednitz and Pegnitz, which join to form the Regnitz to the northwest of the Old Town. To the west of the town, on the far side of the Main-Danube Canal, is the Fürth municipal forest (''Fürther Stadtwald''). To the east of Fürth, at roughly the same latitude, lies Nuremberg, and to the north is the fertile market-gardening area know ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bavarian Ludwig Railway
The Bavarian Ludwig Railway (''Bayerische Ludwigseisenbahn'' or ''Ludwigsbahn'') was the first steam-hauled railway opened in Germany. The ''Königlich privilegierte Ludwigs-Eisenbahn-Gesellschaft'' ("Royal Privileged Ludwig Railway Company", later called the ''Ludwigs-Eisenbahn-Gesellschaft'') received a concession to build a railway from Nuremberg to Fürth (6km) in the state of Bavaria on 19 February 1834. Background The first reports from England over the planning of railways attracted great attention in Germany, particularly in Bavaria, where the road between the important commercial cities of Nuremberg and Fürth was the busiest road connection in the kingdom. Bavarian interest was also stimulated by Friedrich List’s advocacy of an all-German railway system and the reports of Joseph von Baader, whom King Ludwig had sent to England to study railways. After a discussion of this topic in the Bavarian parliament in 1825, it authorised the king to build an experimental ra ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
.jpg)