|
1777 In Science
The year 1777 in science and technology involved some significant events. Exploration * March – Third voyage of James Cook: English explorer Captain Cook discovers Mangaia and Atiu in the Cook Islands. Mathematics * Leonhard Euler introduces the symbol ''i'' to represent the square root of −1. Technology * ''probable date'' – Thomas Arnold of London produces the first watch ("Arnold 36") to be called a ''chronometer''. Awards * Copley Medal: John Mudge Births * February 12 – Bernard Courtois, French chemist (died 1838) * April 30 – Carl Friedrich Gauss, German mathematician (died 1855) * May 4 – Louis Jacques Thénard, French chemist (died 1857) * May 18 – John George Children, English chemist, mineralogist and entomologist (died 1852) * August 14 – Hans Christian Ørsted, Danish physicist (died 1851) Deaths * September 22 – John Bartram, naturalist and explorer considered the "father of American botany" (born 1699) * September 25 – Johann Heinrich L ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Science
Science is a systematic endeavor that builds and organizes knowledge in the form of testable explanations and predictions about the universe. Science may be as old as the human species, and some of the earliest archeological evidence for scientific reasoning is tens of thousands of years old. The earliest written records in the history of science come from Ancient Egypt and Mesopotamia in around 3000 to 1200 BCE. Their contributions to mathematics, astronomy, and medicine entered and shaped Greek natural philosophy of classical antiquity, whereby formal attempts were made to provide explanations of events in the physical world based on natural causes. After the fall of the Western Roman Empire, knowledge of Greek conceptions of the world deteriorated in Western Europe during the early centuries (400 to 1000 CE) of the Middle Ages, but was preserved in the Muslim world during the Islamic Golden Age and later by the efforts of Byzantine Greek scholars who brought Greek ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
1838 In Science
The year 1838 in science and technology involved some significant events, listed below. Astronomy * Friedrich Wilhelm Bessel makes the first accurate measurement of distance to a star, 61 Cygni, using parallax. Thomas Henderson ( Alpha Centauri) and Friedrich Georg Wilhelm Struve (Vega) announce their measurements using parallax shortly afterwards. * Claude Servais Mathias Pouillet makes the first quantitative measurements of the heat emitted by the Sun. * Peter Andreas Hansen publishes a revision of the lunar theory, ''Fundamenta nova investigationis orbitae verae quam luna perlustrat''. Biology * May 9 – Royal Agricultural Society of England established. * Proteins discovered by Gerardus Johannes Mulder and named by Jöns Jakob Berzelius. * Matthias Schleiden discovers that all living plant tissue is composed of cells. * Andrew Smith begins publication of ''Illustrations of the Zoology of South Africa''. Chemistry * Bulat steel alloy developed by Pavel Petrovich Anosov ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
1699 In Science
The year 1699 in science and technology involved some significant events. Biology * English physician Edward Tyson publishes '' Orang-Outang, sive Homo Sylvestris: or, the Anatomy of a Pygmie Compared with that of a Monkey, an Ape, and a Man'', a pioneering work of comparative anatomy. Exploration * July 26 – William Dampier's expedition to New Holland (Australia) in HMS ''Roebuck'' reaches Dirk Hartog Island at the mouth of what he calls Shark Bay in Western Australia and begins producing the first known detailed record of Australian flora and fauna. * ''approx. date'' – Sir Isaac Newton develops a reflecting quadrant. Mathematics * Abraham Sharp calculates π to 72 digits using an arctan sequence (although only 71 are correct). Paleontology * Edward Lhuyd produces the first published scientific treatment of what would now be recognized as a dinosaur, describing and naming a sauropod tooth, " Rutellum implicatum" found at Caswell, near Witney, Oxfordshire, England. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
John Bartram
John Bartram (March 23, 1699 – September 22, 1777) was an American botanist, horticulturist, and explorer, based in Philadelphia, Pennsylvania, for most of his career. Swedish botanist and taxonomist Carl Linnaeus said he was the "greatest natural botanist in the world." Bartram corresponded with and shared North American plants and seeds with a variety of scientists in England and Europe. He started what is known as Bartram's Garden in 1728 at his farm in Kingsessing (now part of Philadelphia). It was considered the first botanic garden in the United States. His sons and descendants operated it until 1850. Still operating in a partnership between the city of Philadelphia and a non-profit foundation, it was designated a National Historic Landmark in 1960. Early life Bartram was born into a Quaker farm family in colonial Darby, Pennsylvania near Philadelphia, on March 23, 1699. He considered himself a plain farmer, with no formal education beyond the local school. He had a li ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
1851 In Science
The year 1851 in science and technology involved some significant events, listed below. Astronomy * February – First public exhibition of a Foucault pendulum, at the Meridian of the Paris Observatory, demonstrating the Earth's rotation. A few weeks later Léon Foucault, Foucault installs one at the Panthéon, Paris, Panthéon. * July 28 – Solar eclipse of July 28, 1851: Total solar eclipse. The first correctly exposed photograph, a daguerrotype, of the solar corona is made during the total phase of the eclipse by Berkowski at Koenigsberg Observatory in Prussia. Astronomers Robert Grant (astronomer), Robert Grant and William Swan (astonomer), William Swan (of the United Kingdom) and Karl Ludwig von Littrow (of Austria) observe this eclipse and determine that solar prominences are part of the Sun because the Moon is seen to cover and uncover them as it moves in front. * October 24 – Ariel (moon), Ariel and Umbriel (moon), Umbriel, natural satellite, moons of Uranus, were disc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Danes
Danes ( da, danskere, ) are a North Germanic ethnic group and nationality native to Denmark and a modern nation identified with the country of Denmark. This connection may be ancestral, legal, historical, or cultural. Danes generally regard themselves as a nationality and reserve the word "ethnic" for the description of recent immigrants, sometimes referred to as "new Danes". The contemporary Danish national identity is based on the idea of "Danishness", which is founded on principles formed through historical cultural connections and is typically not based on racial heritage. History Early history Denmark has been inhabited by various Germanic peoples since ancient times, including the Angles, Cimbri, Jutes, Herules, Teutones and others. The first mentions of " Danes" are recorded in the mid-6th century by historians Procopius ( el, δάνοι) and Jordanes (''danī''), who both refer to a tribe related to the Suetidi inhabiting the peninsula of Jutland, the province of Sc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hans Christian Ørsted
Hans Christian Ørsted ( , ; often rendered Oersted in English; 14 August 17779 March 1851) was a Danish physicist and chemist who discovered that electric currents create magnetic fields, which was the first connection found between electricity and magnetism. Oersted's law and the oersted unit (Oe) are named after him. A leader of the Danish Golden Age, Ørsted was a close friend of Hans Christian Andersen and the brother of politician and jurist Anders Sandøe Ørsted, who served as Prime Minister of Denmark from 1853 to 1854. Early life and studies Ørsted was born in Rudkøbing in 1777. As a young boy he developed an interest in science while working for his father, who owned the local pharmacy. He and his brother Anders received most of their early education through self-study at home, going to Copenhagen in 1793 to take entrance exams for the University of Copenhagen, where both brothers excelled academically. By 1796, Ørsted had been awarded honors for his papers in bo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
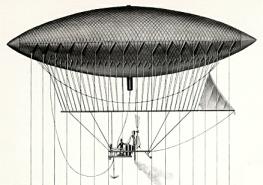
1852 In Science
The year 1852 in science and technology involved some significant events, listed below. Aeronautics * September 24 – French engineer Henri Giffard makes the first airship trip, from Paris to Trappes. Astronomy * September 19 – Annibale de Gasparis discovers the asteroid 20 Massalia from the north dome of the Astronomical Observatory of Capodimonte in Naples. Biology * October 5 – American apiarist L. L. Langstroth patents the Langstroth hive for the cultivation of honey bees. * Last recognised sighting of a great auk, on the Grand Banks of Newfoundland. Chemistry * August Beer proposes Beer's law, which explains the relationship between the composition of a mixture and the amount of light it will absorb. Based partly on earlier work by Pierre Bouguer and Johann Heinrich Lambert, it establishes the analytical technique known as spectrophotometry. Mathematics * October 23 – Francis Guthrie poses the four colour problem to Augustus De Morgan. Medicine * January 15 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
English People
The English people are an ethnic group and nation native to England, who speak the English language in England, English language, a West Germanic languages, West Germanic language, and share a common history and culture. The English identity is of History of Anglo-Saxon England, Anglo-Saxon origin, when they were known in Old English as the ('race or tribe of the Angles'). Their ethnonym is derived from the Angles, one of the Germanic peoples who migrated to Great Britain around the 5th century AD. The English largely descend from two main historical population groups the West Germanic tribes (the Angles, Saxons, Jutes and Frisians) who settled in southern Britain following the withdrawal of the Ancient Rome, Romans, and the Romano-British culture, partially Romanised Celtic Britons already living there.Martiniano, R., Caffell, A., Holst, M. et al. Genomic signals of migration and continuity in Britain before the Anglo-Saxons. Nat Commun 7, 10326 (2016). https://doi.org/10 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
John George Children
John George Children FRS FRSE FLS PRES (18 May 1777 – 1 January 1852 in Halstead, Kent) was a British chemist, mineralogist and zoologist. He invented a method to extract silver from ore without the need for mercury. He was a friend of Sir Humphry Davy, who helped him secure a controversial appointment to a post in the British Museum. Children was also the founding president of the Royal Entomological Society. Personal life John George was born on 18 May 1777 at Ferox Hall, Tonbridge, Kent. His father George Children, FRS (1742–1818), a banker, belonged to a family that lived at the home, "Childrens", near Nether Street in Hildenborough and his mother Susanna, who was the daughter of Rev. Thomas Marshall Jordan of West Farleigh died six days after he was born. Children studied at Tonbridge School, Eton College and Queens' College, Cambridge. In 1798 he married Hester Anna Holwell, granddaughter of John Zephaniah Holwell in 1798. After her death in 1800, he began to travel ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
1857 In Science
The year 1857 in science and technology involved some significant events, listed below. Astronomy * Peter Andreas Hansen's ''Tables of the Moon'' are published in London. Biology * Rev. M. J. Berkeley publishes ''Introduction to Cryptogamic Botany''. Chemistry * Robert Bunsen invents apparatus for measuring effusion. * August Kekulé proposes that carbon is tetravalent, or forms exactly four chemical bonds. * Carl Wilhelm Siemens patents the Siemens cycle. Earth sciences * January 9 – The 7.9 Fort Tejon earthquake shakes Central and Southern California with a maximum Mercalli intensity of IX (''Violent''). The event, which involves slip on the southern segment of the San Andreas Fault, leaves two people dead. * Friedrich Albert Fallou publishes ''Anfangsgründe der Bodenkunde'' irst Principles of Soil Science laying the foundations for the modern study of soil science. Exploration * May 16 – The British North American Exploring Expedition, led by Irish geographer Ca ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Louis Jacques Thénard
Louis Jacques Thénard (4 May 177721 June 1857) was a French chemist. Life He was born in a farm cottage near Nogent-sur-Seine in the Champagne district the son of a farm worker. In the post-Revolution French educational system , most boys received scholarships for education up to age 14, and this allowed him to be educated at the academy at Sens. He then went at the age of sixteen to study pharmacy in Paris. There he attended the lectures of Antoine François Fourcroy and Louis Nicolas Vauquelin. He was allowed into Vauquelin's laboratory even though he was unable to pay the monthly fee of 20 francs, due to the requests of Vauquelin's sisters. But his progress was so rapid that in two or three years he was able to take his master's place at the lecture-table, and Fourcroy and Vauquelin were so satisfied with his performance that they procured for him a school appointment in 1797 as teacher of chemistry, and in 1798 one as at the École Polytechnique. Career In 1804 Vauquelin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |