|
1724 In Science
The year 1724 in science and technology involved some significant events. Astronomy * May 22 – Giacomo F. Maraldi concludes, from his observations during an eclipse, that the corona is part of the Sun. Mathematics * Daniel Bernoulli expresses the numbers of the Fibonacci sequence in terms of the golden ratio. * Isaac Watts publishes ''Logic, or The Right Use of Reason in the Enquiry After Truth With a Variety of Rules to Guard Against Error in the Affairs of Religion and Human Life, as well as in the Sciences''. Medicine * Herman Boerhaave describes Boerhaave syndrome, a fatal tearing of the esophagus. Institutions * January 28 – The Saint Petersburg Academy of Sciences is founded by Peter I of Russia. Births * March 27 – Jane Colden, American botanist (died 1766) * June 8 – John Smeaton, English civil engineer (died 1792) * July 10 – Eva Ekeblad, Swedish agronomist, first woman in the Swedish Royal Academy of Science (died 1786) * September 27 – An ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
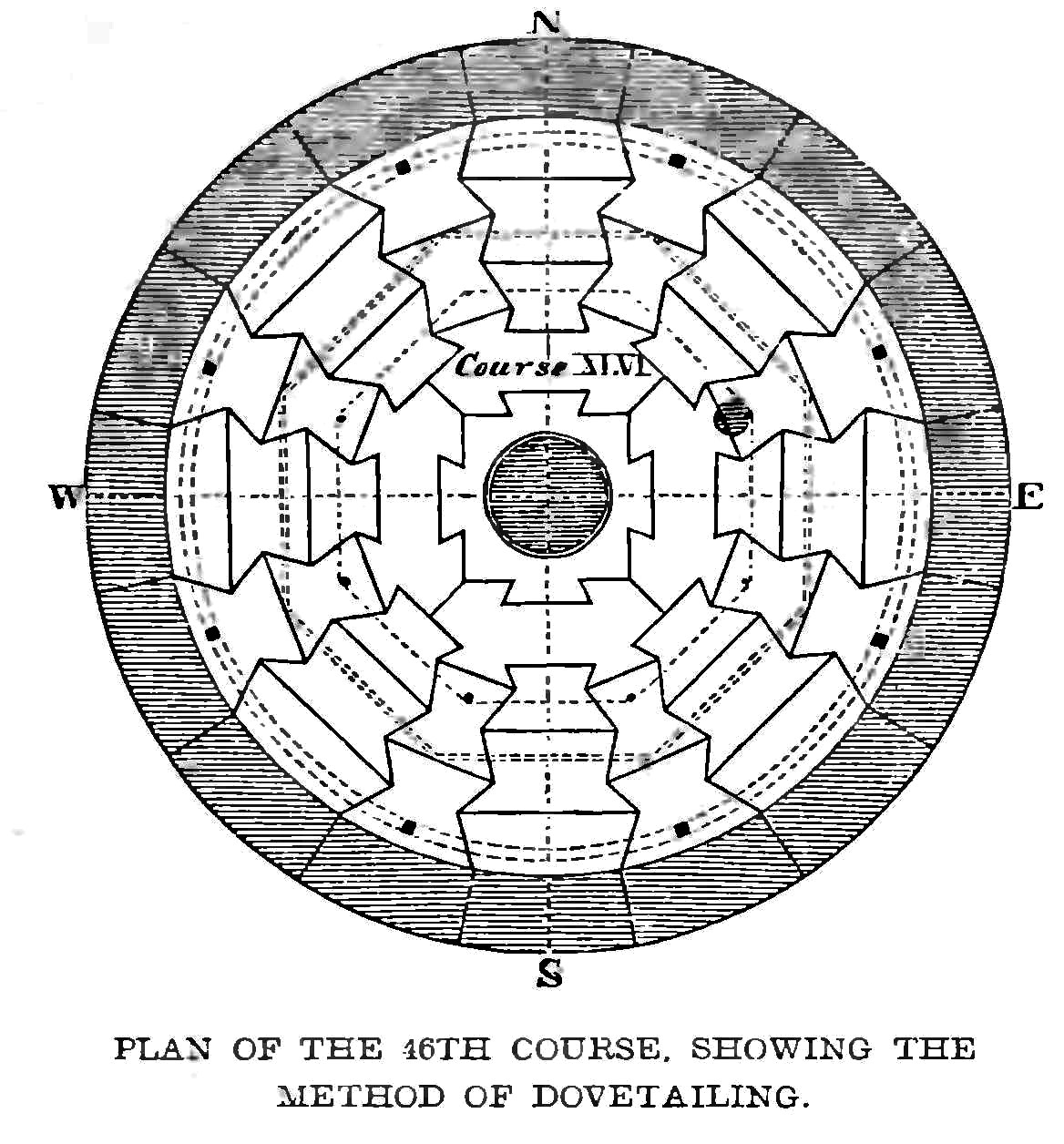
John Smeaton
John Smeaton (8 June 1724 – 28 October 1792) was a British civil engineer responsible for the design of bridges, canals, harbours and lighthouses. He was also a capable mechanical engineer and an eminent physicist. Smeaton was the first self-proclaimed "civil engineer", and is often regarded as the "father of civil engineering".Mark Denny (2007). "Ingenium: Five Machines That Changed the World". p. 34. JHU Press. He pioneered the use of hydraulic lime in concrete, using pebbles and powdered brick as aggregate. Smeaton was associated with the Lunar Society. Law and physics Smeaton was born in Austhorpe, Leeds, England. After studying at Leeds Grammar School he joined his father's law firm, but left to become a mathematical instrument maker (working with Henry Hindley), developing, among other instruments, a pyrometer to study material expansion. In 1750, his premises were in the Great Turnstile in Holborn. He was elected a Fellow of the Royal Society in 1753 and in 1 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
1767 In Science
The year 1767 in science and technology involved some significant events. Agriculture * Arthur Young publishes ''The farmer's letters to the people of England, containing the sentiments of a practical husbandman ... to which is added, Sylvæ, or, Occasional tracts on husbandry and rural oeconomics''. Exploration * June 17 – British Royal Navy Captain Samuel Wallis becomes the first European definitely to visit the island of Tahiti in the Pacific Ocean, during HMS ''Dolphin''s second circumnavigation. * July 3 – Pitcairn Island in the Pacific Ocean is sighted from HMS ''Swallow'' (1766) by 15-year-old Midshipman Robert Pitcairn on a British Royal Navy expeditionary voyage commanded by Philip Carteret, the first definite European sighting. * Autumn – North Carolina woodsman Daniel Boone goes through the Cumberland Gap and reaches Kentucky (in defiance of the Royal Proclamation of 1763). He discovers a rich hunting ground, contested by several Native American tribes. Te ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Marie Anne Victoire Pigeon
Marie Anne Victoire Pigeon d'Osangis (1724, Paris – 1767, Berlin) was a French mathematician and writer. She was the daughter of the scientist Jean Pigeon. In 1744, she eloped with her teacher, mathematician Pierre Le Guay de Prémontval, to Switzerland, where they married, and then to Berlin. In 1752, she was a teacher of princess Wilhelmina of Hesse-Kassel Princess Wilhelmina of Hesse-Kassel (25 February 1726 – 8 October 1808) was a Prussian princess, married to Prince Henry of Prussia. Wilhelmina was the daughter of Prince Maximilian of Hesse-Kassel and Friederike Charlotte of Hesse-Darmstadt .... Works * ''Le méchaniste (sic) philosophe ou Mémoire contenant plusieurs particularités de la vie et des ouvrages du sieur Jean Pigeon on père La Haye, 1750.'' References * Assézat, Œuvres complètes de Diderot. Paris, Garnier, 1875. Vol. 9, p. 77. * * 1724 births 1767 deaths French women mathematicians 18th-century French mathematicians 18th-centur ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
John Michell
John Michell (; 25 December 1724 – 21 April 1793) was an English people, English natural philosophy, natural philosopher and clergyman who provided pioneering insights into a wide range of scientific fields including astronomy, geology, optics, and gravitation. Considered "one of the greatest unsung scientists of all time", he is the first person known to have proposed the existence of black holes, and the first to have suggested that earthquakes travelled in seismic waves, (seismic) waves. Recognizing that double stars were a product of mutual gravitation, he was the first to apply statistics to the Cosmology, study of the cosmos. He invented an apparatus to measure the Earth mass, mass of the Earth, and explained how to manufacture an artificial magnet. He has been called the father both of seismology and of magnetometry. According to one science journalist, "a few specifics of Michell's work really do sound like they are ripped from the pages of a twentieth century astrono ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
1793 In Science
The year 1793 in science and technology involved some significant events. Events * August 8 – The French Academy of Sciences is among the academies suppressed by the National Convention. * October 24 – The French Republican Calendar, devised by Gilbert Romme, is adopted by the National Convention. Exploration * July 20 – Scottish people, Scottish explorer Alexander Mackenzie (explorer), Alexander Mackenzie's 1792–1793 Peace River expedition to the Pacific Ocean reaches its goal at Bella Coola, British Columbia, making him the first known person to complete a transcontinental crossing of northern North America. Biology * June 10 – formally established in Paris by the National Convention The National Convention (french: link=no, Convention nationale) was the parliament of the Kingdom of France for one day and the French First Republic for the rest of its existence during the French Revolution, following the two-year National ... of the French First Republic. * C ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Geographer
A geographer is a physical scientist, social scientist or humanist whose area of study is geography, the study of Earth's natural environment and human society, including how society and nature interacts. The Greek prefix "geo" means "earth" and the Greek suffix, "graphy," meaning "description," so a geographer is someone who studies the earth. The word "geography" is a Middle French word that is believed to have been first used in 1540. Although geographers are historically known as people who make maps, map making is actually the field of study of cartography, a subset of geography. Geographers do not study only the details of the natural environment or human society, but they also study the reciprocal relationship between these two. For example, they study how the natural environment contributes to human society and how human society affects the natural environment. In particular, physical geographers study the natural environment while human geographers study human society ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Germans
, native_name_lang = de , region1 = , pop1 = 72,650,269 , region2 = , pop2 = 534,000 , region3 = , pop3 = 157,000 3,322,405 , region4 = , pop4 = 21,000 3,000,000 , region5 = , pop5 = 125,000 982,226 , region6 = , pop6 = 900,000 , region7 = , pop7 = 142,000 840,000 , region8 = , pop8 = 9,000 500,000 , region9 = , pop9 = 357,000 , region10 = , pop10 = 310,000 , region11 = , pop11 = 36,000 250,000 , region12 = , pop12 = 25,000 200,000 , region13 = , pop13 = 233,000 , region14 = , pop14 = 211,000 , region15 = , pop15 = 203,000 , region16 = , pop16 = 201,000 , region17 = , pop17 = 101,000 148,00 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Anton Friedrich Busching , the championship trophy of the Swedish junior hockey ...
Anton may refer to: People *Anton (given name), including a list of people with the given name *Anton (surname) Places *Anton Municipality, Bulgaria **Anton, Sofia Province, a village *Antón District, Panama **Antón, a town and capital of the district *Anton, Colorado, an unincorporated town *Anton, Texas, a city *Anton, Wisconsin, an unincorporated community *River Anton, Hampshire, United Kingdom Other uses *Case Anton, codename for the German and Italian occupation of Vichy France in 1942 *Anton (computer), a highly parallel supercomputer for molecular dynamics simulations * ''Anton'' (1973 film), a Norwegian film * ''Anton'' (2008 film), an Irish film *Anton Cup The Anton Cup is the championship trophy of the Swedish junior hockey league, J20 SuperElit. The trophy was donated by Anton Johansson, chairman of the Swedish Ice Hockey Association between 1924 and 1948, in 1952, as an award for Sweden's top-rank ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
1786 In Science
The year 1786 in science and technology involved some significant events. Astronomy * January 17 – Pierre Méchain first observes Comet Encke, from Paris. * August 1 – Caroline Herschel becomes the first woman to discover a comet. Biology * Subfossil bones of the Rodrigues solitaire are discovered. Linguistics * February 2 – In a speech before The Asiatic Society in Calcutta, Sir William Jones notes the formal resemblances between Latin, Greek, and Sanskrit, laying the foundation for comparative linguistics and Indo-European studies. Mathematics * Erland Samuel Bring publishes ', proposing algebraic solutions to quintic functions. * Lagrange moves from Prussia to Paris under the patronage of Louis XVI of France. * William Playfair produces the first line and bar charts. Technology * August – James Rumsey tests his first steamboat in the Potomac river at Shepherdstown, Virginia. * Ignaz von Born introduces a method of extracting metals using the patio process in his ''U ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Swedish Royal Academy Of Science
The Royal Swedish Academy of Sciences ( sv, Kungliga Vetenskapsakademien) is one of the royal academies of Sweden. Founded on 2 June 1739, it is an independent, non-governmental scientific organization that takes special responsibility for promoting natural sciences and mathematics and strengthening their influence in society, whilst endeavouring to promote the exchange of ideas between various disciplines. The goals of the academy are: * to be a forum where researchers meet across subject boundaries, * to offer a unique environment for research, * to provide support to younger researchers, * to reward outstanding research efforts, * to communicate internationally among scientists, * to advance the case for science within society and to influence research policy priorities * to stimulate interest in mathematics and science in school, and * to disseminate and popularize scientific information in various forms. Every year, the academy awards the Nobel Prizes in physics and chemis ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Eva Ekeblad
Eva Ekeblad (née De la Gardie; 10 July 1724 – 15 May 1786) was a Swedish countess, salon hostess, agronomist, and scientist. She was widely known for discovering a method in 1746 to make alcohol and flour from potatoes, allowing greater use of scarce grains for food production, significantly reducing Sweden's incidence of famine. Ekeblad was the first female member of the Royal Swedish Academy of Sciences (1748).Riksarkivet Band 12 (1949), p.637 Wilhelmina Stålberg, P. G. Berg. 1864, pp. 130–131 Life Personal life Eva Ekeblad was born in 1724, originally named Eva de la Gardie before her marriage to Co ...[...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |