|
1715 In Science
The year 1715 in science and technology involved some significant events. Astronomy * May 3 – Total solar eclipse across southern England, Sweden and Finland (last total eclipse visible in London for almost 900 years). * Edmond Halley suggests that nebulae are clouds of interstellar gas. * Publication in London of David Gregory's ''The elements of astronomy, physical and geometrical... Done into English'', containing the first recorded use in English of the word ''Physics'' in its modern scientific sense and the first mention of a series approximating the Titius–Bode law on celestial orbits. Discoveries * Mine La Motte, in Madison county, Missouri, is discovered by De la Motte Cadillac. * The "miracle" springs are discovered in Cheltenham, England, a small Cotswold village at the time. Geology * Edmund Halley suggests using the salinity and evaporation of salt lakes to determine the age of the Earth. Mathematics * Brook Taylor's ''Methodus Incrementorum Directa et Inversa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Science
Science is a systematic endeavor that builds and organizes knowledge in the form of testable explanations and predictions about the universe. Science may be as old as the human species, and some of the earliest archeological evidence for scientific reasoning is tens of thousands of years old. The earliest written records in the history of science come from Ancient Egypt and Mesopotamia in around 3000 to 1200 BCE. Their contributions to mathematics, astronomy, and medicine entered and shaped Greek natural philosophy of classical antiquity, whereby formal attempts were made to provide explanations of events in the physical world based on natural causes. After the fall of the Western Roman Empire, knowledge of Greek conceptions of the world deteriorated in Western Europe during the early centuries (400 to 1000 CE) of the Middle Ages, but was preserved in the Muslim world during the Islamic Golden Age and later by the efforts of Byzantine Greek scholars who brought Greek ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
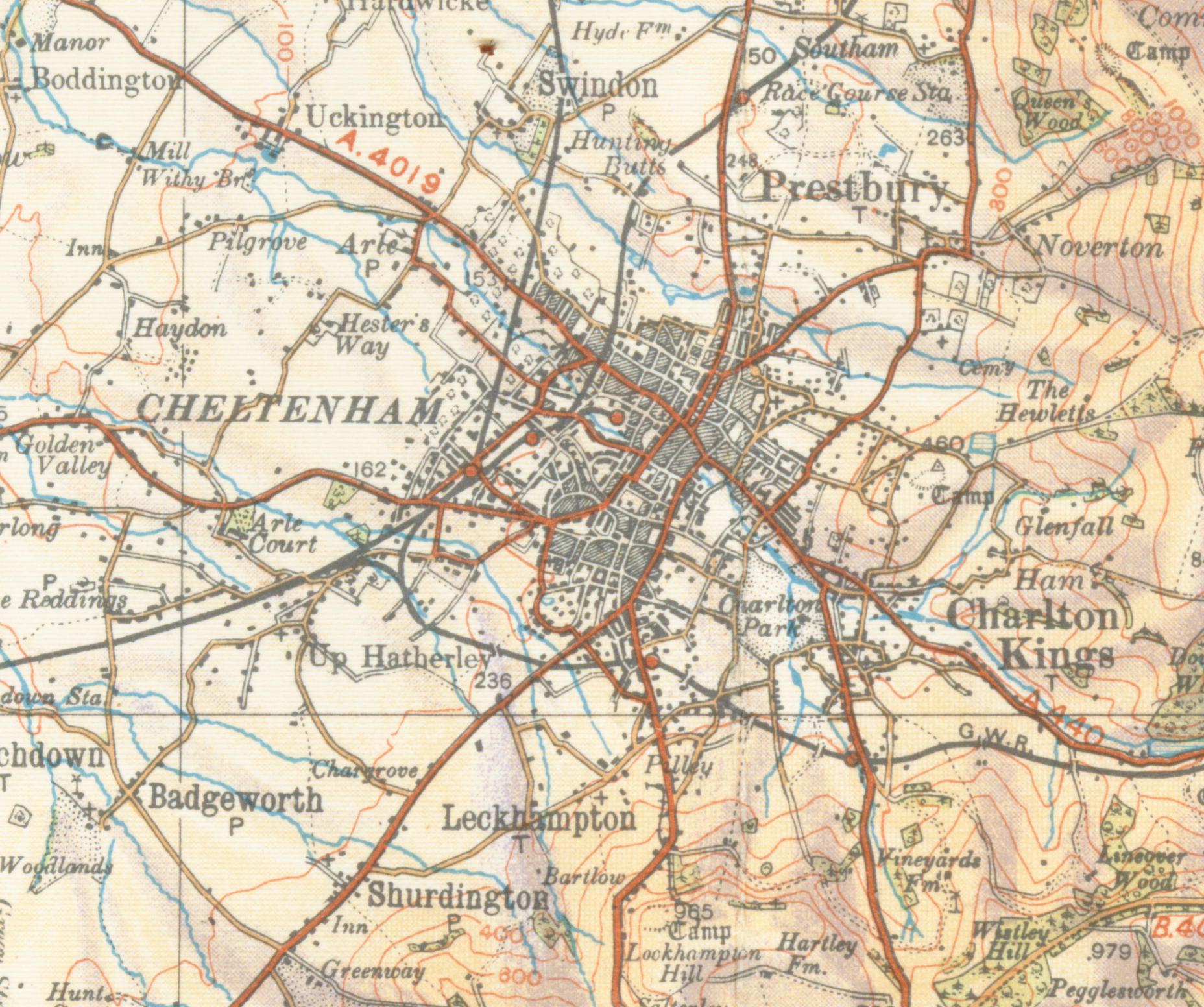
Cheltenham
Cheltenham (), also known as Cheltenham Spa, is a spa town and borough on the edge of the Cotswolds in the county of Gloucestershire, England. Cheltenham became known as a health and holiday spa town resort, following the discovery of mineral springs in 1716, and claims to be the most complete Regency town in Britain. The town hosts several festivals of culture, often featuring nationally and internationally famous contributors and attendees; they include the Cheltenham Literature Festival, the Cheltenham Jazz Festival, the Cheltenham Science Festival, the Cheltenham Music Festival, the Cheltenham Cricket Festival and the Cheltenham Food & Drink Festival. In steeplechase horse racing, the Gold Cup is the main event of the Cheltenham Festival, held every March. History Cheltenham stands on the small River Chelt, which rises nearby at Dowdeswell and runs through the town on its way to the Severn. It was first recorded in 803, as ''Celtan hom''; the meaning has not been resol ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Anatomist
Anatomy () is the branch of biology concerned with the study of the structure of organisms and their parts. Anatomy is a branch of natural science that deals with the structural organization of living things. It is an old science, having its beginnings in prehistoric times. Anatomy is inherently tied to developmental biology, embryology, comparative anatomy, evolutionary biology, and phylogeny, as these are the processes by which anatomy is generated, both over immediate and long-term timescales. Anatomy and physiology, which study the structure and function of organisms and their parts respectively, make a natural pair of related disciplines, and are often studied together. Human anatomy is one of the essential basic sciences that are applied in medicine. The discipline of anatomy is divided into macroscopic and microscopic. Macroscopic anatomy, or gross anatomy, is the examination of an animal's body parts using unaided eyesight. Gross anatomy also includes the branch of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
French People
The French people (french: Français) are an ethnic group and nation primarily located in Western Europe that share a common French culture, history, and language, identified with the country of France. The French people, especially the native speakers of langues d'oïl from northern and central France, are primarily the descendants of Gauls (including the Belgae) and Romans (or Gallo-Romans, western European Celtic and Italic peoples), as well as Germanic peoples such as the Franks, the Visigoths, the Suebi and the Burgundians who settled in Gaul from east of the Rhine after the fall of the Roman Empire, as well as various later waves of lower-level irregular migration that have continued to the present day. The Norse also settled in Normandy in the 10th century and contributed significantly to the ancestry of the Normans. Furthermore, regional ethnic minorities also exist within France that have distinct lineages, languages and cultures such as Bretons in Brittany, Occi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
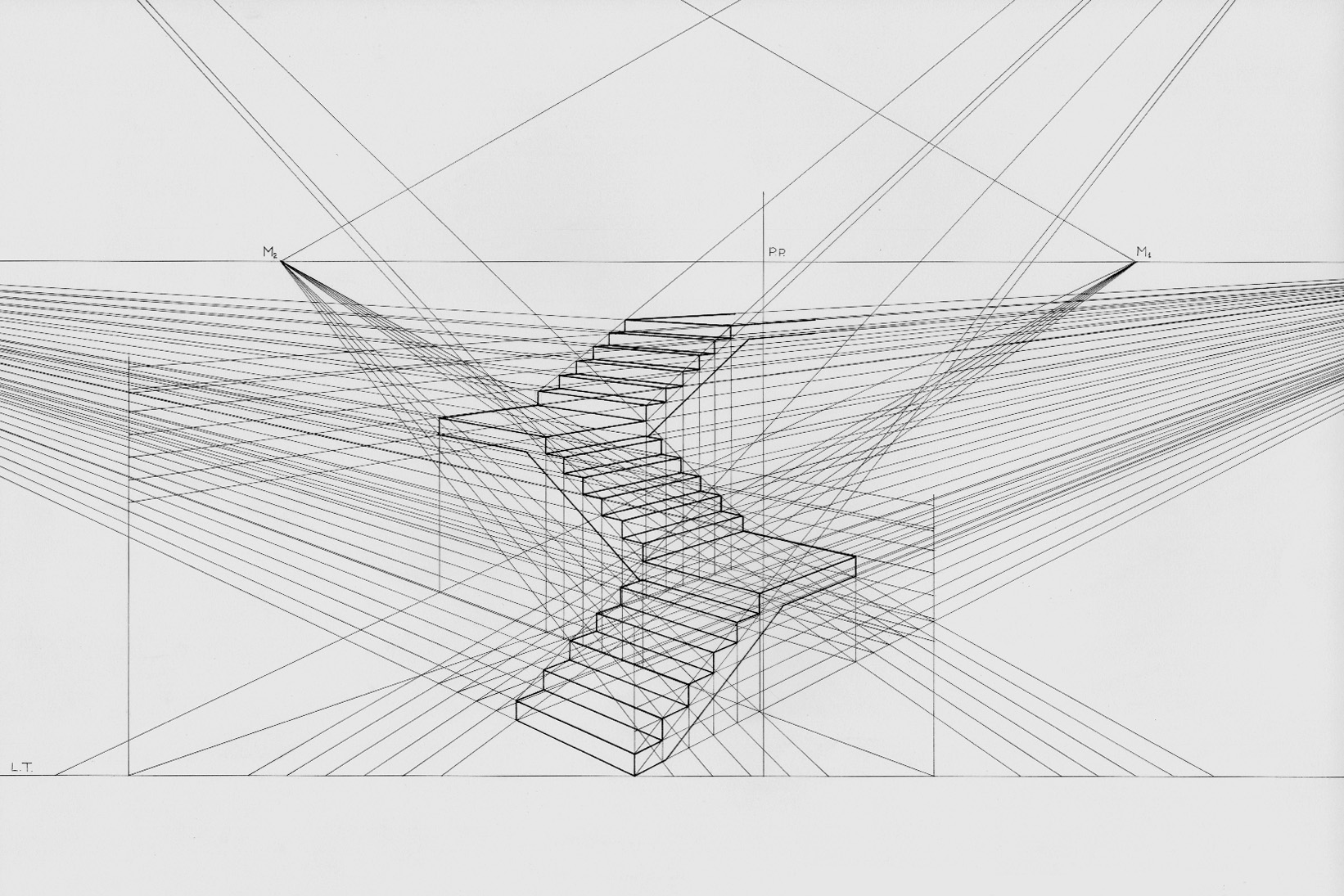
Vanishing Point
A vanishing point is a point on the image plane of a perspective drawing where the two-dimensional perspective projections of mutually parallel lines in three-dimensional space appear to converge. When the set of parallel lines is perpendicular to a picture plane, the construction is known as one-point perspective, and their vanishing point corresponds to the oculus, or "eye point", from which the image should be viewed for correct perspective geometry.Kirsti Andersen (2007) ''Geometry of an Art'', p. xxx, Springer, Traditional linear drawings use objects with one to three sets of parallels, defining one to three vanishing points. Italian humanist polymath and architect Leon Battista Alberti first introduced the concept in his treatise on perspective in art, '' De pictura'', written in 1435. Vector notation The vanishing point may also be referred to as the "direction point", as lines having the same directional vector, say ''D'', will have the same vanishing point. Mathem ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Perspective (graphical)
Linear or point-projection perspective (from la, perspicere 'to see through') is one of two types of 3D projection, graphical projection perspective in the graphic arts; the other is parallel projection. Linear perspective is an approximate representation, generally on a flat surface, of an image as it is seen by the eye. Perspective drawing is useful for representing a three-dimensional scene in a two-dimensional medium, like paper. The most characteristic features of linear perspective are that objects appear smaller as their distance from the observer increases, and that they are subject to ''foreshortening'', meaning that an object's dimensions along the line of sight appear shorter than its dimensions across the line of sight. All objects will recede to points in the distance, usually along the horizon line, but also above and below the horizon line depending on the view used. Italian Renaissance painters and architects including Masaccio, Paolo Uccello, Piero della Fran ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Taylor Series
In mathematics, the Taylor series or Taylor expansion of a function is an infinite sum of terms that are expressed in terms of the function's derivatives at a single point. For most common functions, the function and the sum of its Taylor series are equal near this point. Taylor series are named after Brook Taylor, who introduced them in 1715. A Taylor series is also called a Maclaurin series, when 0 is the point where the derivatives are considered, after Colin Maclaurin, who made extensive use of this special case of Taylor series in the mid-18th century. The partial sum formed by the first terms of a Taylor series is a polynomial of degree that is called the th Taylor polynomial of the function. Taylor polynomials are approximations of a function, which become generally better as increases. Taylor's theorem gives quantitative estimates on the error introduced by the use of such approximations. If the Taylor series of a function is convergent, its sum is the limit of the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Taylor's Theorem
In calculus, Taylor's theorem gives an approximation of a ''k''-times differentiable function around a given point by a polynomial of degree ''k'', called the ''k''th-order Taylor polynomial. For a smooth function, the Taylor polynomial is the truncation at the order ''k'' of the Taylor series of the function. The first-order Taylor polynomial is the linear approximation of the function, and the second-order Taylor polynomial is often referred to as the quadratic approximation. There are several versions of Taylor's theorem, some giving explicit estimates of the approximation error of the function by its Taylor polynomial. Taylor's theorem is named after the mathematician Brook Taylor, who stated a version of it in 1715, although an earlier version of the result was already mentioned in 1671 by James Gregory. Taylor's theorem is taught in introductory-level calculus courses and is one of the central elementary tools in mathematical analysis. It gives simple arithmetic formula ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Finite Difference
A finite difference is a mathematical expression of the form . If a finite difference is divided by , one gets a difference quotient. The approximation of derivatives by finite differences plays a central role in finite difference methods for the numerical solution of differential equations, especially boundary value problems. The difference operator, commonly denoted \Delta is the operator that maps a function to the function \Delta /math> defined by :\Delta x)= f(x+1)-f(x). A difference equation is a functional equation that involves the finite difference operator in the same way as a differential equation involves derivatives. There are many similarities between difference equations and differential equations, specially in the solving methods. Certain recurrence relations can be written as difference equations by replacing iteration notation with finite differences. In numerical analysis, finite differences are widely used for approximating derivatives, and the term " ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Calculus
Calculus, originally called infinitesimal calculus or "the calculus of infinitesimals", is the mathematical study of continuous change, in the same way that geometry is the study of shape, and algebra is the study of generalizations of arithmetic operations. It has two major branches, differential calculus and integral calculus; the former concerns instantaneous Rate of change (mathematics), rates of change, and the slopes of curves, while the latter concerns accumulation of quantities, and areas under or between curves. These two branches are related to each other by the fundamental theorem of calculus, and they make use of the fundamental notions of convergence (mathematics), convergence of infinite sequences and Series (mathematics), infinite series to a well-defined limit (mathematics), limit. Infinitesimal calculus was developed independently in the late 17th century by Isaac Newton and Gottfried Wilhelm Leibniz. Later work, including (ε, δ)-definition of limit, codify ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Brook Taylor
Brook Taylor (18 August 1685 – 29 December 1731) was an English mathematician best known for creating Taylor's theorem and the Taylor series, which are important for their use in mathematical analysis. Life and work Brook Taylor was born in Edmonton (former Middlesex). Taylor was the son of John Taylor, MP of Patrixbourne, Kent and Olivia Tempest, the daughter of Sir Nicholas Tempest, Baronet of Durham. He entered St John's College, Cambridge, as a fellow-commoner in 1701, and took degrees in LL.B. in 1709 and LL.D. in 1714. Taylor studied mathematics under John Machin and John Keill, leading to Taylor obtaining a solution to the problem of "center of oscillation." Taylor's solution remained unpublished until May 1714, when his claim to priority was disputed by Johann Bernoulli. Taylor's ''Methodus Incrementorum Directa et Inversa'' (1715) ("Direct and Indirect Methods of Incrementation") added a new branch to higher mathematics, called "calculus of finite dif ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Age Of The Earth
The age of Earth is estimated to be 4.54 ± 0.05 billion years This age may represent the age of Earth's accretion, or core formation, or of the material from which Earth formed. This dating is based on evidence from radiometric age-dating of meteorite material and is consistent with the radiometric ages of the oldest-known terrestrial and lunar samples. Following the development of radiometric age-dating in the early 20th century, measurements of lead in uranium-rich minerals showed that some were in excess of a billion years old.For the abstract, see: The oldest such minerals analyzed to date—small crystals of zircon from the Jack Hills of Western Australia—are at least 4.404 billion years old. Calcium–aluminium-rich inclusions—the oldest known solid constituents within meteorites that are formed within the Solar System—are 4.567 billion years old, giving a lower limit for the age of the Solar System. It is hypothesised that the accretion of Earth began soon ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |



.jpg)