|
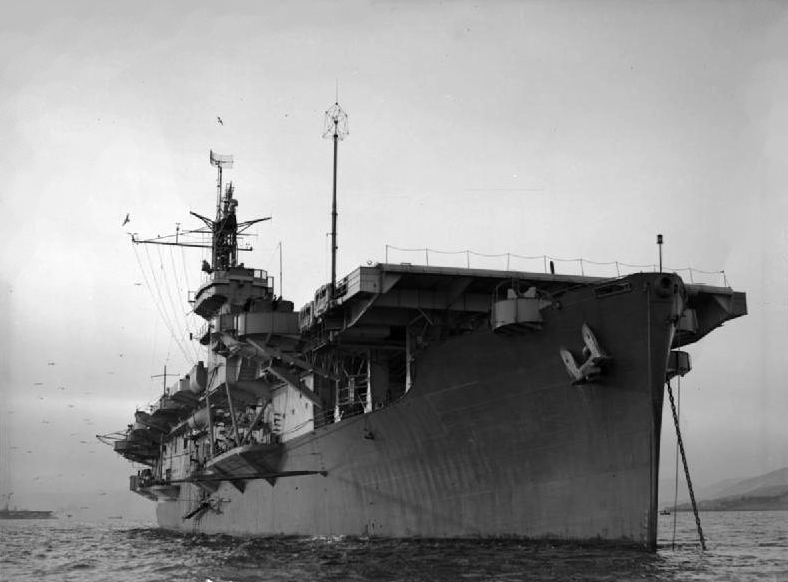
1700 Naval Air Squadron
1700 Naval Air Squadron of the Fleet Air Arm of the Royal Navy was formed in November 1944 at RNAS Lee-on-Solent as an amphibian bomber reconnaissance squadron. It was equipped with the Supermarine Sea Otter, and the squadron joined HMS ''Khedive'' in January 1945 bound for Sulur in India. On arrival the Sea Otters were augmented with Supermarine Walrus amphibian aircraft. The squadron's aircraft were distributed among the escort carriers of the Far East Fleet for air sea rescue and minesweeping duties. By April 1945 aircraft of the squadron were serving in HM Ships ''Stalker'', ''Hunter'', ''Khedive'', ''Emperor'', ''Ameer'', ''Attacker'' and ''Shah''. July saw operations at Car Nicobar, and off Phuket Island. Present day On 31 October 2017, the Maritime Aviation Support Force (MASF) at RNAS Culdrose was recommissioned as 1700 Naval Air Squadron. The unit provides personnel and naval aviation support to operations for ships and land bases globally. Aircraft flown 1700 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fleet Air Arm
The Fleet Air Arm (FAA) is one of the five fighting arms of the Royal Navy and is responsible for the delivery of naval air power both from land and at sea. The Fleet Air Arm operates the F-35 Lightning II for maritime strike, the AW159 Wildcat and AW101 Merlin for commando and anti-submarine warfare and the BAE Hawk as an aggressor. The Fleet Air Arm today is a predominantly rotary force, with helicopters undertaking roles once performed by biplanes such as the Fairey Swordfish. The Fleet Air Arm was formed in 1924 as an organisational unit of the Royal Air Force, which was then operating the aircraft embarked on RN ships—the Royal Naval Air Service having been merged with the Army's Royal Flying Corps in 1918 to form the Royal Air Force—and did not come under the direct control of the Admiralty until mid-1939. During the Second World War, the Fleet Air Arm operated aircraft on ships as well as land-based aircraft that defended the Royal Navy's shore establishments a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Operation Livery
Operation Livery was a series of naval air strikes on northern Japanese occupied Malaya and air cover missions for minesweeping operations by the British in July 1945 during World War II. It was carried out by the 4th and 7th Minesweeping Flotillas, taking place off Phuket Island, Thailand. It was the last action of the Eastern Fleet during the war. British order of battle Aircraft * 804 Naval Air Squadron - 24 Grumman F6F Hellcats * 808 Naval Air Squadron - 24 Grumman F6F Hellcats * 1700 Naval Air Squadron - 1 Supermarine Walrus Ships * * * * * * * - Damaged by Japanese kamikazes and scuttled * - Damaged by a Japanese mine and scuttled * * * * * Operation The escort carrier HMS ''Empress'' sailed on 19 July to partake in Operation Livery. Aircraft from herself and ''Ameer'' were to attack Japanese targets starting 24 July in northern Malaya and southern Thailand (specifically Phuket Island) while also covering the minesweeping operations of the 4th and 7th mineswe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Car Nicobar
Car Nicobar ( in Car language) is the northernmost of the Nicobar Islands. It is also one of three local administrative divisions of the Indian district of Nicobar, part of the Indian union territory of Andaman and Nicobar Islands. Annual rainfall is 2800 millimetres. History The sea farers of the region referred to the island as the "northern land of the nake" i.e. Car Nakkavar which is perhaps the direct predecessor of the current name Car Nicobar. 2004 tsunami devastation The island was severely affected by the tsunami that was caused by the 2004 Indian Ocean earthquake, which led to many deaths and damaged infrastructure. Car Nicobar lies from the epicenter of the 2004 Indian Ocean earthquake, and the ensuing tsunamis struck it with great force. Witnesses reported the waves were as high as 30 ft (9 m). As of December 30, 2004, the number of casualties remained unknown, but were estimated to be high. One survivor told the Associated Press: "There's not a single hut ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
HMS Shah (D21)
USS ''Jamaica'' (CVE-43) (originally AVG-43 then later ACV-43), was an escort carrier of World War II that served in the British Royal Navy as HMS ''Shah'' (D21). Returned to the United States at war's end, she was converted into a merchant vessel and she was sold into civilian service in 1946 as ''Salta''. She was ultimately scrapped in 1966. Design and description HMS ''Shah'' was a in the Royal Navy. The ships in this class were all larger and had a greater aircraft capacity than all preceding American-built escort carriers. Their hulls were designed as merchant ships but they were laid down as escort carriers and were not later conversions. All had a complement of 646 officers and ratings and an overall length of , a beam of and a draught of .Cocker (2008), p.82. Propulsion was provided a steam turbine, two boilers connected to one shaft giving , which could propel the ship at .Cocker (2008), p.79. Aircraft facilities were a small combined bridge–flight control on th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
HMS Attacker (D02)
HMS ''Attacker'' (D02) was an American-built escort carrier that served with the Royal Navy during the Second World War. Converted from a merchantman under construction, she was commissioned by the United States Navy on 30 September 1942, as USS ''Barnes'' (CVE-7), a ; she was decommissioned and transferred to the Royal Navy on the same day under the Lend-Lease agreement. ''Attacker'' served throughout the war, first as a convoy escort in the Battle of the Atlantic. After further conversion by the Royal Navy in October 1943, into an assault carrier, the ship was active in the Mediterranean, and later the war in the Pacific. In late August 1945, ''Attacker'' witnessed the Japanese surrender of Penang, in Malaya, as part of Operation Jurist. Construction The merchantman ''Steel Artisan'' was laid down on 17 April 1941, under a Maritime Commission contract, MC hull 171, by Western Pipe and Steel Company of San Francisco. She was renamed ''Barnes'' (AVG-7) on 3 September 1941, and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
HMS Ameer (D01)
HMS ''Ameer'' (D01) was an American escort carrier, the USS ''Baffins'' (CVE-35), that was transferred to the Royal Navy in mid-1943. As a served in the Far East until the end of the war. ''Ameer'' was returned to the US Navy in 1946 and sold off to commercial service. Design and description These ships were all larger and had a greater aircraft capacity than all the preceding American built escort carriers. They were also all laid down as escort carriers and not converted merchant ships. All the ships had a complement of 646 men and an overall length of , a beam of and a draught of .Cocker (2008), p.82. Propulsion was provided by a steam turbine, two boilers connected to one shaft giving 9,350 brake horsepower (SHP), which could propel the ship at .Cocker (2008), p.79. Aircraft facilities were a small combined bridge–flight control on the starboard side, two aircraft lifts by , one aircraft catapult and nine arrestor wires.Cocker (2008), p.82. Aircraft could be housed in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
HMS Emperor (D98)
USS ''Pybus'' (CVE-34) was initially a United States Navy . The ship was transferred to the United Kingdom for service in the Royal Navy as the HMS ''Emperor'' (D98) as part of the Lend-Lease program of World War II. Entering service in 1943, the ship took part in operations against the and the invasions of Normandy and southern France. Returned to the United States following the war, the carrier was sold for scrap in 1946. Design and description The ''Bogue'' class were all larger and had a greater aircraft capacity than all the preceding American built escort carriers. They were also all laid down as escort carriers and not converted merchant ships. All the ships had a complement of 646 and an overall length of , a beam of and a draught of .Cocker (2008), p.82. Propulsion was provided a steam turbine, two boilers connected to one shaft giving , which could propel the ship at .Cocker (2008), p.79. Aircraft facilities were a small combined bridge–flight control on the s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
HMS Hunter (D80)
USS ''Block Island'' (CVE-8) (originally AVG and then ACV) was an escort aircraft carrier that served during World War II. The ship was laid down on 15 May 1941 as ''Mormacpenn'' under Maritime Commission contract at Pascagoula, Mississippi, by Ingalls Shipbuilding, acquired by the United States Navy on 9 January 1943 and simultaneously transferred via the Lend-Lease program to the United Kingdom as ''Trailer''. On 11 January 1943, the ship was renamed HMS ''Hunter'' (D80) and commissioned by the Royal Navy. In March 1945 was attached to the 21st Aircraft Carrier Squadron. She participated in Operation Jurist and Operation Tiderace in August 1945, the reoccupation of Malaya and Singapore from the Japanese. The vessel was returned to United States' custody 29 December 1945 and sold into merchant service on 17 January 1947 as ''Almdijk''. In October 1965 the ship was sold for scrapping in Spain. Design and description There were eight s in service with the Royal Navy during the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Far East Fleet
The Far East Fleet (also called the Far East Station) was a fleet of the Royal Navy which existed between 1952 and 1971. During the Second World War, the Eastern Fleet included many ships and personnel from other navies, including those of the Netherlands, Australia, New Zealand, and the United States. On 22 November 1944 the Eastern Fleet was re-designated East Indies fleet and continued to be based in Trincomalee. Following its re-designation its remaining ships formed the British Pacific Fleet. In December 1945 the British Pacific Fleet was disbanded and its forces were absorbed into the East Indies Fleet. In 1952 The East Indies Fleet was renamed the Far East Fleet. After the Second World War the East Indies Station continued as a separate command to the Far East until 1958. In 1971 the Far East Fleet was abolished and its remaining forces returned home, coming under the command of the new, unified, Commander-in-Chief Fleet. Post-war After the war, the East Indies Fleet wa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
RNAS Culdrose (HMS Seahawk)
Royal Naval Air Station Culdrose (RNAS Culdrose, also known as HMS ''Seahawk''; ICAO: EGDR) is a Royal Navy airbase near Helston on the Lizard Peninsula of Cornwall UK, and is one of the largest helicopter bases in Europe. Its main role is serving the Fleet Air Arm's front line AgustaWestland Merlin helicopter squadrons. History 1940–1999 Admiralty surveyors first started preliminary surveys of land near Helston in 1942. RNAS ''Culdrose'' was built by John Laing & Son and commissioned as HMS ''Seahawk'' five years after these initial surveys. The station was originally designed to be a wartime airfield lasting about ten years. The initial plans were for ''Culdrose'' to serve as a Naval Fighting School, it soon developed other roles. These varied roles included such things as the trials of the Navy's first jets, training of airborne early warning crews and as a home base for carrier-based aircraft. Over the years the station's emphasis changed from fixed wing aircraft to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Supermarine Walrus
The Supermarine Walrus (originally designated the Supermarine Seagull V) was a British single-engine amphibious biplane reconnaissance aircraft designed by R. J. Mitchell and manufactured by Supermarine at Woolston, Southampton. The Walrus first flew in 1933, the design effort having commenced as a private venture four years earlier. It shared its general configuration with that of the earlier Supermarine Seagull. Having been designed to serve as a fleet spotter for catapult launching from cruisers or battleships, the aircraft was largely employed in other roles, notably as a maritime patrol aircraft and as a rescue aircraft for ditched aircrew. The Walrus featured numerous innovations for the period, being the first British squadron-service aircraft to incorporate in one airframe a fully retractable main undercarriage, completely enclosed crew accommodation and an all-metal fuselage. Early-build aircraft featured the original metal hull design for its greater longevity in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |