|
16PF Questionnaire
The Sixteen Personality Factor Questionnaire (16PF) is a self-reported personality test developed over several decades of empirical research by Raymond B. Cattell, Maurice Tatsuoka and Herbert Eber. The 16PF provides a measure of personality and can also be used by psychologists, and other mental health professionals, as a clinical instrument to help diagnose psychiatric disorders, and help with prognosis and therapy planning. The 16PF can also provide information relevant to the clinical and counseling process, such as an individual's capacity for insight, self-esteem, cognitive style, internalization of standards, openness to change, capacity for empathy, level of interpersonal trust, quality of attachments, interpersonal needs, attitude toward authority, reaction toward dynamics of power, frustration tolerance, and coping style. Thus, the 16PF instrument provides clinicians with a normal-range measurement of anxiety, adjustment, emotional stability and behavioral problems. Cli ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Personality Test
A personality test is a method of assessing human personality construct (psychology), constructs. Most personality assessment instruments (despite being loosely referred to as "personality tests") are in fact introspective (i.e., subjective) self-report questionnaire (Q-data, in terms of LOTS of data, LOTS data) measures or reports from life records (L-data) such as rating scales. Attempts to construct actual performance tests of personality have been very limited even though Raymond Cattell with his colleague Frank Warburton compiled a list of over 2000 separate objective tests that could be used in constructing objective personality tests. One exception, however, was the Objective-Analytic Test Battery, a performance test designed to quantitatively measure 10 factor-analytically discerned personality trait dimensions. A major problem with both L-data and Q-data methods is that because of item transparency, rating scales, and self-report questionnaires are highly susceptible to mo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
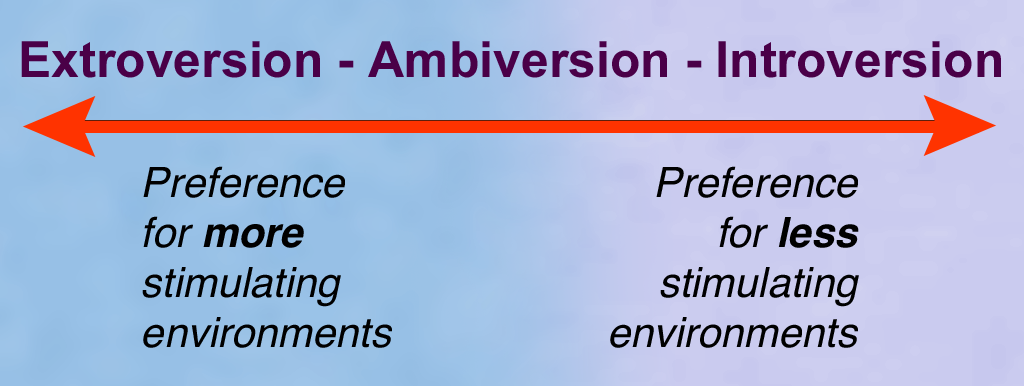
Introversion And Extroversion
Extraversion and introversion are a central trait dimension in human personality theory. The terms were introduced into psychology by Carl Jung, though both the popular understanding and current psychological usage are not the same as Jung's original concept. Extraversion (also spelled ''extroversion'') is typically associated with sociability, talkativeness, and high energy, while introversion is linked to introspection, reserve, and a preference for solitary activities. Jung defined introversion as an "attitude-type characterised by orientation in life through subjective psychic contents", and extraversion as "an attitude-type characterised by concentration of interest on the external object". While often presented as opposite ends of a single continuum, many personality theorists, such as Carl Jung, have suggested that most individuals possesses elements of both traits, with one being more dominant. Jung provides a different perspective and suggests that everyone has both ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Facet (psychology)
In psychology, a facet is a specific and unique aspect of a broader personality trait. Both the concept and the term "facet" were introduced by Paul Costa and Robert McCrae in the first edition of the NEO-Personality Inventory (NEO-PI) Manual. Facets were originally elaborated only for the neuroticism, openness to experience, and extraversion traits; Costa and McCrae introduced facet scales for the agreeableness and conscientiousness traits in the Revised NEO-PI (NEO PI-R). Each of the Big Five personality traits in the five factor model contains six facets, each of which is measured with a separate scale. The use of facets and facet scales has since expanded beyond the NEO PI-R, with alternative facet and domain structures derived from other models of personality. Examples include the HEXACO model of personality structure, psycholexical studies, circumplex models (e.g., Goldberg's Abridged Big-Five Dimensional Circumplex), the Multidimensional Personality Questionnaire (MPQ), ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Orthogonal
In mathematics, orthogonality (mathematics), orthogonality is the generalization of the geometric notion of ''perpendicularity''. Although many authors use the two terms ''perpendicular'' and ''orthogonal'' interchangeably, the term ''perpendicular'' is more specifically used for lines and planes that intersect to form a right angle, whereas ''orthogonal'' is used in generalizations, such as ''orthogonal vectors'' or ''orthogonal curves''. ''Orthogonality'' is also used with various meanings that are often weakly related or not related at all with the mathematical meanings. Etymology The word comes from the Ancient Greek ('), meaning "upright", and ('), meaning "angle". The Ancient Greek (') and Classical Latin ' originally denoted a rectangle. Later, they came to mean a right triangle. In the 12th century, the post-classical Latin word ''orthogonalis'' came to mean a right angle or something related to a right angle. Mathematics Physics Optics In optics, polarization ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Lewis Goldberg
Lewis R. Goldberg (born January 28, 1932) is an American personality psychologist and a professor emeritus at the University of Oregon. He is closely associated Goldberg, L.R. (1993). The structure of phenotypic personality traits. ''American Psychologist, 48'', 26-34. https://dx.doi.org/10.1037/0003-066X.48.1.26 with the lexical hypothesis that any culturally important personality characteristic will be represented in the language of that culture. This hypothesis led to a five factor structure of personality trait adjectives (which he dubbed the Big 5).Lewis R. Goldberg (1990) An alternative "description of personality": The Big-Five factor structure. Journal of Personality and Social Psychology, 59, 6, 1216-1229 https://dx.doi.org/10.1037/0022-3514.59.6.1216Revelle, W. (2008), Biography of Lewis R. Goldberg. In Encyclopedia of Counseling (F.T.L. Leong et al, editors) Sage. https://dx.doi.org/10.4135/9781412963978.n198 When applied to personality items this structure is als ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Angle
In Euclidean geometry, an angle can refer to a number of concepts relating to the intersection of two straight Line (geometry), lines at a Point (geometry), point. Formally, an angle is a figure lying in a Euclidean plane, plane formed by two Ray (geometry), rays, called the ''Side (plane geometry), sides'' of the angle, sharing a common endpoint, called the ''vertex (geometry), vertex'' of the angle. More generally angles are also formed wherever two lines, rays or line segments come together, such as at the corners of triangles and other polygons. An angle can be considered as the region of the plane bounded by the sides. Angles can also be formed by the intersection of two planes or by two intersecting curves, in which case the rays lying tangent to each curve at the point of intersection define the angle. The term ''angle'' is also used for the size, magnitude (mathematics), magnitude or Physical quantity, quantity of these types of geometric figures and in this context an a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Agreeableness
Agreeableness is the trait theory, personality trait of being kind, Sympathy, sympathetic, cooperative, warm, honest, straightforward, and considerate. In personality psychology, agreeableness is one of the Big Five personality traits, five major dimensions of personality structure, reflecting individual differences in cooperation. People who score high on measures of agreeableness are Empathy, empathetic and Altruism, self-sacrificing, while those with low agreeableness are prone to selfishness, insincerity, and zero-sum thinking. Those who score low on agreeableness may show dark triad tendencies, such as narcissism, narcissistic, Antisocial personality disorder, antisocial, and Manipulation (psychology), manipulative behavior. Agreeableness is a superordinate trait, meaning it is a grouping of personality sub-traits that cluster together statistically. Some lower-level traits, or Facet (psychology), facets, that are commonly grouped under agreeableness include Trust (social sci ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Extraversion And Introversion
Extraversion and introversion are a central trait theory, trait dimension in human personality psychology, personality theory. The terms were introduced into psychology by Carl Jung, though both the popular understanding and current psychological usage are not the same as Jung's original concept. Extraversion (also spelled ''extroversion'') is typically associated with sociability, talkativeness, and high energy, while introversion is linked to introspection, reserve, and a preference for solitary activities. Jung defined introversion as an "attitude-type characterised by orientation in life through subjective psychic contents", and extraversion as "an attitude-type characterised by concentration of interest on the external object". While often presented as opposite ends of a single Continuum (theory), continuum, many personality theorists, such as Carl Jung, have suggested that most individuals possesses elements of both traits, with one being more dominant. Jung provides a d ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Openness To Experience
Openness to experience is one of the domains which are used to describe personality psychology, human personality in the Big Five personality traits, Five Factor Model. Openness involves six Facet (psychology), facets, or dimensions: active imagination (fantasy), aesthetic sensitivity, attentiveness to inner feelings, preference for variety (adventurousness), intellectual curiosity, and challenging authority (psychological liberalism). A great deal of psychometric research has demonstrated that these facets or qualities are significantly correlated. Thus, openness can be viewed as a global personality trait consisting of a set of specific traits, habits, and tendencies that cluster together. Openness tends to be Normal distribution, normally distributed, with a small number of people scoring extremely high or low on the trait and most people scoring moderately. People who score low on openness are considered to be ''closed to experience''. They tend to be conventional and traditiona ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Stress (biological)
Stress, whether physiological, biological or psychological, is an organism's response to a stressor, such as an environmental condition or change in life circumstances. When stressed by stimuli that alter an organism's environment, multiple systems respond across the body. In humans and most mammals, the autonomic nervous system and Hypothalamic–pituitary–adrenal axis, hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenal (HPA) axis are the two major systems that respond to stress. Two well-known hormones that humans produce during stressful situations are adrenaline and cortisol. The Sympathoadrenal system, sympathoadrenal medullary axis (SAM) may activate the fight-or-flight response through the sympathetic nervous system, which dedicates energy to more relevant bodily systems to Acute stress reaction, acute adaptation to stress, while the parasympathetic nervous system returns the body to homeostasis. The second major physiological stress-response center, the HPA axis, regulates the release ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Perfectionism (psychology)
Perfectionism, in psychology, is a broad personality trait characterized by a person's concern with striving for flawlessness and perfection and is accompanied by critical self-evaluations and concerns regarding others' evaluations. It is best conceptualized as a multidimensional and multilayered personality characteristic, and initially some psychologists thought that there were many positive and negative aspects. Maladaptive perfectionism drives people to be concerned with achieving unattainable ideals or unrealistic goals that often lead to many forms of adjustment problems such as depression, anxiety, OCD, OCPD and low self-esteem. These adjustment problems often lead to suicidal thoughts and tendencies and influence or invite other psychological, physical, social, and further achievement problems in children, adolescents, and adults. Although perfectionist sights can reduce stress, anxiety, and panic, recent data, compiled by British psychologists Thomas Curran and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Self-sufficiency
Self-sustainability and self-sufficiency are overlapping states of being in which a person, being, or system needs little or no help from, or interaction with others. Self-sufficiency entails the self being enough (to fulfill needs), and a self-sustaining entity can maintain self-sufficiency indefinitely. These states represent types of personal or collective autonomy. A self-sufficient economy is one that requires little or no trade with the outside world and is called an autarky. Description Self-sustainability is a type of sustainable living in which nothing is consumed other than what is produced by the self-sufficient individuals. Self-sustainability is a comprehensive approach to sustainable living that extends beyond mere environmental responsibility to encompass economic independence, reduced reliance on major corporations, and minimizing environmental impact through personal actions. Examples of attempts at self-sufficiency in North America include simple living, fo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |