|
1649 Programme Group
The ''1649 Programme'' of four 370 ton ''Fourth Rate'' vessels was approved by Parliament on 9 January 1647. The ships were to carry a minimum of 32 guns in peacetime and 38 guns in wartime. Each vessel would have 11 pairs lower deck gun ports and eventually an equal number on the upper deck with two pairs on the quarterdeck. The vessels would actually have varying number of guns and the dimensional data would vary considerably. Three vessels were ordered in December 1645. Design and specifications The construction of the vessels was assigned to Chatham Chatham may refer to: Places and jurisdictions Canada * Chatham Islands (British Columbia) * Chatham Sound, British Columbia * Chatham, New Brunswick, a former town, now a neighbourhood of Miramichi * Chatham (electoral district), New Brunswic ..., Woolwich and Deptford dockyards. The ships would be built under the supervision of the Master Shipwrights of each Dockyard. As with most vessels of this time period only launch ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Portsmouth Dockyard
His Majesty's Naval Base, Portsmouth (HMNB Portsmouth) is one of three operating bases in the United Kingdom for the Royal Navy (the others being HMNB Clyde and HMNB Devonport). Portsmouth Naval Base is part of the city of Portsmouth; it is located on the eastern shore of Portsmouth Harbour, north of the Solent and the Isle of Wight. Until the early 1970s, it was officially known as Portsmouth Royal Dockyard (or HM Dockyard, Portsmouth); thereafter the term 'Naval Base' gained currency, acknowledging a greater focus on personnel and support elements alongside the traditional emphasis on building, repairing and maintaining ships. In 1984 Portsmouth's Royal Dockyard function was downgraded and it was formally renamed the 'Fleet Maintenance and Repair Organisation' (FMRO). The FMRO was privatized in 1998, and for a time (from 2002 to 2014), shipbuilding, in the form of Shipbuilding#Modern shipbuilding manufacturing techniques, block construction, returned. Around 2000, the designat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Deptford Dockyard
Deptford Dockyard was an important naval dockyard and base at Deptford on the River Thames, operated by the Royal Navy from the sixteenth to the nineteenth centuries. It built and maintained warships for 350 years, and many significant events and ships have been associated with it. Founded by Henry VIII in 1513, the dockyard was the most significant royal dockyard of the Tudor period and remained one of the principal naval yards for three hundred years. Important new technological and organisational developments were trialled here, and Deptford came to be associated with the great mariners of the time, including Francis Drake and Walter Raleigh. The yard expanded rapidly throughout the sixteenth and seventeenth centuries, encompassing a large area and serving for a time as the headquarters of naval administration, and the associated Victualling Yard became the Victualling Board's main depot. Tsar Peter the Great visited the yard officially incognito in 1698 to learn shi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
English Red Ensign 1620
English usually refers to: * English language * English people English may also refer to: Peoples, culture, and language * ''English'', an adjective for something of, from, or related to England ** English national identity, an identity and common culture ** English language in England, a variant of the English language spoken in England * English languages (other) * English studies, the study of English language and literature * ''English'', an Amish term for non-Amish, regardless of ethnicity Individuals * English (surname), a list of notable people with the surname ''English'' * People with the given name ** English McConnell (1882–1928), Irish footballer ** English Fisher (1928–2011), American boxing coach ** English Gardner (b. 1992), American track and field sprinter Places United States * English, Indiana, a town * English, Kentucky, an unincorporated community * English, Brazoria County, Texas, an unincorporated community ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
1647 Programme Group
The 1647 Programme of four 370 ton fourth-rate vessels was approved by Parliament on 9 January 1647. The ships were to carry a minimum of 32 guns in peacetime and 38 guns in wartime. Each vessel would have 11 pairs lower deck gun ports and eventually an equal number on the upper deck with two pairs on the quarterdeck. The vessels would actually have varying number of guns and the dimensional data would vary considerably. Three vessels were ordered in December 1645. Design and specifications The construction of the vessels was assigned to Chatham, Woolwich and Deptford dockyards. The ships would be built under the supervision of the master shipwright Shipbuilding is the construction of ships and other floating vessels. It normally takes place in a specialized facility known as a shipyard. Shipbuilders, also called shipwrights, follow a specialized occupation that traces its roots to befor ...s of each Dockyard. As with most vessels of this time period only launch years are ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
1650 Programme Group
The ''1650 Programme'' of six 510 ton ''Fourth Rate'' vessels was initiated by the Council of State on 16 November 1649. On 2 January 1650 the Admiralty Committee confirmed that six 'frigrates' had been ordered at a cost of 6.10.0d per ton. The ships would be built under contract with the exception of one ship built in Dockyard. The ships were all named by 16 August 1650 and launched by the end of the year. Each ship was to carry initially 34 guns and 150 men. This would increase over time Design and specifications The construction one vessels was assigned to Deptford dockyard with the remainder contracted to private builders. The contract dimensional data was keel of breadth and a builder's measure tonnage of tons at a contract price of 6.10.0dThe cost accounting for inflation of approximately £ in reference to today per ton. The ships were to have 34 guns and a manning level of 150, however, this was increased to 40 and 44 guns with 180 personnel. The guns would be culveri ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fourth-rate
In 1603 all English warships with a compliment of fewer than 160 men were known as 'small ships'. In 1625/26 to establish pay rates for officers a six tier naval ship rating system was introduced.Winfield 2009 These small ships were divided into three tiers, Fourth, Fifth and Sixth rates. Up to the end of the 17th century the number of guns and the compliment size was adjusted until the rating system was actually clarified. A 'Fourth Rate' was nominally a ship of over thirty guns with a complement of 140 men. In the rating system of the Royal Navy used to categorize sailing warships in the 18th century, a fourth-rate was a ship of the line with 46 to 60 guns mounted. They were phased out of ship of the line service during the French Revolutionary and Napoleonic Wars, as their usefulness was declining; though they were still in service, especially on distant stations such as the East Indies. ''Fourth-rates'' took many forms, initially as small two decked warships, later as lar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Full-rigged Ship
A full-rigged ship or fully rigged ship is a sailing vessel's sail plan with three or more masts, all of them square-rigged. A full-rigged ship is said to have a ship rig or be ship-rigged. Such vessels also have each mast stepped in three segments: lower mast, top mast, and topgallant mast. Other large, multi-masted sailing vessels may be regarded as ships while lacking one of the elements of a full-rigged ship, e.g. having one or more masts support only a fore-and-aft sail or having a mast that only has two segments. Masts The masts of a full-rigged ship, from bow to stern, are: * Foremast, which is the second tallest mast * Mainmast, the tallest * Mizzenmast, the third tallest * Jiggermast, which may not be present but will be fourth tallest if so If the masts are of wood, each mast is in three or more pieces. They are (in order, from bottom up): * The lowest piece is called the ''mast'' or the ''lower''. * Topmast * Topgallant mast * Royal mast, if fitted On steel-ma ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Parliament
In modern politics, and history, a parliament is a legislative body of government. Generally, a modern parliament has three functions: representing the electorate, making laws, and overseeing the government via hearings and inquiries. The term is similar to the idea of a senate, synod or congress and is commonly used in countries that are current or former monarchies. Some contexts restrict the use of the word ''parliament'' to parliamentary systems, although it is also used to describe the legislature in some presidential systems (e.g., the Parliament of Ghana), even where it is not in the official name. Historically, parliaments included various kinds of deliberative, consultative, and judicial assemblies, an example being the French medieval and early modern parlements. Etymology The English term is derived from Anglo-Norman and dates to the 14th century, coming from the 11th century Old French , "discussion, discourse", from , meaning "to talk". The meanin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
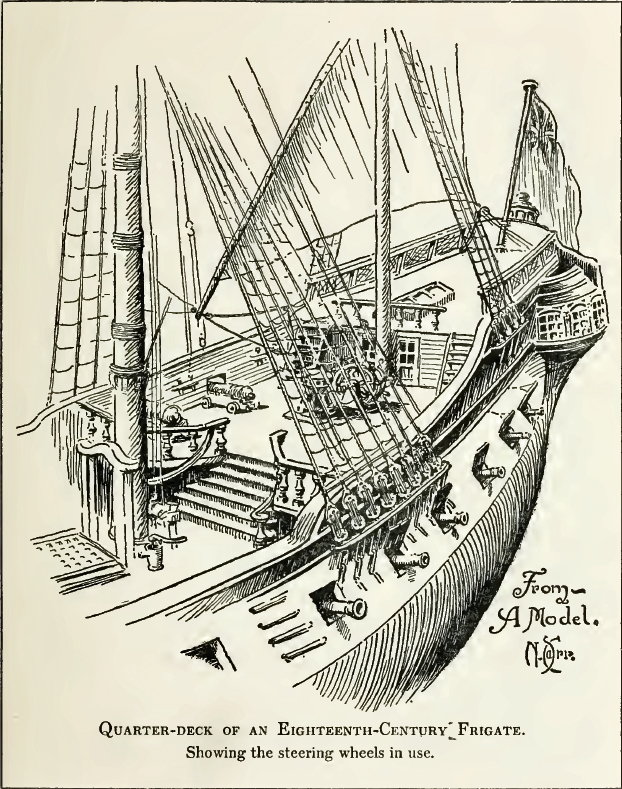
Quarterdeck
The quarterdeck is a raised deck behind the main mast of a sailing ship. Traditionally it was where the captain commanded his vessel and where the ship's colours were kept. This led to its use as the main ceremonial and reception area on board, and the word is still used to refer to such an area on a ship or even in naval establishments on land. Many such facilities have areas decorated like shipboard quarterdecks. In the 20th century the word came to be applied to the area at the stern of the ship, often (on naval vessels) used for secondary weapons and (on battleships) seaplane catapults. In modern military designs the stern has been roofed over by the helicopter deck but a large space remains underneath which is typically used for sonar equipment or small boats and which is still referred to as the quarterdeck in Commonwealth navies. Ceremonial use There are ancient traditions of offering special deference to the quarterdeck. Greek, Roman, and Carthaginian warships all ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chatham Dockyard
Chatham Dockyard was a Royal Navy Dockyard located on the River Medway in Kent. Established in Chatham in the mid-16th century, the dockyard subsequently expanded into neighbouring Gillingham (at its most extensive, in the early 20th century, two-thirds of the dockyard lay in Gillingham, one-third in Chatham). It came into existence at the time when, following the Reformation, relations with the Catholic countries of Europe had worsened, leading to a requirement for additional defences. Over 414 years Chatham Royal Dockyard provided more than 500 ships for the Royal Navy, and was at the forefront of shipbuilding, industrial and architectural technology. At its height, it employed over 10,000 skilled artisans and covered . Chatham dockyard closed in 1984, and of the Georgian dockyard is now managed as the Chatham Historic Dockyard visitor attraction by the Chatham Historic Dockyard Trust. Overview Joseph Farington (1747-1821) was commissioned by the Navy Board to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Woolwich Dockyard
Woolwich Dockyard (formally H.M. Dockyard, Woolwich, also known as The King's Yard, Woolwich) was an English naval dockyard along the river Thames at Woolwich in north-west Kent, where many ships were built from the early 16th century until the late 19th century. William Camden called it 'the Mother Dock of all England'. By virtue of the size and quantity of vessels built there, Woolwich Dockyard is described as having been 'among the most important shipyards of seventeenth-century Europe'. During the Age of Sail, the yard continued to be used for shipbuilding and repair work more or less consistently; in the 1830s a specialist factory within the dockyard oversaw the introduction of steam power for ships of the Royal Navy. At its largest extent it filled a 56-acre site north of Woolwich Church Street, between Warspite Road and New Ferry Approach; 19th-century naval vessels were fast outgrowing the yard, however, and it eventually closed in 1869 (though a large part of the si ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Frigates Of The Royal Navy
A frigate () is a type of warship. In different eras, the roles and capabilities of ships classified as frigates have varied somewhat. The name frigate in the 17th to early 18th centuries was given to any full-rigged ship built for speed and maneuverability, intended to be used in scouting, escort and patrol roles. The term was applied loosely to ships varying greatly in design. In the second quarter of the 18th century, the 'true frigate' was developed in France. This type of vessel was characterised by possessing only one armed deck, with an unarmed deck below it used for berthing the crew. Late in the 19th century (British and French prototypes were constructed in 1858), armoured frigates were developed as powerful ironclad warships, the term frigate was used because of their single gun deck. Later developments in ironclad ships rendered the frigate designation obsolete and the term fell out of favour. During the Second World War the name 'frigate' was reintroduced to de ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |


_-_02.jpg)