|
1614 In England
Events from the 1610s in England. Incumbents * Monarch – James I * Parliament – Blessed (until 9 February 1611), Addled (starting 5 April, until 7 June 1614) Events * 1610 ** 9 February – Parliament assembles and debates the Great Contract proposed by Robert Cecil whereby in return for an annual grant of £200,000, the Crown should give up its feudal rights of Wardship and Purveyance, as well as New Impositions. ** 23 May – the House of Commons petitions King James I against imposed duties. ** 9 July – Arbella Stuart, a claimant to the throne, imprisoned for marrying William Seymour, 2nd Duke of Somerset, another claimant, on 22 June. ** 23 July – Parliament prorogued. ** 3 August – Henry Hudson leads an expedition to Hudson Bay. ** 20 September – Case of Proclamations rules that the monarch cannot make decisions by proclamation unsupported by legislation. ** 16 October – Parliament assembles. ** 6 December – Parliament prorogued and does not assemble again u ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Flag Of England
The flag of England is the national flag of England, a constituent country of the United Kingdom. It is derived from Saint George's Cross (heraldic blazon: ''Argent, a cross gules''). The association of the red cross as an emblem of England can be traced back to the Late Middle Ages when it was gradually, increasingly, used alongside the Royal Banner. It became the only saint's flag permitted to be flown in public as part of the English Reformation and at a similar time became the pre-eminent maritime flag referred to as a white ensign. It was used as a component in the design of the Union Jack in 1606. It has been widely used since the 1990s, specifically at national sporting events, especially during the campaigns of England's national football teams. Origins In 1188 Henry II of England and Philip II of France agreed to go on a crusade, and that Henry would use a white cross and Philip a red cross. Thirteenth-century authorities are unanimous on this reversal to the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
New Impositions
The Crown of England traditionally exercised the right to impose import duties for the regulation of trade and the protection of domestic industry. New impositions of this kind were imposed by Elizabeth I on currants and tobacco (1601) and extended by King James I to most imports (1608) after a favourable ruling in Bates' Case (1606). John Bates was a merchant from the Levant Company who refused to pay the import duty on currants; this was taken to the Court of the Exchequer, where he lost, and so impositions were extended giving the treasury a "windfall". In the face of Parliament's angry protests in 1610, the tax was amended to ensure that the greatest impact fell on foreign merchants.''The Stuart Age, 1603–1714'', by John Wroughton. Pages 151–152 Impositions were among the prerogative rights that King James I was to give up under the Great Contract of 1610, as drawn up by Lord Treasurer Robert Cecil, then Lord Salisbury, in return for an immediate sum to pay off Royal d ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
English Reformation
The English Reformation took place in 16th-century England when the Church of England broke away from the authority of the pope and the Catholic Church. These events were part of the wider European Protestant Reformation, a religious and political movement that affected the practice of Christianity in Western Europe, Western and Central Europe. Ideologically, the groundwork for the Reformation was laid by Renaissance humanism, Renaissance humanists who believed that the Bible, Scriptures were the only source of Christian faith and criticized religious practices which they considered superstitious. By 1520, Martin Luther, Martin Luther's new ideas were known and debated in England, but Protestants were a religious minority and heretics under the law. The English Reformation began as more of a political affair than a theological dispute. In 1527, Henry VIII requested an annulment of his marriage, but Pope Clement VII refused. In response, the English Reformation Parliament, Refo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hatfield House
Hatfield House is a country house set in a large park, the Great Park, on the eastern side of the town of Hatfield, Hertfordshire, England. The present Jacobean house, a leading example of the prodigy house, was built in 1611 by Robert Cecil, 1st Earl of Salisbury and Chief Minister to King James I. It is a prime example of Jacobean architecture. The estate includes extensive grounds and surviving parts of an earlier palace. The house is currently the home of Robert Gascoyne-Cecil, 7th Marquess of Salisbury. It is open to the public. History An earlier building on the site was the Royal Palace of Hatfield. Only part of this still exists a short distance from the present house. That palace was the childhood home and favourite residence of Queen Elizabeth I. Built in 1497 by the Archbishop of Canterbury (formerly Bishop of Ely), King Henry VII's minister, John Cardinal Morton, it comprised four wings in a square surrounding a central courtyard. The palace was seized by He ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Stained Glass
Stained glass is coloured glass as a material or works created from it. Throughout its thousand-year history, the term has been applied almost exclusively to the windows of churches and other significant religious buildings. Although traditionally made in flat panels and used as windows, the creations of modern stained glass artists also include three-dimensional structures and sculpture. Modern vernacular usage has often extended the term "stained glass" to include domestic lead light and ''objets d'art'' created from foil glasswork exemplified in the famous lamps of Louis Comfort Tiffany. As a material ''stained glass'' is glass that has been coloured by adding metallic salts during its manufacture, and usually then further decorating it in various ways. The coloured glass is crafted into ''stained glass windows'' in which small pieces of glass are arranged to form patterns or pictures, held together (traditionally) by strips of lead and supported by a rigid frame. Painte ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Common Law
In law, common law (also known as judicial precedent, judge-made law, or case law) is the body of law created by judges and similar quasi-judicial tribunals by virtue of being stated in written opinions."The common law is not a brooding omnipresence in the sky, but the articulate voice of some sovereign or quasi sovereign that can be identified," ''Southern Pacific Company v. Jensen'', 244 U.S. 205, 222 (1917) (Oliver Wendell Holmes, dissenting). By the early 20th century, legal professionals had come to reject any idea of a higher or natural law, or a law above the law. The law arises through the act of a sovereign, whether that sovereign speaks through a legislature, executive, or judicial officer. The defining characteristic of common law is that it arises as precedent. Common law courts look to the past decisions of courts to synthesize the legal principles of past cases. '' Stare decisis'', the principle that cases should be decided according to consistent principled rules so ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sunspot
Sunspots are phenomena on the Sun's photosphere that appear as temporary spots that are darker than the surrounding areas. They are regions of reduced surface temperature caused by concentrations of magnetic flux that inhibit convection. Sunspots appear within active regions, usually in pairs of opposite magnetic polarity. Their number varies according to the approximately 11-year solar cycle. Individual sunspots or groups of sunspots may last anywhere from a few days to a few months, but eventually decay. Sunspots expand and contract as they move across the surface of the Sun, with diameters ranging from to . Larger sunspots can be visible from Earth without the aid of a telescope. They may travel at relative speeds, or proper motions, of a few hundred meters per second when they first emerge. Indicating intense magnetic activity, sunspots accompany other active region phenomena such as coronal loops, prominences, and reconnection events. Most solar flares and coronal mas ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Thomas Harriot
Thomas Harriot (; – 2 July 1621), also spelled Harriott, Hariot or Heriot, was an English astronomer, mathematician, ethnographer and translator to whom the theory of refraction is attributed. Thomas Harriot was also recognized for his contributions in navigational techniques, working closely with John White to create advanced maps for navigation. While Harriot worked extensively on numerous papers on the subjects of astronomy, mathematics and navigation, he remains obscure because he published little of it, namely only ''The Briefe and True Report of the New Found Land of Virginia'' (1588). This book includes descriptions of English settlements and financial issues in Virginia at the time. He is sometimes credited with the introduction of the potato to the British Isles. Harriot was the first person to make a drawing of the Moon through a telescope, on 5 August 1609, about four months before Galileo Galilei. After graduating from St Mary Hall, Oxford, Harriot traveled to t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Case Of Proclamations
The ''Case of Proclamations'' English constitutional law case during the reign of King James I">UK constitutional law">English constitutional law case during the reign of King James I (1603–1625) which defined some limitations on the Royal Prerogative at that time. Principally, it established that the Monarch could make laws only through Parliament. The judgment began to set out the principle in English law (later developed by future Parliament of the United Kingdom, parliaments and other members of the judiciary in subsequent cases, for example '' Dr. Bonham's Case'') that when a case involving an alleged exercise of prerogative power came before the courts, the courts could determine: * whether the proclaimed prerogative existed in law and how far it extended; * whether it had been limited by statute, and if so, in what way; and * whether there was any requirement that the Crown pay compensation after the exercise of the prerogative. Facts Tudor monarchs believed that they ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
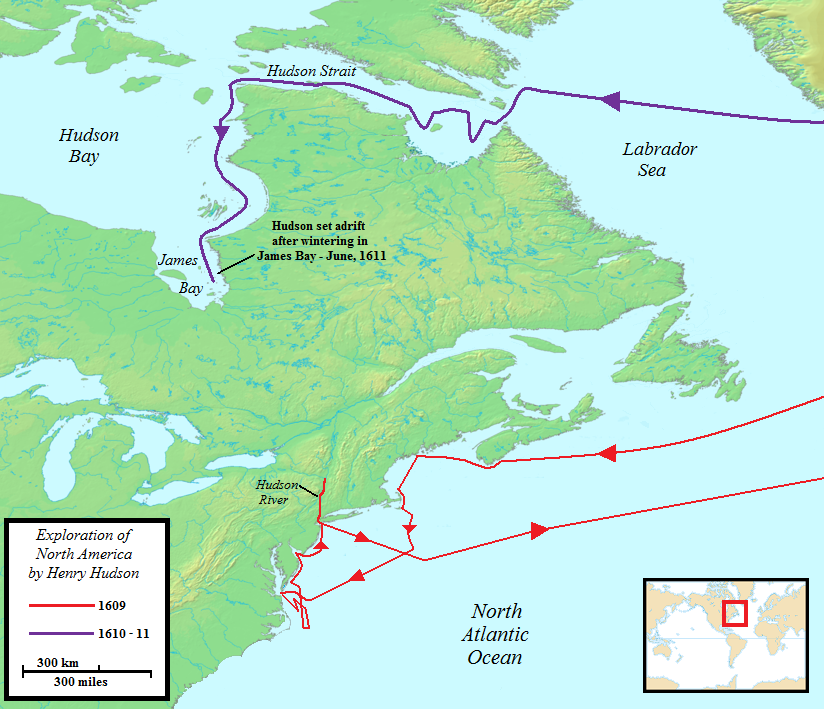
Hudson Bay
Hudson Bay ( crj, text=ᐐᓂᐯᒄ, translit=Wînipekw; crl, text=ᐐᓂᐹᒄ, translit=Wînipâkw; iu, text=ᑲᖏᖅᓱᐊᓗᒃ ᐃᓗᐊ, translit=Kangiqsualuk ilua or iu, text=ᑕᓯᐅᔭᕐᔪᐊᖅ, translit=Tasiujarjuaq; french: baie d'Hudson), sometimes called Hudson's Bay (usually historically), is a large body of saltwater in northeastern Canada with a surface area of . It is located north of Ontario, west of Quebec, northeast of Manitoba and southeast of Nunavut, but politically entirely part of Nunavut. Although not geographically apparent, it is for climatic reasons considered to be a marginal sea of the Arctic Ocean. It Hudson Bay drainage basin, drains a very large area, about , that includes parts of southeastern Nunavut, Alberta, Saskatchewan, Ontario, Quebec, all of Manitoba, and parts of the U.S. states of North Dakota, South Dakota, Minnesota, and Montana. Hudson Bay's southern arm is called James Bay. The Cree language, Eastern Cree name for Hudson an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Henry Hudson
Henry Hudson ( 1565 – disappeared 23 June 1611) was an English sea explorer and navigator during the early 17th century, best known for his explorations of present-day Canada and parts of the northeastern United States. In 1607 and 1608, Hudson made two attempts on behalf of English merchants to find a rumoured Northeast Passage to Cathay via a route above the Arctic Circle. In 1609, he landed in North America on behalf of the Dutch East India Company and explored the region around the modern New York metropolitan area. Looking for a Northwest Passage to Asia on his ship ''Halve Maen'' ("Half Moon"), he sailed up the Hudson River, which was later named after him, and thereby laid the foundation for Dutch colonization of the region. On his final expedition, while still searching for the Northwest Passage, Hudson became the first European to see Hudson Strait and the immense Hudson Bay. In 1611, after wintering on the shore of James Bay, Hudson wanted to press on to t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
William Seymour, 2nd Duke Of Somerset
William Seymour, 2nd Duke of Somerset, (158824 October 1660) was an English nobleman and Royalist commander in the English Civil War. Origins Seymour was the son of Edward Seymour, Lord Beauchamp (who predeceased his own father) by his wife Honora Rogers. He was the grandson of Edward Seymour, 1st Earl of Hertford, by his wife Lady Katherine Grey, a sister of Lady Jane Grey, "The Nine Days Queen", which thus gave him a distant claim to the throne through Katherine's descent from Mary Tudor, younger sister of King Henry VIII. He was the great-grandson of Edward Seymour, 1st Duke of Somerset (c. 1500–1552), the uncle of King Edward VI and Lord Protector of England. Life Seymour made a secret marriage at Greenwich on 22 June 1610 to Arbella Stuart (died 1615), daughter of Charles Stuart, 1st Earl of Lennox and Elizabeth Cavendish. Arbella was thirteen years his senior, and King James I disapproved of the marriage as the union of two potential Tudor pretenders to the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |




.png)
_2007-04-30_T001456.gif)
%2C_Attributed_to_Gilbert_Jackson_(1622_-_1640).jpg)