|
1537 In Science
The year 1537 in science and technology included many events, some of which are listed here. Mathematics * Niccolò Fontana Tartaglia publishes ''La Nova Scientia'' in Venice, applying mathematics to the study of ballistics. * Pedro Nunes publishes several treatises on navigation: ''Tratado em defensam da carta de marear'', ''Tratado sobre certas dúvidas da navegação'' (including discussion of a rhumb line course) and ''Tratado da sphera com a Theorica do Sol e da Lua''. * The first known complete English language arithmetic book, ''An Introduction for to Lerne to Recken with the Pen and with the Counters after the True Cast of Arsmetyke or Awgrym'', an anonymous translation of Luca Pacioli's '' Summa de arithmetica, geometria, proportioni et proportionalità'' (Venice, 1494), is published at St Albans St Albans () is a cathedral city in Hertfordshire, England, east of Hemel Hempstead and west of Hatfield, Hertfordshire, Hatfield, north-west of London, south-west of We ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Science
Science is a systematic endeavor that builds and organizes knowledge in the form of testable explanations and predictions about the universe. Science may be as old as the human species, and some of the earliest archeological evidence for scientific reasoning is tens of thousands of years old. The earliest written records in the history of science come from Ancient Egypt and Mesopotamia in around 3000 to 1200 BCE. Their contributions to mathematics, astronomy, and medicine entered and shaped Greek natural philosophy of classical antiquity, whereby formal attempts were made to provide explanations of events in the physical world based on natural causes. After the fall of the Western Roman Empire, knowledge of Greek conceptions of the world deteriorated in Western Europe during the early centuries (400 to 1000 CE) of the Middle Ages, but was preserved in the Muslim world during the Islamic Golden Age and later by the efforts of Byzantine Greek scholars who brought Greek ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Technology
Technology is the application of knowledge to reach practical goals in a specifiable and reproducible way. The word ''technology'' may also mean the product of such an endeavor. The use of technology is widely prevalent in medicine, science, industry, communication, transportation, and daily life. Technologies include physical objects like utensils or machines and intangible tools such as software. Many technological advancements have led to societal changes. The earliest known technology is the stone tool, used in the prehistoric era, followed by fire use, which contributed to the growth of the human brain and the development of language in the Ice Age. The invention of the wheel in the Bronze Age enabled wider travel and the creation of more complex machines. Recent technological developments, including the printing press, the telephone, and the Internet have lowered communication barriers and ushered in the knowledge economy. While technology contributes to econom ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Niccolò Fontana Tartaglia
Niccolò Fontana Tartaglia (; 1499/1500 – 13 December 1557) was an Italian mathematician, engineer (designing fortifications), a surveyor (of topography, seeking the best means of defense or offense) and a bookkeeper from the then Republic of Venice. He published many books, including the first Italian translations of Archimedes and Euclid, and an acclaimed compilation of mathematics. Tartaglia was the first to apply mathematics to the investigation of the paths of cannonballs, known as ballistics, in his ''Nova Scientia'' (''A New Science'', 1537); his work was later partially validated and partially superseded by Galileo's studies on falling bodies. He also published a treatise on retrieving sunken ships. Personal life Niccolò Fontana was born in Brescia, the son of Michele Fontana, a dispatch rider who travelled to neighbouring towns to deliver mail. In 1506, Michele was murdered by robbers, and Niccolò, his two siblings, and his mother were left impoverished. Niccol� ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Venice
Venice ( ; it, Venezia ; vec, Venesia or ) is a city in northeastern Italy and the capital of the Veneto Regions of Italy, region. It is built on a group of 118 small islands that are separated by canals and linked by over 400 bridges. The islands are in the shallow Venetian Lagoon, an enclosed bay lying between the mouths of the Po River, Po and the Piave River, Piave rivers (more exactly between the Brenta (river), Brenta and the Sile (river), Sile). In 2020, around 258,685 people resided in greater Venice or the ''Comune di Venezia'', of whom around 55,000 live in the historical island city of Venice (''centro storico'') and the rest on the mainland (''terraferma''). Together with the cities of Padua, Italy, Padua and Treviso, Italy, Treviso, Venice is included in the Padua-Treviso-Venice Metropolitan Area (PATREVE), which is considered a statistical metropolitan area, with a total population of 2.6 million. The name is derived from the ancient Adri ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ballistics
Ballistics is the field of mechanics concerned with the launching, flight behaviour and impact effects of projectiles, especially ranged weapon munitions such as bullets, unguided bombs, rockets or the like; the science or art of designing and accelerating projectiles so as to achieve a desired performance. A ballistic body is a free-moving body with momentum which can be subject to forces such as the forces exerted by pressurized gases from a gun barrel or a propelling nozzle, normal force by rifling, and gravity and air drag during flight. A ballistic missile is a missile that is guided only during the relatively brief initial phase of powered flight and the trajectory is subsequently governed by the laws of classical mechanics; in contrast to (for example) a cruise missile which is aerodynamically guided in powered flight like a fixed-wing aircraft. History and prehistory The earliest known ballistic projectiles were stones and spears, and the throwing stick. The oldes ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pedro Nunes
Pedro Nunes (; Latin: ''Petrus Nonius''; 1502 – 11 August 1578) was a Portuguese mathematician, cosmographer, and professor, from a New Christian (of Jewish origin) family. Considered one of the greatest mathematicians of his time, Nunes is best known for his contributions to the nautical sciences (navigation and cartography), which he approached, for the first time, in a mathematical way. He was the first to propose the idea of a loxodrome, and was the inventor of several measuring devices, including the nonius (from which Vernier scale was derived), named after his Latin surname. Life Little is known about Nunes' early education, life or family background, only that he was born in Alcácer do Sal, his origins are Jewish and that his grandchildren spent a few years behind bars after they were accused by the Portuguese Inquisition of professing and secretly practicing Judaism. He studied at the University of Salamanca, maybe from 1521 until 1522, and at the University o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Navigation
Navigation is a field of study that focuses on the process of monitoring and controlling the movement of a craft or vehicle from one place to another.Bowditch, 2003:799. The field of navigation includes four general categories: land navigation, marine navigation, aeronautic navigation, and space navigation. It is also the term of art used for the specialized knowledge used by navigators to perform navigation tasks. All navigational techniques involve locating the navigator's position compared to known locations or patterns. Navigation, in a broader sense, can refer to any skill or study that involves the determination of position and direction. In this sense, navigation includes orienteering and pedestrian navigation. History In the European medieval period, navigation was considered part of the set of '' seven mechanical arts'', none of which were used for long voyages across open ocean. Polynesian navigation is probably the earliest form of open-ocean navigation; it was ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
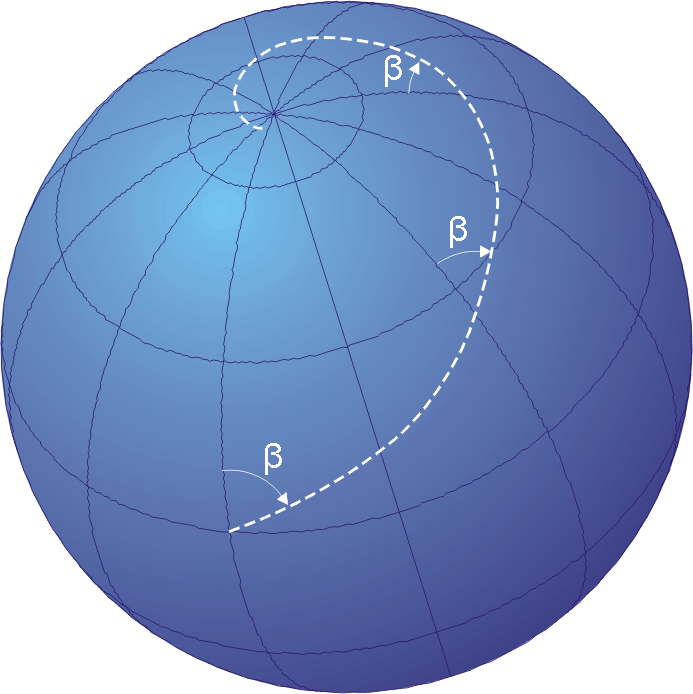
Rhumb Line
In navigation, a rhumb line, rhumb (), or loxodrome is an arc crossing all meridians of longitude at the same angle, that is, a path with constant bearing as measured relative to true north. Introduction The effect of following a rhumb line course on the surface of a globe was first discussed by the Portuguese mathematician Pedro Nunes in 1537, in his ''Treatise in Defense of the Marine Chart'', with further mathematical development by Thomas Harriot in the 1590s. A rhumb line can be contrasted with a great circle, which is the path of shortest distance between two points on the surface of a sphere. On a great circle, the bearing to the destination point does not remain constant. If one were to drive a car along a great circle one would hold the steering wheel fixed, but to follow a rhumb line one would have to turn the wheel, turning it more sharply as the poles are approached. In other words, a great circle is locally "straight" with zero geodesic curvature, whereas a r ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Arithmetic
Arithmetic () is an elementary part of mathematics that consists of the study of the properties of the traditional operations on numbers— addition, subtraction, multiplication, division, exponentiation, and extraction of roots. In the 19th century, Italian mathematician Giuseppe Peano formalized arithmetic with his Peano axioms, which are highly important to the field of mathematical logic today. History The prehistory of arithmetic is limited to a small number of artifacts, which may indicate the conception of addition and subtraction, the best-known being the Ishango bone from central Africa, dating from somewhere between 20,000 and 18,000 BC, although its interpretation is disputed. The earliest written records indicate the Egyptians and Babylonians used all the elementary arithmetic operations: addition, subtraction, multiplication, and division, as early as 2000 BC. These artifacts do not always reveal the specific process used for solving problems, but t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Luca Pacioli
Fra Luca Bartolomeo de Pacioli (sometimes ''Paccioli'' or ''Paciolo''; 1447 – 19 June 1517) was an Italian mathematician, Franciscan friar, collaborator with Leonardo da Vinci, and an early contributor to the field now known as accounting. He is referred to as the father of accounting and bookkeeping and he was the first person to publish a work on the double-entry system of book-keeping on the continent. He was also called Luca di Borgo after his birthplace, Borgo Sansepolcro, Tuscany. Several of his works were plagiarised from Piero della Francesca, in what has been called "probably the first full-blown case of plagiarism in the history of mathematics". Life Luca Pacioli was born between 1446 and 1448 in the Tuscan town of Sansepolcro where he received an abbaco education. This was education in the vernacular (''i.e.'', the local tongue) rather than Latin and focused on the knowledge required of merchants. His father was Bartolomeo Pacioli; however, Luca Pacioli was ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Summa De Arithmetica
' (''Summary of arithmetic, geometry, proportions and proportionality'') is a book on mathematics written by Luca Pacioli and first published in 1494. It contains a comprehensive summary of Renaissance mathematics, including practical arithmetic, basic algebra, basic geometry and accounting, written for use as a textbook and reference work. Written in vernacular Italian, the ''Summa'' is the first printed work on algebra, and it contains the first published description of the double-entry bookkeeping system. It set a new standard for writing and argumentation about algebra, and its impact upon the subsequent development and standardization of professional accounting methods was so great that Pacioli is sometimes referred to as the "father of accounting". Contents The ''Summa de arithmetica'' as originally printed consists of ten chapters on a series of mathematical topics, collectively covering essentially all of Renaissance mathematics. The first seven chapters form a summary ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |


.jpg)