|
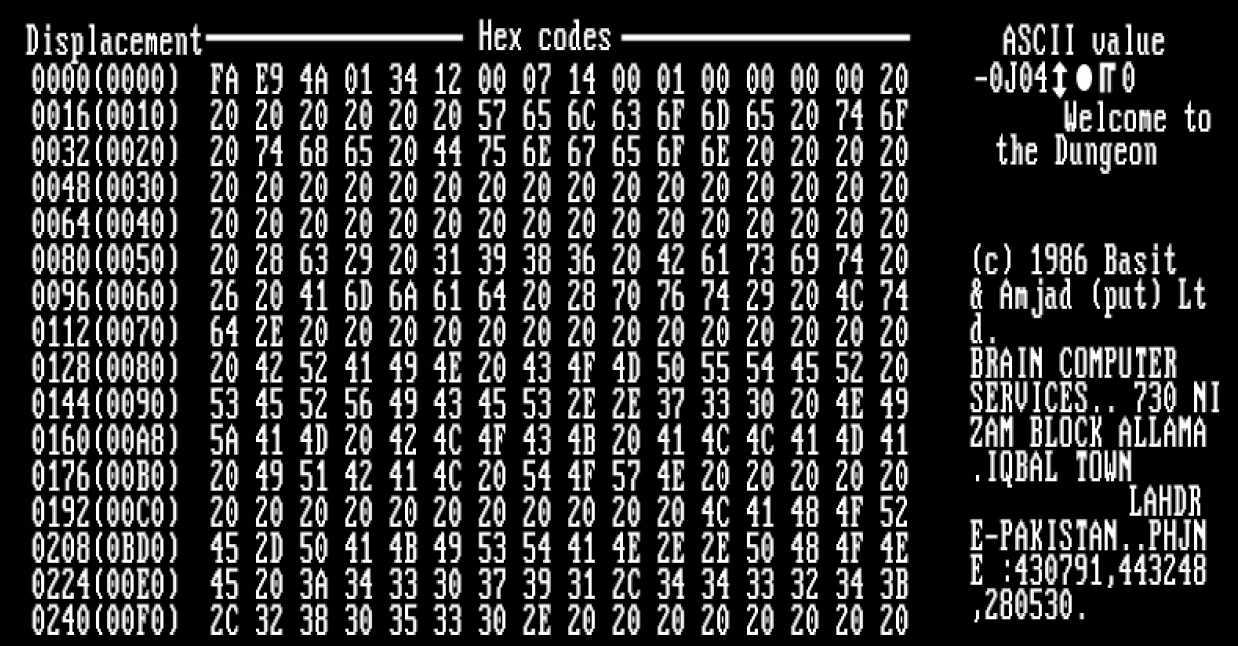
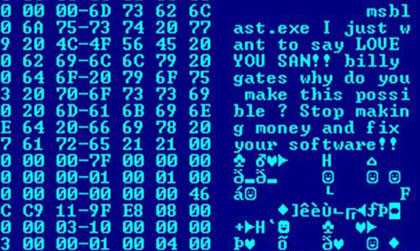
1260 (computer Virus)
1260, or V2PX, was a polymorphic computer virus written in 1990 by Mark Washburn. Derived from Ralf Burger's publication of the disassembled Vienna Virus source code, the 1260 added a cipher and varied its signature by randomizing its decryption algorithm. Both the 1260 and Vienna infect .COM files in the current or PATH directories upon execution. Changing an authenticated executable file is detected by most modern computer operating system An operating system (OS) is system software that manages computer hardware and software resources, and provides common daemon (computing), services for computer programs. Time-sharing operating systems scheduler (computing), schedule tasks for ...s. article. References {{Hacking in the 1980s[...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Computer Virus
A computer virus is a type of malware that, when executed, replicates itself by modifying other computer programs and Code injection, inserting its own Computer language, code into those programs. If this replication succeeds, the affected areas are then said to be "infected" with a computer virus, a metaphor derived from biological viruses. Computer viruses generally require a Computer program, host program. The virus writes its own code into the host program. When the program runs, the written virus program is executed first, causing infection and damage. By contrast, a computer worm does not need a host program, as it is an independent program or code chunk. Therefore, it is not restricted by the Computer program, host program, but can run independently and actively carry out attacks. Virus writers use social engineering (security), social engineering deceptions and exploit detailed knowledge of vulnerability (computing), security vulnerabilities to initially infect systems an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Polymorphic Code
In computing, polymorphic code is code that uses a polymorphic engine to mutate while keeping the original algorithm intact - that is, the ''code'' changes itself every time it runs, but the ''function'' of the code (its semantics) stays the same. For example, the simple math expressions 3+1 and 6-2 both achieve the same result, yet run with different machine code in a CPU. This technique is sometimes used by computer viruses, shellcodes and computer worms to hide their presence. Encryption is the most common method to hide code. With encryption, the main body of the code (also called its payload) is encrypted and will appear meaningless. For the code to function as before, a decryption function is added to the code. When the code is ''executed'', this function reads the payload and decrypts it before executing it in turn. Encryption alone is not polymorphism. To gain polymorphic behavior, the encryptor/decryptor pair is mutated with each copy of the code. This allows differen ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Computer Virus
A computer virus is a type of malware that, when executed, replicates itself by modifying other computer programs and Code injection, inserting its own Computer language, code into those programs. If this replication succeeds, the affected areas are then said to be "infected" with a computer virus, a metaphor derived from biological viruses. Computer viruses generally require a Computer program, host program. The virus writes its own code into the host program. When the program runs, the written virus program is executed first, causing infection and damage. By contrast, a computer worm does not need a host program, as it is an independent program or code chunk. Therefore, it is not restricted by the Computer program, host program, but can run independently and actively carry out attacks. Virus writers use social engineering (security), social engineering deceptions and exploit detailed knowledge of vulnerability (computing), security vulnerabilities to initially infect systems an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Reverse Engineering
Reverse engineering (also known as backwards engineering or back engineering) is a process or method through which one attempts to understand through deductive reasoning how a previously made device, process, system, or piece of software accomplishes a task with very little (if any) insight into exactly how it does so. Depending on the system under consideration and the technologies employed, the knowledge gained during reverse engineering can help with repurposing obsolete objects, doing security analysis, or learning how something works. Although the process is specific to the object on which it is being performed, all reverse engineering processes consist of three basic steps: information extraction, modeling, and review. Information extraction is the practice of gathering all relevant information for performing the operation. Modeling is the practice of combining the gathered information into an abstract model, which can be used as a guide for designing the new object or syst ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vienna Virus
This timeline of computer viruses and worms presents a chronological timeline of noteworthy computer viruses, computer worms, Trojan horses, similar malware, related research and events. 1960s * John von Neumann's article on the "Theory of self-reproducing automata" is published in 1966. The article is based on lectures given by von Neumann at the University of Illinois about the "Theory and Organization of Complicated Automata" in 1949. 1970s 1970 * The first story written about a computer virus, ''The Scarred Man'' by Gregory Benford, was published in the May 1970 issue of ''Venture Science Fiction''. 1971 * The Creeper system, an experimental self-replicating program, is written by Bob Thomas at BBN Technologies to test John von Neumann's theory. Creeper infected DEC PDP-10 computers running the TENEX operating system. Creeper gained access via the ARPANET and copied itself to the remote system where the message "I'm the creeper, catch me if you can!" was displ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Source Code
In computing, source code, or simply code or source, is a plain text computer program written in a programming language. A programmer writes the human readable source code to control the behavior of a computer. Since a computer, at base, only understands machine code, source code must be Translator (computing), translated before a computer can Execution (computing), execute it. The translation process can be implemented three ways. Source code can be converted into machine code by a compiler or an assembler (computing), assembler. The resulting executable is machine code ready for the computer. Alternatively, source code can be executed without conversion via an interpreter (computing), interpreter. An interpreter loads the source code into memory. It simultaneously translates and executes each statement (computer science), statement. A method that combines compilation and interpretation is to first produce bytecode. Bytecode is an intermediate representation of source code tha ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cipher
In cryptography, a cipher (or cypher) is an algorithm for performing encryption or decryption—a series of well-defined steps that can be followed as a procedure. An alternative, less common term is ''encipherment''. To encipher or encode is to convert information into cipher or code. In common parlance, "cipher" is synonymous with "code (cryptography), code", as they are both a set of steps that encrypt a message; however, the concepts are distinct in cryptography, especially classical cryptography. Codes generally substitute different length strings of characters in the output, while ciphers generally substitute the same number of characters as are input. A code maps one meaning with another. Words and phrases can be coded as letters or numbers. Codes typically have direct meaning from input to key. Codes primarily function to save time. Ciphers are algorithmic. The given input must follow the cipher's process to be solved. Ciphers are commonly used to encrypt written info ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Antivirus Software
Antivirus software (abbreviated to AV software), also known as anti-malware, is a computer program used to prevent, detect, and remove malware. Antivirus software was originally developed to detect and remove computer viruses, hence the name. However, with the proliferation of other malware, antivirus software started to protect against other computer threats. Some products also include protection from malicious URLs, spam, and phishing. History 1971–1980 period (pre-antivirus days) The first known computer virus appeared in 1971 and was dubbed the " Creeper virus". This computer virus infected Digital Equipment Corporation's ( DEC) PDP-10 mainframe computers running the TENEX operating system.From the first email to the first YouTube video: a d ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Randomization
Randomization is a statistical process in which a random mechanism is employed to select a sample from a population or assign subjects to different groups.Oxford English Dictionary "randomization" The process is crucial in ensuring the random allocation of experimental units or treatment protocols, thereby minimizing selection bias and enhancing the Validity (statistics), statistical validity. It facilitates the objective comparison of treatment effects in Design of experiments, experimental design, as it equates groups statistically by balancing both known and unknown factors at the outset of the study. In statistical terms, it underpins the principle of probabilistic equivalence among groups, allowing for the unbiased estimation of treatment effects and the generalizability of conclusions drawn from sample data to the broader population. Randomization is not haphazard; instead, a stochastic process, random process is a sequence of random variables describing a process whose outcom ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Decryption
In cryptography, encryption (more specifically, encoding) is the process of transforming information in a way that, ideally, only authorized parties can decode. This process converts the original representation of the information, known as plaintext, into an alternative form known as ciphertext. Despite its goal, encryption does not itself prevent interference but denies the intelligible content to a would-be interceptor. For technical reasons, an encryption scheme usually uses a pseudo-random encryption key generated by an algorithm. It is possible to decrypt the message without possessing the key but, for a well-designed encryption scheme, considerable computational resources and skills are required. An authorized recipient can easily decrypt the message with the key provided by the originator to recipients but not to unauthorized users. Historically, various forms of encryption have been used to aid in cryptography. Early encryption techniques were often used in military m ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Algorithm
In mathematics and computer science, an algorithm () is a finite sequence of Rigour#Mathematics, mathematically rigorous instructions, typically used to solve a class of specific Computational problem, problems or to perform a computation. Algorithms are used as specifications for performing calculations and data processing. More advanced algorithms can use Conditional (computer programming), conditionals to divert the code execution through various routes (referred to as automated decision-making) and deduce valid inferences (referred to as automated reasoning). In contrast, a Heuristic (computer science), heuristic is an approach to solving problems without well-defined correct or optimal results.David A. Grossman, Ophir Frieder, ''Information Retrieval: Algorithms and Heuristics'', 2nd edition, 2004, For example, although social media recommender systems are commonly called "algorithms", they actually rely on heuristics as there is no truly "correct" recommendation. As an e ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
PATH (variable)
PATH is an environment variable on Unix-like operating systems, DOS, OS/2, and Microsoft Windows, specifying a set of directories where executable programs are located. In general, each executing process or user session has its own PATH setting. History Multics originated the idea of a search path. The early Unix shell only looked for program names in /bin, but by Version 3 Unix the directory was too large and /usr/bin, and a search path, became part of the operating system. Unix and Unix-like On POSIX and Unix-like operating systems, the $PATH variable is specified as a list of one or more directory names separated by colon (:) characters. Directories in the PATH-string are not meant to be escaped, making it impossible to have directories with : in their name. The /bin, /usr/bin, and /usr/local/bin directories are typically included in most users' $PATH setting (although this varies from implementation to implementation). The superuser also typically has /sbin and /usr/sbin en ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |