|
11th Strategic Group
The 11th Wing is a United States Air Force unit assigned to the Air Force District of Washington. It is the host unit at Joint Base Anacostia-Bolling in Washington, D.C. on from June 2020. It previously was stationed at Joint Base Andrews, Maryland where it was the host unit. The 11th Wing was one of the largest wings in the Air Force. It is known as "The Chief's Own", an honorific originally intended to reflect that the Chief of Staff of the United States Air Force personally created the organization. The 11th Wing traces its roots back to the 11th Observation Group which was established on 1 October 1933, but not activated. The group was redesignated as the 11 Bombardment Group (Medium) on 1 January 1938, although not activated until 1 February 1940. Later that year it became a heavy bombardment unit. The group fought in combat in the Pacific Theater of Operations with Boeing B-17 Flying Fortresses and Consolidated B-24 Liberators. The 11th Bombardment Group earned a Navy Pr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
United States Air Force
The United States Air Force (USAF) is the air service branch of the United States Armed Forces, and is one of the eight uniformed services of the United States. Originally created on 1 August 1907, as a part of the United States Army Signal Corps, the USAF was established as a separate branch of the United States Armed Forces in 1947 with the enactment of the National Security Act of 1947. It is the second youngest branch of the United States Armed Forces and the fourth in order of precedence. The United States Air Force articulates its core missions as air supremacy, global integrated intelligence, surveillance and reconnaissance, rapid global mobility, global strike, and command and control. The United States Air Force is a military service branch organized within the Department of the Air Force, one of the three military departments of the Department of Defense. The Air Force through the Department of the Air Force is headed by the civilian Secretary of the Air Force ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
RAF Fairford
Royal Air Force Fairford or more simply RAF Fairford is a Royal Air Force (RAF) station in Gloucestershire, England which is currently a standby airfield and therefore not in everyday use. Its most prominent use in recent years has been as an airfield for United States Air Force B-52s during the 2003 Iraq War, Operation Allied Force in 1999, and the first Gulf War in 1991. It is the US Air Force's only European airfield for heavy bombers. RAF Fairford was the only TransOceanic Abort Landing site for NASA's Space Shuttle in the UK. As well as having a sufficiently long runway for a shuttle landing (the runway is long), it also had NASA-trained fire and medical crews stationed on the airfield. The runway is rated with an unrestricted load-bearing capacity, meaning that it can support any aircraft with any type of load. RAF Fairford is also the home of the Royal International Air Tattoo (RIAT), an annual air display. RIAT is one of the largest airshows in the world, with the 2 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
B-18 Bolo
The Douglas B-18 Bolo is an American heavy bomber which served with the United States Army Air Corps and the Royal Canadian Air Force (as the Digby) during the late 1930s and early 1940s. The Bolo was developed by the Douglas Aircraft Company from their DC-2, to replace the Martin B-10. By 1940 standards, it was slow, had an inadequate defensive armament, and carried too small a bomb load. A B-18 was one of the first USAAF aircraft to sink a German U-boat, on 22 August 1942 in the Caribbean. By 1942, surviving B-18s were relegated to antisubmarine, training and transport duties. Design and development In 1934, the United States Army Air Corps requested for a twin-engine heavy bomber with double the bomb load and range of the Martin B-10 then entering service. During the evaluation at Wright Field the following year, Douglas offered its DB-1. It was competing against the Boeing Model 299 (later developed into the Boeing B-17 Flying Fortress) and Martin 146. While the Boeing de ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Seventh Air Force
The Seventh Air Force (Air Forces Korea) (7 AF) is a Numbered Air Force of the United States Pacific Air Forces (PACAF). It is headquartered at Osan Air Base, South Korea. The command's mission is to plan and direct air component operations in the Republic of Korea and in the Northwest Pacific. Established on 19 October 1940 as the Hawaiian Air Force at Fort Shafter, Territory of Hawaii, the 7 AF was a United States Army Air Forces combat unit in the Pacific Theater of World War II, providing air defense of the Hawaiian Islands and engaging in combat operations primarily in the Central Pacific AOR. It was assigned units engaging enemy forces in the Gilbert Islands; Marshall Islands; Caroline Islands; Mariana Islands, and in the last major battle of the Pacific War, the Battle of Okinawa. Returning to its defense role in Hawaii after the war, 7 AF became the primary USAF command and control organization in South Vietnam during the Vietnam War. 7 AF is commanded by Lt Gen Scot ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Attack On Pearl Harbor
The attack on Pearl HarborAlso known as the Battle of Pearl Harbor was a surprise military strike by the Imperial Japanese Navy Air Service upon the United States against the naval base at Pearl Harbor in Honolulu, Territory of Hawaii, just before 8:00a.m. (local time) on Sunday, December 7, 1941. The United States was a neutral country at the time; the attack led to its formal entry into World War II the next day. The Japanese military leadership referred to the attack as the Hawaii Operation and Operation AI, and as Operation Z during its planning. Japan intended the attack as a preventive action. Its aim was to prevent the United States Pacific Fleet from interfering with its planned military actions in Southeast Asia against overseas territories of the United Kingdom, the Netherlands, and those of the United States. Over the course of seven hours there were coordinated Japanese attacks on the US-held Philippines, Guam, and Wake Island and on the British Empire ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
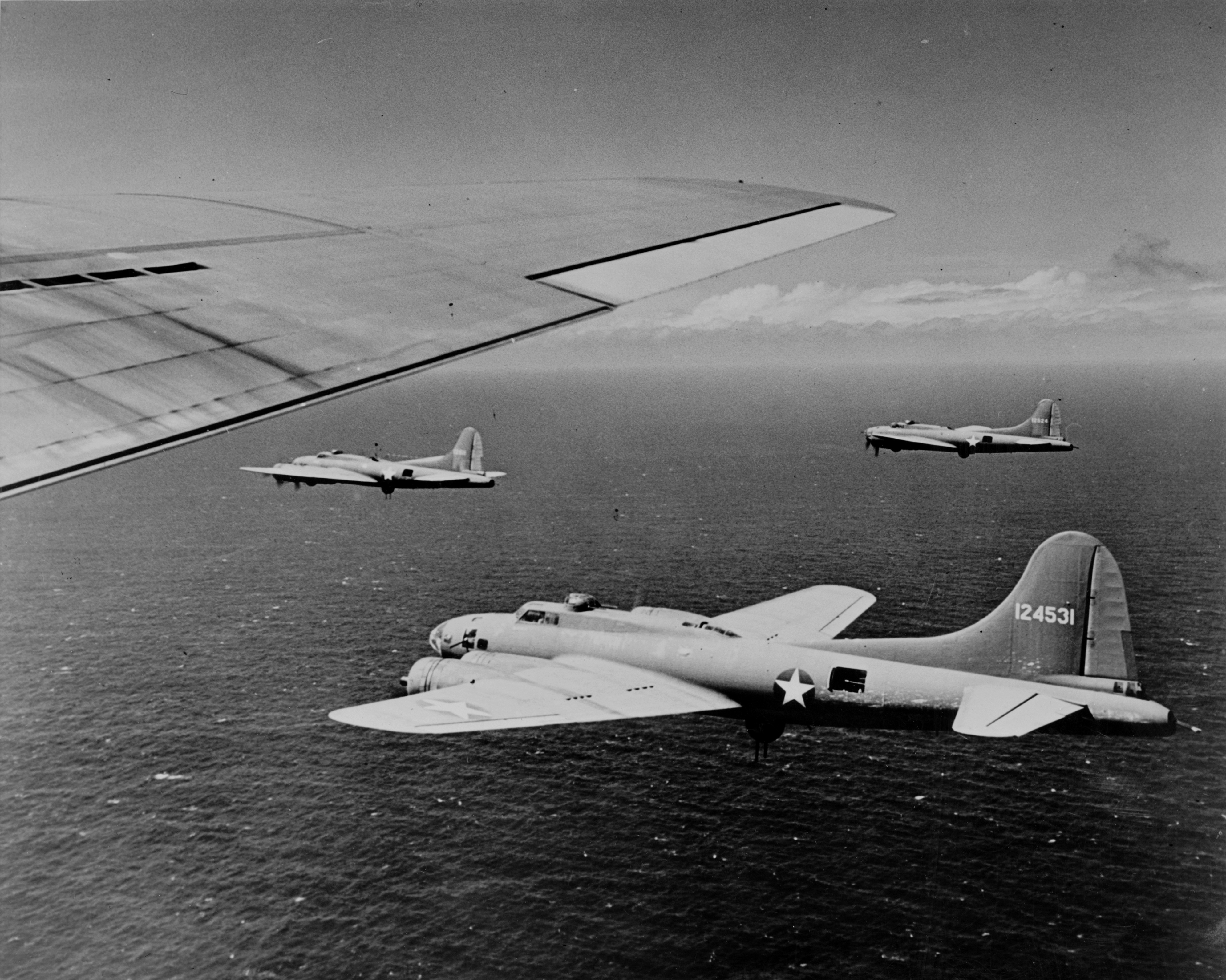
B-17 Flying Fortress
The Boeing B-17 Flying Fortress is a four-engined heavy bomber developed in the 1930s for the United States Army Air Corps (USAAC). Relatively fast and high-flying for a bomber of its era, the B-17 was used primarily in the European Theater of Operations, United States Army, European Theater of Operations and dropped more bombs than any other aircraft during World War II. It is the List of most-produced aircraft, third-most produced bomber of all time, behind the four-engined Consolidated B-24 Liberator and the multirole, twin-engined Junkers Ju 88. It was also employed as a transport, antisubmarine aircraft, drone controller, and search-and-rescue aircraft. In a USAAC competition, Boeing, Boeing's prototype Model 299/XB-17 outperformed two other entries but crashed, losing the initial 200-bomber contract to the Douglas B-18 Bolo. Still, the Air Corps ordered 13 more B-17s for further evaluation, then introduced it into service in 1938. The B-17 evolved through numerous Boei ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
USAAF Bombardment Group
A bombardment group or bomb group was a unit of organizational command and control group of the United States Army Air Forces (USAAF) during World War II. A bombardment group was normally commanded by a colonel. The table of allowances (TOA) for personnel, aircraft and equipment grew steadily over the course of the war doubling from 35 aircraft in 1941 to 72 in February, 1945. The aircrew end strength reached upwards to two crews per aircraft. Categories U.S. bomb groups were numbered and classified into four types: Very Heavy (VH), Heavy (H), Medium (M), and Light (L). Groups which combined bombers of differing categories into a single administrative organization were designated "Composite" groups. Bomber aircraft were assigned to groups by category: * Very Heavy: B-29 Superfortress, B-32 Dominator * Heavy: B-17 Flying Fortress, B-24 Liberator * Medium: B-25 Mitchell, B-26 Marauder * Light: A-20 Havoc, A-26 Invader (The USAAF also operated two fighter-bombers during the pe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
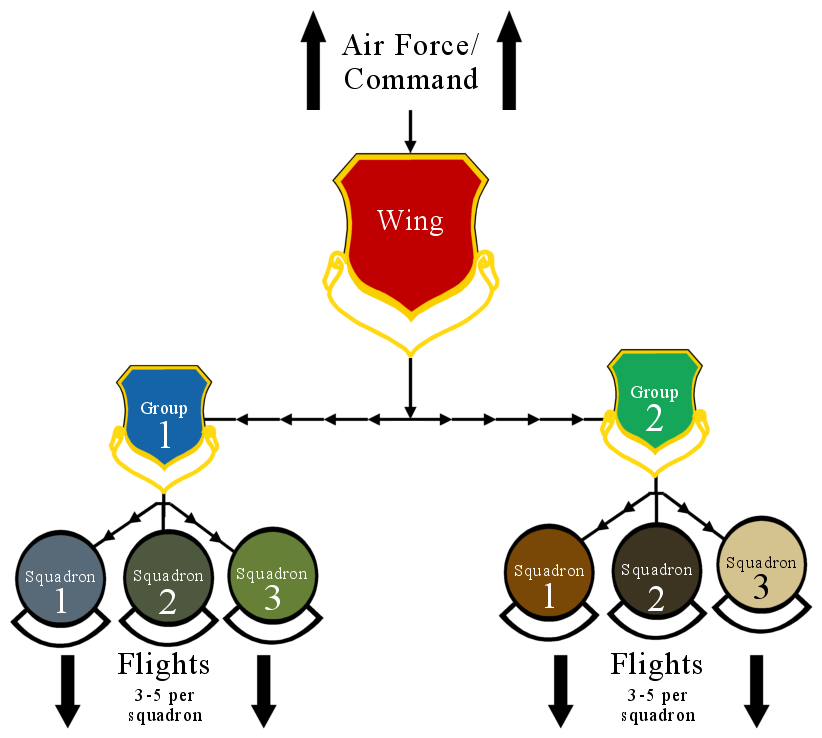
Wing (military Aviation Unit)
In military aviation, a wing is a unit of command. In most military aviation services, a wing is a relatively large formation of planes. In Commonwealth countries a wing usually comprises three squadrons, with several wings forming a group (around 10 squadrons). Each squadron will contain around 20 planes. Commonwealth usage Origins On its establishment in 1912, the British Royal Flying Corps (RFC) was intended to be an inter-service, combined force of the British Army and Royal Navy. Given the rivalry that existed between the army and navy, new terminology was used, in order to avoid marking the corps out as having an army or navy ethos. While the term "wing" had been used in the cavalry, its more general use predominated. Accordingly, the word "wing", with its allusion of flight, was chosen as the term of subdivision and the corps was split into a "Military Wing" (i.e. an army wing) and a "Naval Wing". Each wing consisted of a number of squadrons (the term "squadro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
SM-65 Atlas
The SM-65 Atlas was the first operational intercontinental ballistic missile (ICBM) developed by the United States and the first member of the Atlas rocket family. It was built for the U.S. Air Force by the Convair Division of General Dynamics at an assembly plant located in Kearny Mesa, San Diego. Atlas became operational in October 1959, but was soon made obsolete as an ICBM by new development, and was retired from this role by 1965. Atlas required long preparation times which made it unsuitable for a quick launch ICBM. However, this was not a requirement for planned space launches, and so Atlas-derived launch vehicles served a long history as space launchers. Even before its ICBM use ended in 1965, Atlas had placed four Project Mercury astronauts in orbit and was becoming the foundation for a family of successful space launch vehicles, most notably Atlas Agena and Atlas Centaur. Mergers led to the acquisition of the Atlas Centaur line by the United Launch Alliance. Tod ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Boeing KC-135 Stratotanker
The Boeing KC-135 Stratotanker is an American military aerial refueling aircraft that was developed from the Boeing 367-80 prototype, alongside the Boeing 707 airliner. It is the predominant variant of the C-135 Stratolifter family of transport aircraft. The KC-135 was the United States Air Force's first jet-powered refueling tanker and replaced the KC-97 Stratofreighter. The KC-135 was initially tasked with refueling strategic bombers, but it was used extensively in the Vietnam War and later conflicts such as Operation Desert Storm to extend the range and endurance of US tactical fighters and bombers. The KC-135 entered service with the United States Air Force (USAF) in 1957; it is one of nine military fixed-wing aircraft with over 60 years of continuous service with its original operator. The KC-135 is supplemented by the larger McDonnell Douglas KC-10 Extender. Studies have concluded that many of the aircraft could be flown until 2030, although maintenance costs have great ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Boeing KC-97 Stratofreighter
The Boeing KC-97 Stratofreighter is a four-engined, piston-powered United States strategic tanker aircraft based on the Boeing C-97 Stratofreighter. It replaced the KB-29 and was succeeded by the Boeing KC-135 Stratotanker. Design and development The KC-97 Stratofreighter was an aerial refueling tanker variant of the C-97 Stratofreighter (which was itself based on the Boeing B-29 Superfortress), greatly modified with all the necessary tanks, plumbing, and a flying boom first developed for the KB-29 bomber. The cavernous upper deck was capable of accommodating oversize cargo accessed through a very large right-side door. In addition, transferable jet fuel was contained in tanks on the lower deck (G-L models). Both decks were heated and pressurized for high altitude operations. The boom operator lay prone, viewing operations through a window at the bottom of the tail, a configuration later used on the KC-135 ''Note: Occasionally the KC-97 has been referred to as "Stratotanker". ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |