|
11th Michigan Volunteer Infantry Regiment
The 11th Michigan Infantry Regiment, initially known as Colonel May’s Independent Regiment, was a unit in the Union army during the American Civil War. The regiment fought with the Army of the Cumberland in numerous battles, including Stones River, Chickamauga, and Missionary Ridge. Regimental history The regiment was recruited in southern Michigan between April and September 1861, with the majority of the soldiers coming from St. Joseph County. The unit formally mustered into the Union army between August 24 and September 11. It formed independent from the state government, as allowed for by the War Department, but fell under Michigan’s control when the Federal authorization for independent units was revoked. The regiment received its formal designation as the 11th regiment on October 11. The soldiers elected their officers, selecting William J. May, the former proprietor of the White Pigeon Railroad Dining Hall, as colonel. U.S. district attorney William Lewis Stoughton ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Union (Civil War)
During the American Civil War, the Union, also known as the North, referred to the United States led by President Abraham Lincoln. It was opposed by the secessionist Confederate States of America (CSA), informally called "the Confederacy" or "the South". The Union is named after its declared goal of preserving the United States as a constitutional union. "Union" is used in the U.S. Constitution to refer to the founding formation of the people, and to the states in union. In the context of the Civil War, it has also often been used as a synonym for "the northern states loyal to the United States government;" in this meaning, the Union consisted of 20 free states and five border states. The Union Army was a new formation comprising mostly state units, together with units from the regular U.S. Army. The border states were essential as a supply base for the Union invasion of the Confederacy, and Lincoln realized he could not win the war without control of them, especially Maryla ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Union Army
During the American Civil War, the Union Army, also known as the Federal Army and the Northern Army, referring to the United States Army, was the land force that fought to preserve the Union (American Civil War), Union of the collective U.S. state, states. It proved essential to the preservation of the United States as a working, viable republic. The Union Army was made up of the permanent Regular Army (United States), regular army of the United States, but further fortified, augmented, and strengthened by the many temporary units of dedicated United States Volunteers, volunteers, as well as including those who were drafted in to service as Conscription in the United States, conscripts. To this end, the Union Army fought and ultimately triumphed over the efforts of the Confederate States Army in the American Civil War. Over the course of the war, 2,128,948 men enlisted in the Union Army, including 178,895 United States Colored Troops, colored troops; 25% of the white men who s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Confederate States Of America
The Confederate States of America (CSA), commonly referred to as the Confederate States or the Confederacy was an unrecognized breakaway republic in the Southern United States that existed from February 8, 1861, to May 9, 1865. The Confederacy comprised U.S. states that declared secession and warred against the United States during the American Civil War: South Carolina, Mississippi, Florida, Alabama, Georgia, Louisiana, Texas, Virginia, Arkansas, Tennessee, and North Carolina. Kentucky and Missouri also declared secession and had full representation in the Confederate Congress, though their territory was largely controlled by Union forces. The Confederacy was formed on February 8, 1861, by seven slave states: South Carolina, Mississippi, Florida, Alabama, Georgia, Louisiana, and Texas. All seven were in the Deep South region of the United States, whose economy was heavily dependent upon agriculture—particularly cotton—and a plantation system that relied upon enslaved ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
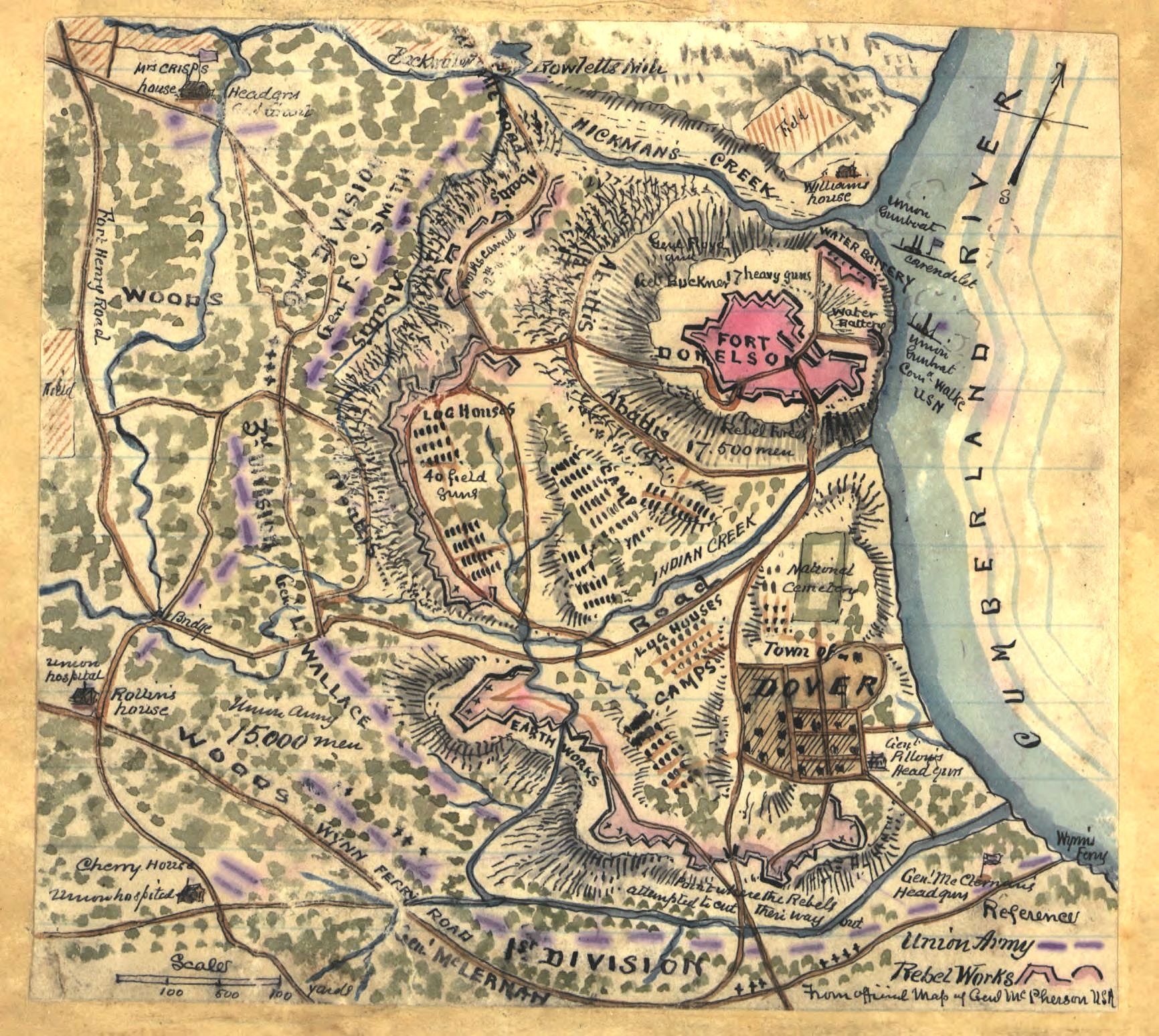
Fort Donelson
Fort Donelson was a fortress built early in 1862 by the Confederacy during the American Civil War to control the Cumberland River, which led to the heart of Tennessee, and thereby the Confederacy. The fort was named after Confederate general Daniel S. Donelson. The Union Army of the Tennessee, commanded by Major General Ulysses S. Grant, who later became president, captured the fort in February 1862 from the Confederate Army in the Battle of Fort Donelson. This was a great strategic victory for the Union forces, and part of Grant's campaign to gain control of the Mississippi River. Union forces occupied the fort (and much of Tennessee) for the remainder of the war. A small detachment of Confederate troops made one unsuccessful attempt in 1863 to regain it. History Bushrod Johnson of the Confederate Corps of Engineers had approved the build site and supervised construction completed in early 1862. The site commanded a bend on the west side of the Cumberland River, It was planne ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Battle Of Fort Henry
The Battle of Fort Henry was fought on February 6, 1862, in Stewart County, Tennessee, during the American Civil War. It was the first important victory for the Union and Brig. Gen. Ulysses S. Grant in the Western Theater. On February 4 and 5, Grant landed two divisions just north of Fort Henry on the Tennessee River. (The troops serving under Grant were the nucleus of the Union's successful Army of the Tennessee, although that name was not yet in use.) Grant's plan was to advance upon the fort on February 6 while it was being simultaneously attacked by Union gunboats commanded by Flag Officer Andrew Hull Foote. A combination of accurate and effective naval gunfire, heavy rain, and the poor siting of the fort, nearly inundated by rising river waters, caused its commander, Brig. Gen. Lloyd Tilghman, to surrender to Foote before the Union Army arrived. The surrender of Fort Henry opened the Tennessee River to Union traffic south of the Alabama border. In the days following the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bardstown
Bardstown is a home rule-class city in Nelson County, Kentucky, United States. The population was 11,700 in the 2010 census. It is the county seat of Nelson County. Bardstown is named for the pioneering Bard brothers. David Bard obtained a land grant in 1785 in what was then Jefferson County, Virginia. William Bard surveyed and platted the town. It was originally chartered as Baird's Town in 1788, and has been known as Beardstown, and Beards Town.Commonwealth of Kentucky. Office of the Secretary of State. Land Office. "Bardstown, Kentucky". Accessed July 15, 2013. The production of bourbon whiskey is a major industry. History First settled by European Americans in 1780, Bardstown is the second oldest city in Kentucky."History of Bardstown steeped in bourbon" '' |
Kentucky
Kentucky ( , ), officially the Commonwealth of Kentucky, is a state in the Southeastern region of the United States and one of the states of the Upper South. It borders Illinois, Indiana, and Ohio to the north; West Virginia and Virginia to the east; Tennessee to the south; and Missouri to the west. Its northern border is defined by the Ohio River. Its capital is Frankfort, and its two largest cities are Louisville and Lexington. Its population was approximately 4.5 million in 2020. Kentucky was admitted into the Union as the 15th state on June 1, 1792, splitting from Virginia in the process. It is known as the "Bluegrass State", a nickname based on Kentucky bluegrass, a species of green grass found in many of its pastures, which has supported the thoroughbred horse industry in the center of the state. Historically, it was known for excellent farming conditions for this reason and the development of large tobacco plantations akin to those in Virginia and North Carolina i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
White Pigeon, Michigan
White Pigeon is a village in St. Joseph County, Michigan, St. Joseph County in the U.S. state of Michigan. The population was 1,522 at the 2010 United States Census, 2010 census. The village is located within White Pigeon Township, Michigan, White Pigeon Township. Geography According to the United States Census Bureau, the village has a total area of , of which is land and is water. The White Pigeon River flows through the south end of town, emptying into the St. Joseph River (Lake Michigan), St. Joseph River that flows to Lake Michigan. Major highways * * History White Pigeon was incorporated by European Americans in 1837. The General Land Office (White Pigeon, MI), United States Land Office, located in downtown White Pigeon, is the oldest surviving U.S. Land office in the state of Michigan. Following the cession of Native American lands in this area by leaders of regional tribes, the U.S. government sold more than 250,000 acres of land in Michigan for $1.25 an acre in the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lieutenant Colonel
Lieutenant colonel ( , ) is a rank of commissioned officers in the armies, most marine forces and some air forces of the world, above a major and below a colonel. Several police forces in the United States use the rank of lieutenant colonel. The rank of lieutenant colonel is often shortened to simply "colonel" in conversation and in unofficial correspondence. Sometimes, the term 'half-colonel' is used in casual conversation in the British Army. In the United States Air Force, the term 'light bird' or 'light bird colonel' (as opposed to a 'full bird colonel') is an acceptable casual reference to the rank but is never used directly towards the rank holder. A lieutenant colonel is typically in charge of a battalion or regiment in the army. The following articles deal with the rank of lieutenant colonel: * Lieutenant-colonel (Canada) * Lieutenant colonel (Eastern Europe) * Lieutenant colonel (Turkey) * Lieutenant colonel (Sri Lanka) * Lieutenant colonel (United Kingdom) * L ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
William Lewis Stoughton
William Lewis Stoughton (March 20, 1827 – June 6, 1888) was a politician and soldier from U.S. state of Michigan who served in the United States Congress, as well as serving as an officer and brigade commander in the Union Army during the American Civil War. Biography Stoughton was born in Bangor, New York. He attended Kirtland, Painesville, and Madison Academies in Lake County, Ohio. He studied law in Ohio, Indiana, and Michigan from 1849 to 1851 when he was admitted to the bar and commenced practice in Sturgis, Michigan. Stoughton was a prosecuting attorney of St. Joseph County from 1855 to 1859 and a delegate to the 1860 Republican National Convention. He was appointed by President Abraham Lincoln as United States District Attorney for the District of Michigan in March 1861, but resigned a few months later to enter the Union Army following the outbreak of the Civil War. He served as colonel of the 11th Michigan Infantry. Stoughton commanded the 2nd Bri ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Colonel
Colonel (abbreviated as Col., Col or COL) is a senior military officer rank used in many countries. It is also used in some police forces and paramilitary organizations. In the 17th, 18th and 19th centuries, a colonel was typically in charge of a regiment in an army. Modern usage varies greatly, and in some cases, the term is used as an honorific title that may have no direct relationship to military service. The rank of colonel is typically above the rank of lieutenant colonel. The rank above colonel is typically called brigadier, brigade general or brigadier general. In some smaller military forces, such as those of Monaco or the Vatican, colonel is the highest rank. Equivalent naval ranks may be called captain or ship-of-the-line captain. In the Commonwealth's air force ranking system, the equivalent rank is group captain. History and origins By the end of the late medieval period, a group of "companies" was referred to as a "column" of an army. According to Raymond Ol ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
United States Department Of War
The United States Department of War, also called the War Department (and occasionally War Office in the early years), was the United States Cabinet department originally responsible for the operation and maintenance of the United States Army, also bearing responsibility for naval affairs until the establishment of the Navy Department in 1798, and for most land-based air forces until the creation of the Department of the Air Force on September 18, 1947. The Secretary of War, a civilian with such responsibilities as finance and purchases and a minor role in directing military affairs, headed the War Department throughout its existence. The War Department existed from August 7, 1789 until September 18, 1947, when it split into the Department of the Army and the Department of the Air Force. The Department of the Army and Department of the Air Force later joined the Department of the Navy under the United States Department of Defense in 1949. History 18th century The Departme ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |