|
112 Signals Unit Stornoway
112 Signals Unit, RAF Stornoway (112 S.U.) was a classified Royal Air Force (RAF) Electronic countermeasures (ECM) measurement and evaluation unit based at Stornoway Airport on the Isle of Lewis in the Outer Hebrides.Document AIR 14/4317 ''1974–1980'', The National Archives, Kew. (Memo No. 247 from ORB, HQBC discusses ECM measurement results by 112 S.U.) It was an RAF Bomber Command Headquarters ( HQBC) directly administered unit established during the height of the Cold War. Role Once 112 S.U. had been established at Stornoway Airport from 1 January 1960, under the auspices of the Operational Research Branch (O.R.B) at HQBC, the unit measured the signal strength, frequency bandwidths and aerial performance of the operational Handley Page Victor and Avro Vulcan V bombers as they flew a course towards, over or away from the unit varying from straight-lines to polar patterns.Document AIR 29/4736 ''1974–1980'', The National Archives, Kew. (map showing aircraft track to/from 1 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
RAF Bomber Command
RAF Bomber Command controlled the Royal Air Force's bomber forces from 1936 to 1968. Along with the United States Army Air Forces, it played the central role in the strategic bombing of Germany in World War II. From 1942 onward, the British bombing campaign against Germany became less restrictive and increasingly targeted industrial sites and the civilian manpower base essential for German war production. In total 364,514 operational sorties were flown, 1,030,500 tons of bombs were dropped and 8,325 aircraft lost in action. Bomber Command crews also suffered a high casualty rate: 55,573 were killed out of a total of 125,000 aircrew, a 44.4% death rate. A further 8,403 men were wounded in action, and 9,838 became prisoners of war. Bomber Command stood at the peak of its post-war military power in the 1960s, the V bombers holding the United Kingdom's nuclear deterrent and a supplemental force of Canberra light bombers. In August 2006, a memorial was unveiled at Lincoln Cathe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Yellow Sun (nuclear Weapon)
''Yellow Sun'' was the first British operational high-yield strategic nuclear weapon warhead. The name refers only to the outer casing; the warhead (or physics package) was known as "Green Grass" in Yellow Sun Mk.1 and "Red Snow" in Yellow Sun Mk.2. Yellow Sun was designed to contain a variety of warheads. The initial plan was that it would carry an alarm-clock-type warhead known as "Green Bamboo", and then replace it with a true thermonuclear warhead known as "Green Granite". After signing a weapon technology agreement with the US, both concepts were dropped. Green Granite would be replaced by the US Mark 28 at an earlier service date. This meant the interim Green Bamboo was less important and it was replaced by the less powerful and simpler "Green Grass". A unique feature of the Yellow Sun casing was its completely flat nose. This provided two benefits, one was that the drag allowed the bomb to fall behind the bomber a safe distance before detonation, and the other was that i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kindley Air Force Base
Kindley Air Force Base was a United States Air Force base in Bermuda from 1948–1970, having been operated from 1943 to 1948 by the United States Army Air Forces as ''Kindley Field''. History World War II Prior to American entry into the Second World War, the governments of the United Kingdom and the US led by Prime Minister Winston Churchill and President Roosevelt came to an agreement exchanging a number of obsolete ex-US Naval destroyers for 99-year base rights in a number of British Empire West Indian territories. Bases were also granted in Bermuda and Newfoundland, though Britain received no loans in exchange for these. This was known as the destroyers for bases deal. As the government of Bermuda had not been party to the agreement, the arrival of US engineers in 1941 came as rather a surprise to many in Bermuda. The US engineers began surveying the colony for the construction of an airfield that was envisioned as taking over most of the West End of the Island. Fr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Orkneys
Orkney (; sco, Orkney; on, Orkneyjar; nrn, Orknøjar), also known as the Orkney Islands, is an archipelago in the Northern Isles of Scotland, situated off the north coast of the island of Great Britain. Orkney is 10 miles (16 km) north of the coast of Caithness and has about 70 islands, of which 20 are inhabited. The largest island, the Mainland, has an area of , making it the sixth-largest Scottish island and the tenth-largest island in the British Isles. Orkney’s largest settlement, and also its administrative centre, is Kirkwall. Orkney is one of the 32 council areas of Scotland, as well as a constituency of the Scottish Parliament, a lieutenancy area, and an historic county. The local council is Orkney Islands Council, one of only three councils in Scotland with a majority of elected members who are independents. The islands have been inhabited for at least years, originally occupied by Mesolithic and Neolithic tribes and then by the Picts. Orkney was coloniz ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
NOTAM
A Notice to Airmen/Notice to Air Missions (NOTAM), is a notice filed with an aviation authority to alert aircraft pilots of potential hazards along a flight route or at a location that could affect the flight. NOTAMs are unclassified notices or advisories distributed by means of telecommunication that contain information concerning the establishment, conditions or change in any aeronautical facility, service, procedure or hazard, the timely knowledge of which is essential to personnel and systems concerned with flight operations. NOTAMs are created and transmitted by government agencies and airport operators under guidelines specified by Annex 15: Aeronautical Information Services of the Convention on International Civil Aviation (CICA). The acronym ''NOTAM'' came into common use following the ratification of the CICA, which came into effect on 4 April 1947. Notices to airmen were normally published in a regular publication by each country's air authorities (e.g., in ''Flight Inte ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
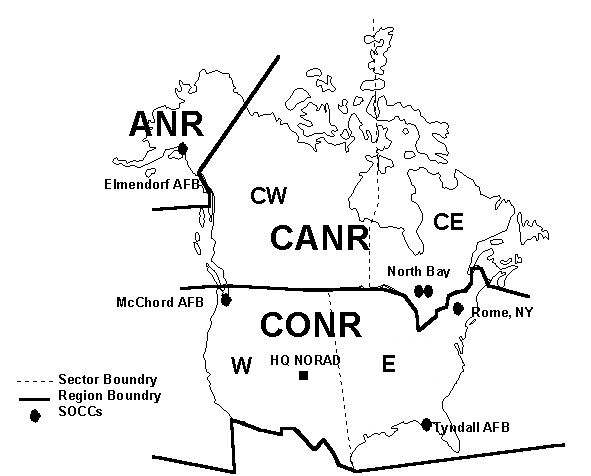
North American Aerospace Defense Command
North American Aerospace Defense Command (NORAD ), known until March 1981 as the North American Air Defense Command, is a combined organization of the United States and Canada that provides aerospace warning, air sovereignty, and protection for Canada and the continental United States. Headquarters for NORAD and the NORAD/ United States Northern Command (USNORTHCOM) center are located at Peterson Space Force Base in El Paso County, near Colorado Springs, Colorado. The nearby Cheyenne Mountain Complex has the Alternate Command Center. The NORAD commander and deputy commander (CINCNORAD) are, respectively, a United States four-star general or equivalent and a Canadian lieutenant-general or equivalent. Organization CINCNORAD maintains the NORAD headquarters at Peterson Space Force Base near Colorado Springs, Colorado. The NORAD and USNORTHCOM Command Center at Peterson SFB serves as a central collection and coordination facility for a worldwide system of sensors desig ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ural Mountains
The Ural Mountains ( ; rus, Ура́льские го́ры, r=Uralskiye gory, p=ʊˈralʲskʲɪjə ˈɡorɨ; ba, Урал тауҙары) or simply the Urals, are a mountain range that runs approximately from north to south through western Russia, from the coast of the Arctic Ocean to the river Ural and northwestern Kazakhstan.Ural Mountains Encyclopædia Britannica on-line The mountain range forms part of the conventional boundary between the regions of and |
RAF Museum Cosford
The Royal Air Force Museum Cosford, located in Cosford in Shropshire, is a free (currently, 2022) museum dedicated to the history of aviation and the Royal Air Force in particular. The museum is part of the Royal Air Force Museum, a non-departmental public body sponsored by the Ministry of Defence and also a registered charity. The museum is spread over two sites in England; the other site is at the Royal Air Force Museum London at Colindale (near Hendon) in north London. History The London museum was officially opened at the Colindale (then part of Hendon) London site on 15 November 1972 by Queen Elizabeth II. The hangars housed just 36 aircraft at opening. Over the years, the collection increased and aircraft were stored at RAF stations around the country when they were not on display to the public. On 1 May 1979, the Cosford site was opened at RAF Cosford, one of the RAF stations which had been used to store the museum's collection of aircraft. On opening, the museum initi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Polaris Missile
The UGM-27 Polaris missile was a two-stage solid-fueled nuclear-armed submarine-launched ballistic missile (SLBM). As the United States Navy's first SLBM, it served from 1961 to 1980. In the mid-1950s the Navy was involved in the Jupiter missile project with the U.S. Army, and had influenced the design by making it squat so it would fit in submarines. However, they had concerns about the use of liquid fuel rockets on board ships, and some consideration was given to a solid fuel version, Jupiter S. In 1956, during an anti-submarine study known as Project Nobska, Edward Teller suggested that very small hydrogen bomb warheads were possible. A crash program to develop a missile suitable for carrying such warheads began as Polaris, launching its first shot less than four years later, in February 1960. As the Polaris missile was fired underwater from a moving platform, it was essentially invulnerable to counterattack. This led the Navy to suggest, starting around 1959, that they be g ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Blue Steel Missile
The Avro Blue Steel was a British air-launched, rocket-propelled nuclear armed standoff missile, built to arm the V bomber force. It allowed the bomber to launch the missile against its target while still outside the range of surface-to-air missiles (SAMs). The missile proceeded to the target at speeds up to Mach 3, and would trigger within 100 m of the pre-defined target point. Blue Steel entered service in 1963, by which point improved SAMs with longer range had greatly eroded the advantages of the design. A longer-range version, Blue Steel II, was considered, but cancelled in favour of the much longer-range GAM-87 Skybolt system from the US. When development of that system was cancelled in 1962, the V-bomber fleet was considered highly vulnerable. Blue Steel remained the primary British nuclear deterrent weapon until the Royal Navy started operating Polaris ballistic missiles from ''Resolution''-class submarines. Development Blue Steel was the result of a Min ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cuban Missile Crisis
The Cuban Missile Crisis, also known as the October Crisis (of 1962) ( es, Crisis de Octubre) in Cuba, the Caribbean Crisis () in Russia, or the Missile Scare, was a 35-day (16 October – 20 November 1962) confrontation between the United States and the Soviet Union, which escalated into an international crisis when American deployments of missiles in Italy and Turkey were matched by Soviet deployments of similar ballistic missiles in Cuba. Despite the short time frame, the Cuban Missile Crisis remains a defining moment in national security and nuclear war preparation. The confrontation is often considered the closest the Cold War came to escalating into a full-scale nuclear war. In response to the presence of American Jupiter ballistic missiles in Italy and Turkey, the failed Bay of Pigs Invasion of 1961, and Soviet fears of a Cuban drift towards China, Soviet First Secretary Nikita Khrushchev agreed to Cuba's request to place nuclear missiles on the island to deter a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gary Powers
Francis Gary Powers (August 17, 1929 – August 1, 1977) was an American pilot whose Central Intelligence Agency (CIA) Lockheed U-2 spy plane was shot down while flying a reconnaissance mission in Soviet Union airspace, causing the 1960 U-2 incident. He later worked as a helicopter pilot for KNBC in Los Angeles and died in a 1977 helicopter crash. Early life and education Powers was born August 17, 1929, in Jenkins, Kentucky, the son of Oliver Winfield Powers (1904–1970), a coal miner, and his wife Ida Melinda Powers (; 1905–1991). His family eventually moved to Pound, Virginia, just across the state border. He was the second born and only male of six children. His family lived in a mining town, and because of the hardships associated with living in such a town, his father wanted Powers to become a physician. He hoped his son would achieve the higher earnings of such a profession and felt that this would involve less hardship than any job in his hometown. Education and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |





_(2).jpg)