|
108 Hecuba
Hecuba (minor planet designation: 108 Hecuba) is a fairly large and bright main-belt asteroid. It was discovered by Karl Theodor Robert Luther on 2 April 1869, and named after Hecuba, wife of King Priam in the legends of the Trojan War in Greek Mythology. This object is orbiting the Sun with a period of 5.83 years and an eccentricity of 0.06. It became the first asteroid discovered to orbit near a 2:1 mean-motion resonance with the planet Jupiter, and is the namesake of the Hecuba group of asteroids. In the Tholen classification system, it is categorized as a stony S-type asteroid, while the Bus asteroid taxonomy system lists it as an Sw asteroid. Observations performed at the Palmer Divide Observatory in Colorado Springs, Colorado in during 2007 produced a light curve with a period of 17.859 ± 0.005 hours with a brightness variation of 0.11 ± 0.02 in magnitude. Hecuba orbits within the Hygiea family of asteroids but is not otherwise related to other family members bec ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Karl Theodor Robert Luther
Karl Theodor Robert Luther (April 16, 1822, Świdnica – February 15, 1900 Düsseldorf), normally published as Robert Luther, was a German astronomer. While working at the Bilk Observatory in Düsseldorf, Germany, he searched for asteroids and discovered 24 of them between 1852 and 1890. Seven times Lalande Prize winner. Biography Karl Theodor Robert Luther was born on April 16, 1822 to August Luther and Wilhelmine von Ende. He was home schooled and studied in the local high school. In 1841, he moved to Breslau where he studied until 1843. In 1843 Luther moved to Berlin to study astronomy. He was a student of Johann Franz Encke and helped him in his astronomical calculations and creating the astronomical almanac. In 1850 he became a second observer. In 1851, Franz Brünnow invited Luther to the Düsseldorf-Bilk Observatory to become a director of the observatory after him. Luther married Caroline (nee Marker) and they had one son, William. Luther died in 1900 after a shor ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tholen Classification
An asteroid spectral type is assigned to asteroids based on their emission spectrum, color, and sometimes albedo. These types are thought to correspond to an asteroid's surface composition. For small bodies that are not internally differentiated, the surface and internal compositions are presumably similar, while large bodies such as Ceres and Vesta are known to have internal structure. Over the years, there has been a number of surveys that resulted in a set of different taxonomic systems such as the Tholen, SMASS and Bus–DeMeo classifications. Taxonomic systems In 1975, astronomers Clark R. Chapman, David Morrison, and Ben Zellner developed a simple taxonomic system for asteroids based on color, albedo, and spectral shape. The three categories were labelled " C" for dark carbonaceous objects, " S" for stony (silicaceous) objects, and "U" for those that did not fit into either C or S. This basic division of asteroid spectra has since been expanded and clarified.Thom ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hygiea Asteroids , a series of practices performed to preserve health
{{disambig ...
Hygiea may refer to: * An alternative spelling of Hygieia, the Greek goddess of preventive healthcare/medicine * The asteroid 10 Hygiea See also * '' Hygia'', a large genus of Asian seed bugs * Hygieia (other) * Hygiene Hygiene is a series of practices performed to preserve health. According to the World Health Organization (WHO), "Hygiene refers to conditions and practices that help to maintain health and prevent the spread of diseases." Personal hygiene refer ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
S-type Asteroids (Tholen)
S-type asteroids are asteroids with a spectral type that is indicative of a siliceous (i.e. stony) mineralogical composition, hence the name. They have relatively high density. Approximately 17% of asteroids are of this type, making it the second most common after the carbonaceous C-type. Characteristics S-type asteroids, with an astronomical albedo of typically 0.20, are moderately bright and consist mainly of iron- and magnesium- silicates. They are dominant in the inner part of the asteroid belt within 2.2 AU, common in the central belt within about 3 AU, but become rare farther out. The largest are 3 Juno (about 240–250 km across) and 15 Eunomia (230 km), with other large S-types being 29 Amphitrite, 532 Herculina and 7 Iris. These largest S-types are visible in 10x50 binoculars at most oppositions; the brightest, 7 Iris, can occasionally become brighter than +7.0, which is a higher magnitude than any asteroid except the unusually reflective 4 Vest ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Brian D
Brian (sometimes spelled Bryan in English) is a male given name of Irish and Breton origin, as well as a surname of Occitan origin. It is common in the English-speaking world. It is possible that the name is derived from an Old Celtic word meaning "high" or "noble". For example, the element ''bre'' means "hill"; which could be transferred to mean "eminence" or "exalted one". The name is quite popular in Ireland, on account of Brian Boru, a 10th-century High King of Ireland. The name was also quite popular in East Anglia during the Middle Ages. This is because the name was introduced to England by Bretons following the Norman Conquest. Bretons also settled in Ireland along with the Normans in the 12th century, and 'their' name was mingled with the 'Irish' version. Also, in the north-west of England, the 'Irish' name was introduced by Scandinavian settlers from Ireland. Within the Gaelic speaking areas of Scotland, the name was at first only used by professional families of Ir ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Monthly Notices Of The Royal Astronomical Society
''Monthly Notices of the Royal Astronomical Society'' (MNRAS) is a peer-reviewed scientific journal covering research in astronomy and astrophysics. It has been in continuous existence since 1827 and publishes letters and papers reporting original research in relevant fields. Despite the name, the journal is no longer monthly, nor does it carry the notices of the Royal Astronomical Society. History The first issue of MNRAS was published on 9 February 1827 as ''Monthly Notices of the Astronomical Society of London'' and it has been in continuous publication ever since. It took its current name from the second volume, after the Astronomical Society of London became the Royal Astronomical Society (RAS). Until 1960 it carried the monthly notices of the RAS, at which time these were transferred to the newly established '' Quarterly Journal of the Royal Astronomical Society'' (1960–1996) and then to its successor journal '' Astronomy & Geophysics'' (since 1997). Until 1965, MNRAS wa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
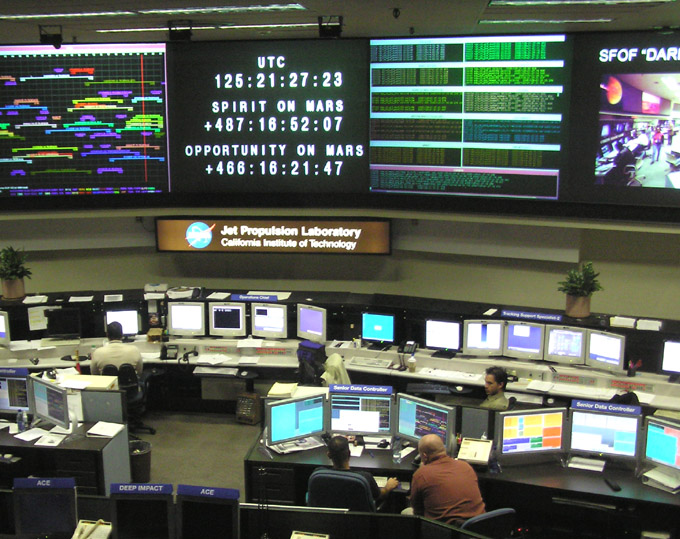
NASA Jet Propulsion Laboratory
The Jet Propulsion Laboratory (JPL) is a federally funded research and development center and NASA field center in the City of La Cañada Flintridge, California, United States. Founded in the 1930s by Caltech researchers, JPL is owned by NASA and managed by the nearby California Institute of Technology (Caltech). The laboratory's primary function is the construction and operation of planetary robotic spacecraft, though it also conducts Earth-orbit and astronomy missions. It is also responsible for operating the NASA Deep Space Network. Among the laboratory's major active projects are the Mars 2020 mission, which includes the '' Perseverance'' rover and the '' Ingenuity'' Mars helicopter; the Mars Science Laboratory mission, including the ''Curiosity'' rover; the InSight lander (''Interior Exploration using Seismic Investigations, Geodesy and Heat Transport''); the ''Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter''; the '' Juno'' spacecraft orbiting Jupiter; the ''SMAP'' satellite for earth surfac ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
C-type Asteroid
C-type (carbonaceous) asteroids are the most common variety, forming around 75% of known asteroids. They are volatile-rich and distinguished by a very low albedo because their composition includes a large amount of carbon, in addition to rocks and minerals. Their density averages at about . They occur most frequently at the outer edge of the asteroid belt, 3.5 astronomical units (AU) from the Sun, where 80% of the asteroids are of this type, whereas only 40% of asteroids at 2 AU from the Sun are C-type. The proportion of C-types may actually be greater than this, because C-types are much darker (and therefore less detectable) than most other asteroid types except for D-types and others that are mostly at the extreme outer edge of the asteroid belt. Characteristics Asteroids of this class have spectra very similar to those of carbonaceous chondrite meteorites (types CI and CM). The latter are very close in chemical composition to the Sun and the primitive solar nebula minus ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
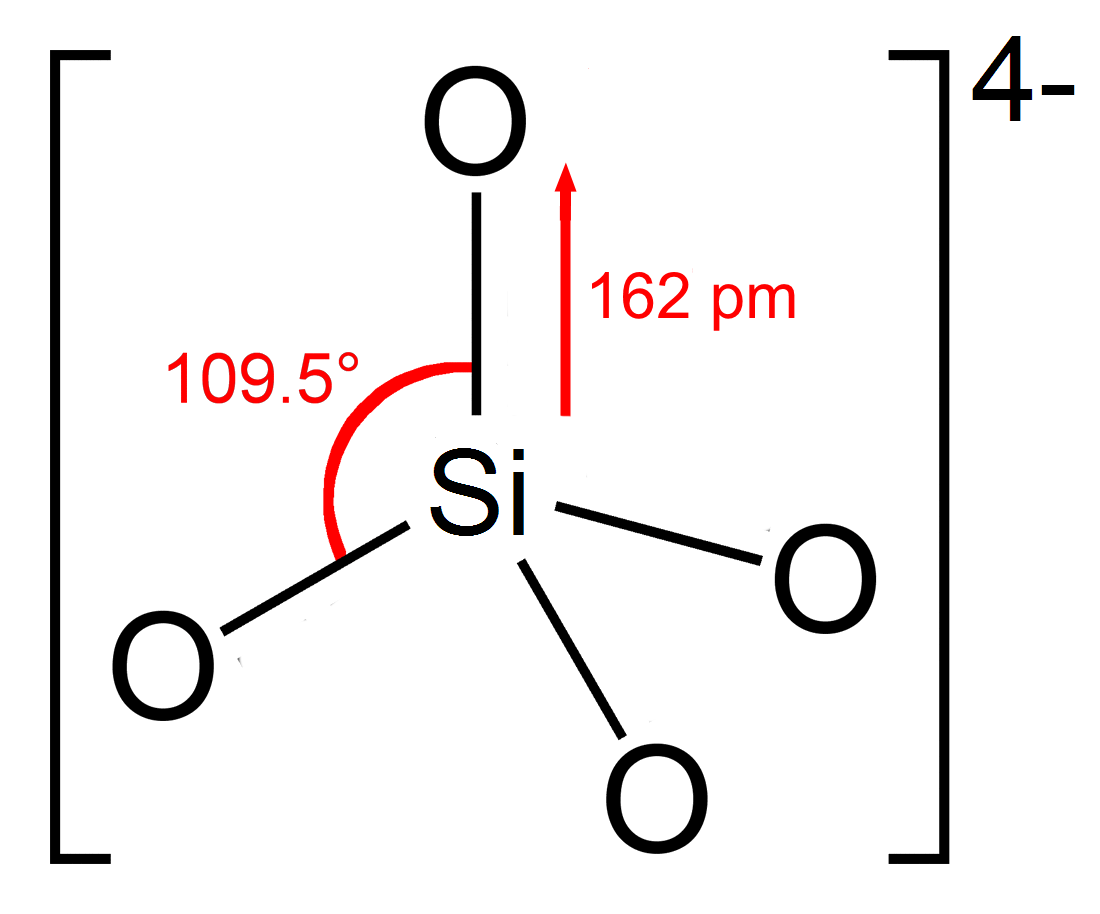
Silicate
In chemistry, a silicate is any member of a family of polyatomic anions consisting of silicon and oxygen, usually with the general formula , where . The family includes orthosilicate (), metasilicate (), and pyrosilicate (, ). The name is also used for any salt of such anions, such as sodium metasilicate; or any ester containing the corresponding chemical group, such as tetramethyl orthosilicate. The name "silicate" is sometimes extended to any anions containing silicon, even if they do not fit the general formula or contain other atoms besides oxygen; such as hexafluorosilicate .Most commonly, silicates are encountered as silicate minerals. For diverse manufacturing, technological, and artistic needs, silicates are versatile materials, both natural (such as granite, gravel, and garnet) and artificial (such as Portland cement, ceramics, glass, and waterglass). Structural principles In all silicates, silicon atom occupies the center of an idealized tetrahedro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hygiea Family
The Hygiea or Hygiean family is a grouping of dark, carbonaceous C-type and B-type asteroids in outer asteroid belt, the largest member of which is 10 Hygiea. About 1% of all known asteroids in the asteroid belt belong to this family. Characteristics By far the largest member is 10 Hygiea, a 400 km diameter C-type asteroid that is the fourth largest in the belt. The remaining members are much smaller so Hygiea contains about 94–98% of the mass in the family (depending on the exact criteria for inclusion). The two next largest members are 333 Badenia, and 538 Friederike, both just over 70 km in diameter. After that, the remaining members have diameters of less than 30 km. The Hygiea family is thought to have arisen from a catastrophically disruptive impact, after which Hygiea re-accumulated. The two 70-kilometer-diameter bodies, which are much larger than, for example, the Vesta family, which contains no members above around 10 km in diameter, are consisten ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Magnitude (astronomy)
In astronomy, magnitude is a unitless measure of the brightness of an object in a defined passband, often in the visible or infrared spectrum, but sometimes across all wavelengths. An imprecise but systematic determination of the magnitude of objects was introduced in ancient times by Hipparchus. The scale is logarithmic and defined such that a magnitude 1 star is exactly 100 times brighter than a magnitude 6 star. Thus each step of one magnitude is \sqrt \approx 2.512 times brighter than the magnitude 1 higher. The brighter an object appears, the lower the value of its magnitude, with the brightest objects reaching negative values. Astronomers use two different definitions of magnitude: apparent magnitude and absolute magnitude. The ''apparent'' magnitude () is the brightness of an object as it appears in the night sky from Earth. Apparent magnitude depends on an object's intrinsic luminosity, its distance, and the extinction reducing its brightness. The ''absolute'' magnitu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |


.jpg)