|
1,2,3-trichloropropane
1,2,3-Trichloropropane (TCP) is an organic compound with the formula CHCl(CH2Cl)2. It is a colorless liquid that is used as a solvent and in other specialty applications. Production 1,2,3-Trichloropropane is produced by the addition of chlorine to allyl chloride. TCP also may be produced as a by-product also is produced in significant quantities as an unwanted by-product of the production of other chlorinated compounds such as epichlorohydrin and dichloropropene. Uses Historically, TCP has been used as a paint or varnish remover, a cleaning and degreasing agent, an anaesthetic and a solvent. It is also used as an intermediate in the production of hexafluoropropylene. It is a crosslinking agent for polysulfide polymers and sealants. Effects of exposure Humans can be exposed to TCP by inhaling its fumes or through skin contact and ingestion. TCP is recognized in California as a human carcinogen, and extensive animal studies have shown that it causes cancer. Short term exp ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Thiokol (polymer)
''Thiokol'' is a trade mark for various organic polysulfide polymers. Thiokol polymers are used as an elastomer in seals and sealants. The distinction between the polymers first commercialized by the Thiokol Chemical Company and subsequent polysulfide materials is often unclear. The name Thiokol is a portmanteau of the Greek words for sulfur () and glue () Preparation and structure A variety of thiokols are recognized. Typically they are prepared by the combination of 2-chloroethanol, formaldehyde, and sodium polysulfide (Na2S''x''). The chloroethanol is produced in situ from ethylene oxide and hydrogen chloride. The rank ''x'' of the polysulfide is an important variable. Crosslinking agents are used, such as 1,2,3-trichloropropane. An idealized polymer is represented by this formula HS(CH2CH2OCH2OCH2CH2SS)''n''CH2CH2OCH2OCH2CH2SH. Thiol-terminated resins can be cured oxidatively. History In 1838, Swiss chemists reported the preparation of hydrophobic rubbery materials by the a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chloroform
Chloroform, or trichloromethane (often abbreviated as TCM), is an organochloride with the formula and a common solvent. It is a volatile, colorless, sweet-smelling, dense liquid produced on a large scale as a precursor to refrigerants and polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE). Chloroform was once used as an inhalational anesthetic between the 19th century and the first half of the 20th century. It is miscible with many solvents but it is only very slightly soluble in water (only 8 g/L at 20°C). Structure and name The molecule adopts a tetrahedral molecular geometry with C3v symmetry. The chloroform molecule can be viewed as a methane molecule with three hydrogen atoms replaced with three chlorine atoms, leaving a single hydrogen atom. The name "chloroform" is a portmanteau of ''terchloride'' (tertiary chloride, a trichloride) and ''formyle'', an obsolete name for the methylylidene radical (CH) derived from formic acid. Natural occurrence Many kinds of seaweed produce chlor ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nematicide
A nematicide is a type of chemical pesticide used to kill plant- parasitic nematodes. Nematicides have tended to be broad-spectrum toxicants possessing high volatility or other properties promoting migration through the soil. Aldicarb (Temik), a carbamate insecticide marketed by Bayer CropScience, is an example of a commonly used commercial nematicide. It is important in potato production, where it has been used for control of soil-borne nematodes. Aldicarb is a cholinesterase inhibitor, which prevents the breakdown of acetylcholine in the synapse. In case of severe poisoning, the victim dies of respiratory failure. It is no longer authorised for use in the EU and, in August 2010, Bayer CropScience announced that it planned to discontinue aldicarb by 2014. Human health safety and environmental concerns have resulted in the widespread deregistration of several other agronomically important nematicides. Prior to 1985, the persistent halocarbon DBCP was a widely used nematicide and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chloroalkanes
Organochlorine chemistry is concerned with the properties of organochlorine compounds, or organochlorides, organic compounds that contain one or more carbon–chlorine Chemical bond, bonds. The chloroalkane class (alkanes with one or more hydrogens substituted by chlorine) includes common examples. The wide structural variety and divergent chemical properties of organochlorides lead to a broad range of names, applications, and properties. Organochlorine compounds have wide use in many applications, though some are of profound environmental concern, with 2,3,7,8-Tetrachlorodibenzodioxin, TCDD being one of the most notorious. Organochlorides such as trichloroethylene, tetrachloroethylene, dichloromethane and chloroform are commonly used as solvents and are referred to as "chlorinated solvents". Physical and chemical properties Chlorination reaction, Chlorination modifies the physical properties of hydrocarbons in several ways. These compounds are typically denser than water due to t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
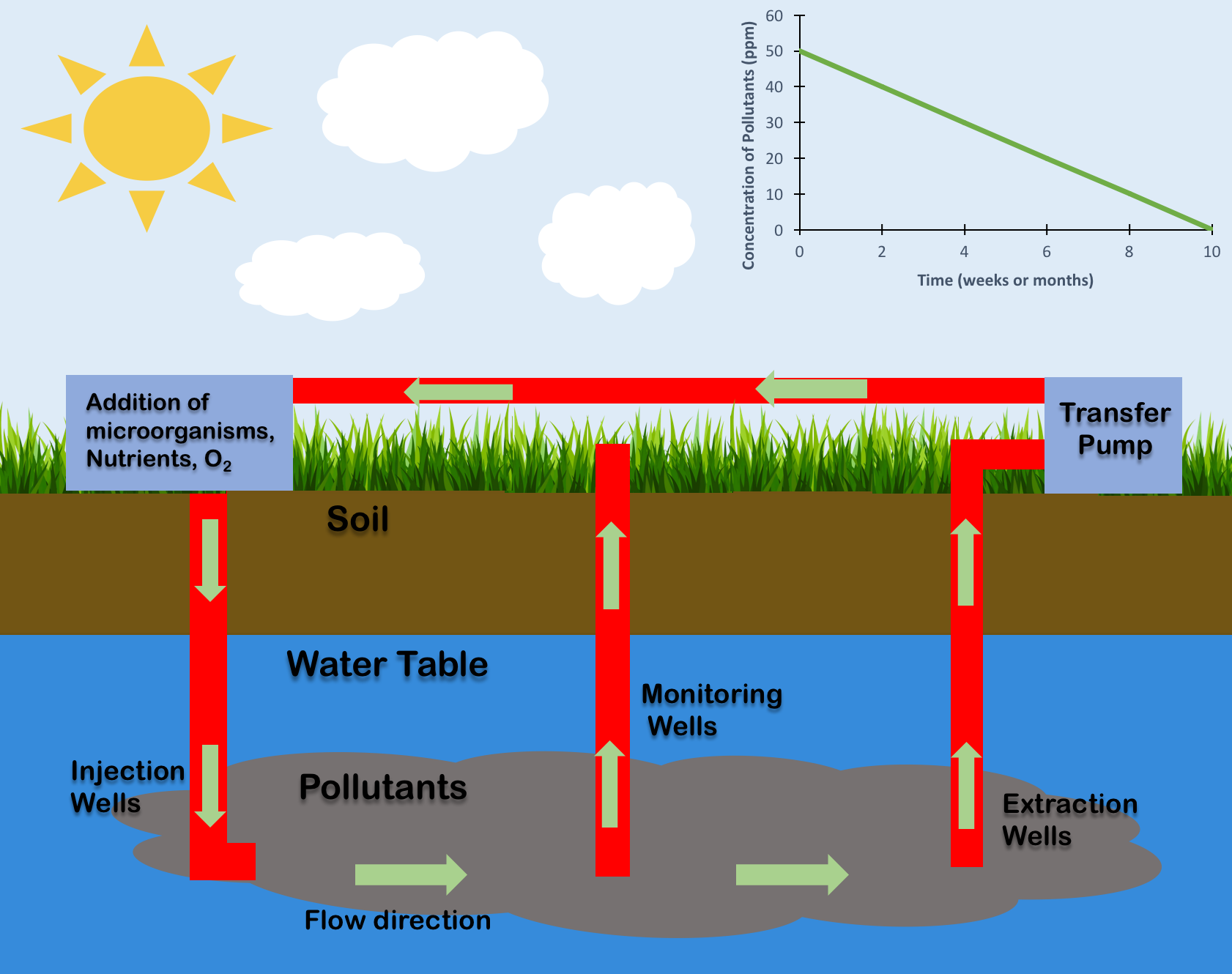
Bioremediation
Bioremediation broadly refers to any process wherein a biological system (typically bacteria, microalgae, fungi in mycoremediation, and plants in phytoremediation), living or dead, is employed for removing environmental pollutants from air, water, soil, fuel gasses, industrial effluents etc., in natural or artificial settings. The natural ability of organisms to adsorb, accumulate, and degrade common and emerging pollutants has attracted the use of biological resources in treatment of contaminated environment. In comparison to conventional physicochemical treatment methods bioremediation may offer advantages as it aims to be sustainable, eco-friendly, cheap, and scalable. This technology is rarely implemented however because it is slow or inefficient. Most bioremediation is inadvertent, involving native organisms. Research on bioremediation is heavily focused on stimulating the process by inoculation of a polluted site with organisms or supplying nutrients to promote their growt ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Permeable Reactive Barrier
A permeable reactive barrier (PRB), also referred to as a permeable reactive treatment zone (PRTZ), is a developing technology that has been recognized as being a cost-effective technology for ''in situ'' (at the site) groundwater remediation. PRBs are barriers which allow some—but not all—materials to pass through. One definition for PRBs is an ''in situ'' treatment zone that passively captures a plume of contaminants and removes or breaks down the contaminants, releasing uncontaminated water.Gillham, R.; Vogan, J.; Gui, L.; Duchene M.; Son J. (2010). Iron barrier walls for chlorinated solvent remediation. In: Stroo, H. F.; Ward, C. H. (eds.), ''In Situ'' Remediation of Chlorinated Solvent Plumes. Springer Science+Business Media, New York, NY, p. 537. The primary removal methods include: (1) sorption and precipitation, (2) chemical reaction, and (3) reactions involving biological mechanisms.Tratnyek, P. G.; M. M. Scherer; T. J. Johnson; Matheson, L.J. (2003). Permeable reactive ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
In Situ Chemical Oxidation
In situ chemical oxidation (ISCO), a form of advanced oxidation process, is an environmental remediation technique used for soil and/or groundwater remediation to lower the concentrations of targeted environmental contaminants to acceptable levels. ISCO is accomplished by introducing strong chemical oxidizers into the contaminated medium (soil or groundwater) to destroy chemical contaminants in place. It can be used to remediate a variety of organic compounds, including some that are resistant to natural degradation. The ''in situ'' in ISCO is just Latin for "in place", signifying that ISCO is a chemical oxidation reaction that occurs at the site of the contamination. The remediation of certain organic substances such as chlorinated solvents (trichloroethene and tetrachloroethene), and gasoline-related compounds (benzene, toluene, ethylbenzene, MTBE, and xylenes) by ISCO is effective. Some other contaminants can be made less toxic through chemical oxidation. A wide range of g ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dense Nonaqueous Phase Liquid
A dense non-aqueous phase liquid or DNAPL is a denser-than-water NAPL, i.e. a liquid that is both denser than water and is immiscible in or does not dissolve in water. * in situ surfactant flushing * air sparging * heating Most DNAPLs remain denser than water after they are released into the environment (e.g. spilled trichloroethene does not become lighter than water, it will remain denser than water). However, when the DNAPL is a complex mixture of chemicals, the density of the mixture can change over time as the mixture interacts with the natural environment. As an example, a mixture of trichloroethene and cutting oil may be released and originally be denser than water—a DNAPL. As the mixture of trichloroethene and oil is leached by groundwater, the trichloroethene may preferentially leach out of the oil and the mixture may become less dense than water and become buoyant (e.g. the liquid may become an LNAPL). Similarly changes can be seen at some coal gasification plants or m ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Density
Density (volumetric mass density or specific mass) is the ratio of a substance's mass to its volume. The symbol most often used for density is ''ρ'' (the lower case Greek letter rho), although the Latin letter ''D'' (or ''d'') can also be used: \rho = \frac, where ''ρ'' is the density, ''m'' is the mass, and ''V'' is the volume. In some cases (for instance, in the United States oil and gas industry), density is loosely defined as its weight per unit volume, although this is scientifically inaccurate this quantity is more specifically called specific weight. For a pure substance, the density is equal to its mass concentration. Different materials usually have different densities, and density may be relevant to buoyancy, purity and packaging. Osmium is the densest known element at standard conditions for temperature and pressure. To simplify comparisons of density across different systems of units, it is sometimes replaced by the dimensionless quantity "relative den ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Groundwater
Groundwater is the water present beneath Earth's surface in rock and Pore space in soil, soil pore spaces and in the fractures of stratum, rock formations. About 30 percent of all readily available fresh water in the world is groundwater. A unit of rock or an unconsolidated deposit is called an ''aquifer'' when it can yield a usable quantity of water. The depth at which soil pore spaces or fractures and voids in rock become completely saturated with water is called the ''water table''. Groundwater is Groundwater recharge, recharged from the surface; it may discharge from the surface naturally at spring (hydrosphere), springs and Seep (hydrology), seeps, and can form oasis, oases or wetlands. Groundwater is also often withdrawn for agricultural, municipal, and industrial use by constructing and operating extraction water well, wells. The study of the distribution and movement of groundwater is ''hydrogeology'', also called groundwater hydrology. Typically, groundwater is thought o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
United States Environmental Protection Agency
The Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) is an independent agency of the United States government tasked with environmental protection matters. President Richard Nixon proposed the establishment of EPA on July 9, 1970; it began operation on December 2, 1970, after Nixon signed an executive order. The order establishing the EPA was ratified by committee hearings in the House and Senate. The agency is led by its administrator, who is appointed by the president and approved by the Senate. The current administrator is Lee Zeldin. The EPA is not a Cabinet department, but the administrator is normally given cabinet rank. The EPA has its headquarters in Washington, D.C. There are regional offices for each of the agency's ten regions, as well as 27 laboratories around the country. The agency conducts environmental assessment, research, and education. It has the responsibility of maintaining and enforcing national standards under a variety of environmental laws, in consultat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Soil Fumigant
Fumigation is a method of pest control or the removal of harmful microorganisms by completely filling an area with gaseous pesticides, or fumigants, to suffocate or poison the pests within. It is used to control pests in buildings (structural fumigation), soil, grain, and produce. Fumigation is also used during the processing of goods for import or export to prevent the transfer of exotic organisms. Structural fumigation targets pests inside buildings (usually residences), including pests that inhabit the physical structure itself, such as woodborers and drywood termites. Commodity fumigation, on the other hand, is also to be conducted inside a physical structure, such as a storage unit, but it aims to eliminate pests from infesting physical goods, usually food products, by killing pests within the container which will house them. Each fumigation lasts for a certain duration. This is because after spraying the pesticides, or fumigants, only the pests around are eradicated. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |