|
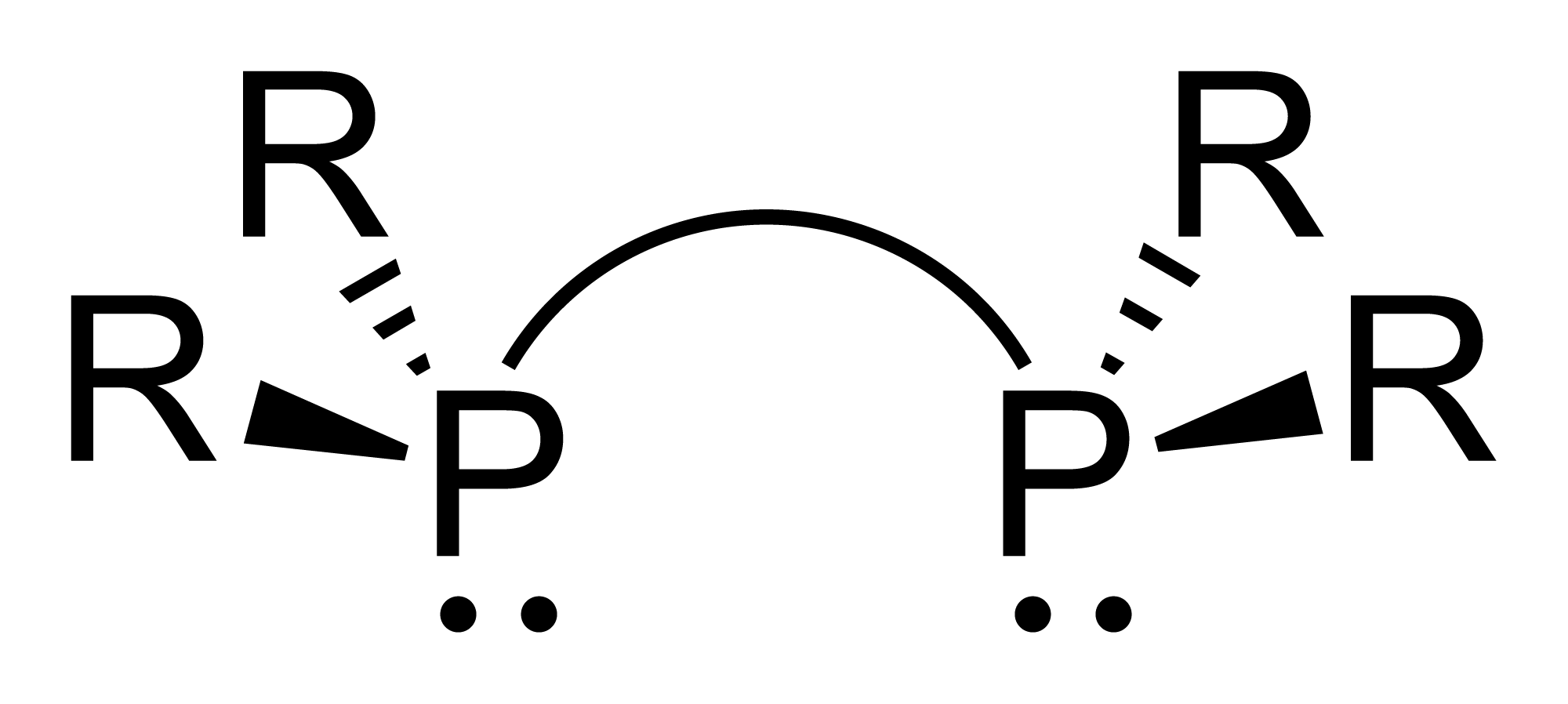
1,1-Bis(diphenylphosphino)methane
1,1-Bis(diphenylphosphino)methane (dppm), is an organophosphorus compound with the formula CH2(PPh2)2. Dppm, a white, crystalline powder, is used in inorganic and organometallic chemistry as a ligand. It is more specifically a chelating ligand because it is a ligand that can bond to metals with two phosphorus donor atoms. The natural bite angle is 73°. Synthesis and reactivity 1,1-Bis(diphenylphosphino)methane was first prepared by the reaction of sodium diphenylphosphide (Ph2PNa) with dichloromethane: :Ph3P + 2 Na → Ph2PNa + NaPh :2NaPPh2 + CH2Cl2 → Ph2PCH2PPh2 + 2 NaCl The methylene group (CH2) in dppm (and especially its complexes) is mildly acidic. The ligand can be oxidized to give the corresponding oxides and sulfides CH2 (E)Ph2sub>2 (E = O, S). The methylene group is even more acidic in these derivatives. Coordination chemistry As a chelating ligand, 1,1-bis(diphenylphosphino)methane forms a four-membered ring with the constituents MP2C. The ligand promotes the format ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
A-frame Complex
In organometallic chemistry, A-frame complexes are coordination compounds that contain two bridging bidentate ligands and a single atom bridge. They have the formula , where ''bd'' is a bidentate ligand like dppm, and X and L are a wide variety of ligands. The term was coined to describe products arising from the oxidative addition to Rh(I)Rh(I) complexes. Scope of compounds A-frame complexes typically consist of a pair of square-planar metal centres. Consequently, this family of complexes is found for those metals that tend to adopt that geometry, Rh, Ir, Ni, Pd, Pt, and Au. In addition to dppm, the analogous tetramethyldiphosphine (dmpm) also forms such complexes as do some related ligands, such as diphenyl-2-pyridylphosphine. The bridging site can be occupied by a variety of ligands, including CO, SO, NO, CH2, hydride, and chloride. Preparation A frame complexes are often produced by the addition of reagents of the type AX2 to low valent complexes of dppm: :2 M(0) ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Organophosphorus Compound
Organophosphorus compounds are organic compounds containing phosphorus. They are used primarily in pest control as an alternative to chlorinated hydrocarbons that persist in the environment. Some organophosphorus compounds are highly effective insecticides, although some are extremely toxic to humans, including sarin and VX nerve agents. Organophosphorus chemistry is the corresponding science of the properties and reactivity of organophosphorus compounds. Phosphorus, like nitrogen, is in group 15 of the periodic table, and thus phosphorus compounds and nitrogen compounds have many similar properties. The definition of organophosphorus compounds is variable, which can lead to confusion. In industrial and environmental chemistry, an organophosphorus compound need contain only an organic substituent, but need not have a direct phosphorus-carbon (P-C) bond. Thus a large proportion of pesticides (e.g., malathion), are often included in this class of compounds. Phosphorus can adopt ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Organometallics
''Organometallics'' is a biweekly journal published by the American Chemical Society. Its area of focus is organometallic and organometalloid chemistry. This peer-reviewed journal has an impact factor of 3.837 as reported by the 2021 Journal Citation Reports by Thomson Reuters. Since 2015 Paul Chirik is the editor-in-chief of ''Organometallics''. He is an American chemist and the Edwards S. Sanford Professor of Chemistry at Princeton University, and associate director for external partnerships of the Andlinger Center for Energy and the Environment. He writes about the catalysis of hydrocarbons. Past editors-in-chief are Dietmar Seyferth and John Gladysz. Retrieved on 2014-07-30. This journal is indexed in |
Chelating Ligand
Chelation is a type of bonding of ions and molecules to metal ions. It involves the formation or presence of two or more separate coordinate bonds between a polydentate (multiple bonded) ligand and a single central metal atom. These ligands are called chelants, chelators, chelating agents, or sequestering agents. They are usually organic compounds, but this is not a necessity, as in the case of zinc and its use as a maintenance therapy to prevent the absorption of copper in people with Wilson's disease. Chelation is useful in applications such as providing nutritional supplements, in chelation therapy to remove toxic metals from the body, as contrast agents in MRI scanning, in manufacturing using homogeneous catalysts, in chemical water treatment to assist in the removal of metals, and in fertilizers. Chelate effect The chelate effect is the greater affinity of chelating ligands for a metal ion than that of similar nonchelating (monodentate) ligands for the same metal. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bite Angle
In coordination chemistry the bite angle is the ligand–metal–ligand bond angle of coordination complex containing a bidentate ligand. This geometric parameter is used to classify chelation, chelating ligands, including those in organometallic complexes. It is most often discussed in terms of catalysis, as changes in bite angle can affect not just the activity and selectivity of a catalytic reaction but even allow alternative reaction pathways to become accessible. Although the parameter can be applied generally to any chelating ligand, it is commonly applied to describe diphosphine ligands, as they can adopt a wide range of bite angles. Diamines Diamines form a wide range of coordination complexes. They typically form 5- and 6-membered chelate rings. Examples of the former include ethylenediamine and 2,2'-bipyridine, 2,2′-bipyridine. Six-membered chelate rings are formed by 1,3-diaminopropane. The bite angle in such complexes is usually near 90°. Longer chain diamines, whi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lithium Diphenylphosphide
Lithium diphenylphosphide contains lithium and the organophosphorus anion with the formula (C6H5)2PLi. It is an air-sensitive solid that is used in the preparation of diphenylphosphino compounds. As an ether complex, the lithium salt is dark red. Synthesis and reactions The lithium, sodium, and potassium salts are prepared by reduction of chlorodiphenylphosphine, triphenylphosphine, or tetraphenyldiphosphine with alkali metals (M): :(C6H5)2PCl + 2 M → (C6H5)2PM + MCl :(C6H5)3P + 2 M → (C6H5)2PM + MC6H5 :(C6H5)4P2 + 2 M → 2 (C6H5)2PM They can also be obtained by deprotonation of diphenylphosphine. With water, the salts convert to diphenylphosphine: :(C6H5)2PLi + H2O → (C6H5)2PH + LiOH With halocarbons, the salts react to give tertiary phosphines: :(C6H5)2PM + RX → (C6H5)2PR + MX When treated with metal halides, lithium diphenylphosphide gives transition metal phosphido complexes. Structure Although treated as salts, alkali diphe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Encyclopedia Of Inorganic Chemistry
An encyclopedia (American English) or encyclopædia (British English) is a reference work or compendium providing summaries of knowledge either general or special to a particular field or discipline. Encyclopedias are divided into articles or entries that are arranged alphabetically by article name or by thematic categories, or else are hyperlinked and searchable. Encyclopedia entries are longer and more detailed than those in most dictionaries. Generally speaking, encyclopedia articles focus on '' factual information'' concerning the subject named in the article's title; this is unlike dictionary entries, which focus on linguistic information about words, such as their etymology, meaning, pronunciation, use, and grammatical forms.Béjoint, Henri (2000)''Modern Lexicography'', pp. 30–31. Oxford University Press. Encyclopedias have existed for around 2,000 years and have evolved considerably during that time as regards language (written in a major international or a vern ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pd2Cl2(dppm)2-from-xtal-3D-ball-stick-hybrid
PD, P.D., or Pd may refer to: Arts and media * ''People's Democracy'' (newspaper), weekly organ of the Communist Party of India (Marxist) * ''The Plain Dealer'', a Cleveland, Ohio, US newspaper * Post Diaspora, a time frame in the ''Honorverse'' series of science fiction novels * ''Principia Discordia'', a 1965 holy text in Discordianism * Production designer, a profession in film or television * Production diary, a promotional video podcast * Public domain, a copyright status Economics and business * Personnel department, of an organization * Price discrimination, a microeconomic pricing strategy * Probability of default, used in finance (Basel II) * Professional degree, or first professional degree * Professional development, learning to earn or maintain professional credentials * Program director, in service industries * Public Debt, of a government Organizations Companies * Phelps Dodge, a former American mining company, now part of Freeport-McMoRan * Polyphony Digital, d ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Diphosphines
Diphosphines, sometimes called bisphosphanes, are organophosphorus compounds most commonly used as bidentate phosphine ligands in inorganic and organometallic chemistry. They are identified by the presence of two phosphino groups linked by a backbone, and are usually chelating. A wide variety of diphosphines have been synthesized with different linkers and R-groups. Alteration of the linker and R-groups alters the electronic and steric properties of the ligands which can result in different coordination geometries and catalytic behavior in homogeneous catalysts. Synthesis 222px, Chlorodiisopropylphosphine is a popular building block for the preparation of diphosphines. From phosphide building blocks Many widely used diphosphine ligands have the general formula Ar2P(CH2)nPAr2. These compounds can be prepared from the reaction of X(CH2)nX (X=halogen) and MPPh2 (M = alkali metal): :Cl(CH2)nCl + 2 NaPPh2 → Ph2P(CH2)nPPh2 + 2 NaCl Diphosphine ligands can also be prepare ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
2-from-xtal-3D-ball-stick-hybrid.png)
(dppm)2.png)
-3D-balls.png)