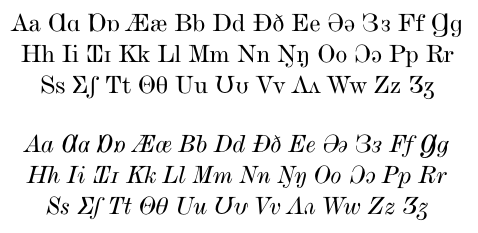|
·¥ô
The International Phonetic Alphabet (IPA) possesses a variety of obsolete and nonstandard symbols. Throughout the history of the IPA, characters representing phonetic values have been modified or completely replaced. An example is for standard . Several symbols indicating secondary articulation have been dropped altogether, with the idea that they should be indicated with diacritics: for is one. In addition, the rare voiceless implosive series has been dropped. Other characters have been added in for specific phonemes which do not possess a specific symbol in the IPA. Those studying modern Chinese phonology have used to represent the sound of ''-i'' in Pinyin ''hanzi'' which has been variously described as , , or . (See the sections ''Vowels'' and ''Syllabic consonants'' of the article Standard Chinese phonology.) There are also unsupported symbols from local traditions that find their way into publications that otherwise use the standard IPA. This is especially common ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
History Of The IPA
The International Phonetic Alphabet was created soon after the International Phonetic Association was established in the late 19th century. It was intended as an international system of phonetic transcription for oral languages, originally for pedagogical purposes. The Association was established in Paris in 1886 by French and British language teachers led by Paul Passy. The prototype of the alphabet appeared in . The Association based their alphabet upon the Romic alphabet of Henry Sweet, which in turn was based on the English Phonotypic Alphabet, Phonotypic Alphabet of Isaac Pitman and the Palaeotype alphabet, Palæotype of Alexander John Ellis. The alphabet has undergone a number of revisions during its history, the most significant being the one put forth at the Kiel Convention in 1989. Changes to the alphabet are proposed and discussed in the Association's organ, ''Journal of the International Phonetic Association'', previously known as ''Le Maître Phonétique'' and before ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
History Of The International Phonetic Alphabet
The International Phonetic Alphabet was created soon after the International Phonetic Association was established in the late 19th century. It was intended as an international system of phonetic transcription for oral languages, originally for pedagogical purposes. The Association was established in Paris in 1886 by French and British language teachers led by Paul Passy. The prototype of the alphabet appeared in . The Association based their alphabet upon the Romic alphabet of Henry Sweet, which in turn was based on the Phonotypic Alphabet of Isaac Pitman and the Palæotype of Alexander John Ellis. The alphabet has undergone a number of revisions during its history, the most significant being the one put forth at the Kiel Convention in 1989. Changes to the alphabet are proposed and discussed in the Association's organ, '' Journal of the International Phonetic Association'', previously known as ''Le Maître Phonétique'' and before that as ''The Phonetic Teacher'', and t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Case Variants Of IPA Letters
With the adoption of letters from the International Phonetic Alphabet (IPA) in various national alphabets, letter case forms have been developed. This usually means capital (uppercase) forms were developed, but in the case of the glottal stop , both uppercase and lowercase are used. The adoption of IPA letters has been particularly notable in Sub-Saharan Africa, in languages such as Hausa, Fula, Akan, Gbe languages, Manding languages, and Lingala. The most common are open o , open e , and eng , but several others are found. Kabiyé of northern Togo, for example, has (or ), as in this newspaper headline: : ''MBƱ AJƐYA KIGBƐNDƱƱ ŊGBƐYƐ KEDIƔZAƔ SƆSƆƆ TƆM SE.'' Some of the IPA letters that were adopted into language orthographies have since become obsolete in the IPA itself. Chart Following are IPA letters and their capital forms. A few of these capitals have lowercase forms that are either a variant of or distinct from the IPA letter. Others letters a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Small Capital
In typography, small caps (short for small capitals) are characters typeset with glyphs that resemble uppercase letters but reduced in height and weight close to the surrounding lowercase letters or text figures. Small caps are used in running text as a form of emphasis that is less dominant than all uppercase text, and as a method of emphasis or distinctiveness for text alongside or instead of italics, or when boldface is inappropriate. For example, the text "Text in small caps" appears as in small caps. Small caps can be used to draw attention to the opening phrase or line of a new section of text, or to provide an additional style in a dictionary entry where many parts must be typographically differentiated. Well-designed small capitals are not simply scaled-down versions of normal capitals; they normally retain the same stroke weight as other letters and have a wider aspect ratio for readability. Typically, the height of a small capital glyph will be one ex, the same he ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cyrillic
The Cyrillic script ( ) is a writing system used for various languages across Eurasia. It is the designated national script in various Slavic, Turkic, Mongolic, Uralic, Caucasian and Iranic-speaking countries in Southeastern Europe, Eastern Europe, the Caucasus, Central Asia, North Asia, and East Asia, and used by many other minority languages. , around 250 million people in Eurasia use Cyrillic as the official script for their national languages, with Russia accounting for about half of them. With the accession of Bulgaria to the European Union on 1 January 2007, Cyrillic became the third official script of the European Union, following the Latin and Greek alphabets. The Early Cyrillic alphabet was developed during the 9th century AD at the Preslav Literary School in the First Bulgarian Empire during the reign of Tsar Simeon I the Great, probably by the disciples of the two Byzantine brothers Cyril and Methodius, who had previously created the Gl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Maltese Language
Maltese (, also or ) is a Semitic languages, Semitic language derived from Siculo-Arabic, late medieval Sicilian Arabic with Romance languages, Romance Stratum (linguistics), superstrata. It is the only Semitic languages, Semitic language predominantly written in the Latin script. It is spoken by the Maltese people and is the national language of Malta, and is the only languages of the European Union, official Semitic and Afroasiatic language of the European Union. According to John L. Hayes, it descended from a Maghrebi Arabic, North African dialect of Colloquial Arabic which was introduced to Malta when the Aghlabid dynasty, Aghlabids captured it in 869/870 CE. It is also said to have descended from Siculo-Arabic, which developed as a Maghrebi Arabic dialect in the Emirate of Sicily between 831 and 1091. As a result of the Norman invasion of Malta and the subsequent history of religion in Malta#Arrival of Christianity, re-Christianization of the islands, Maltese evolved indepe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Khmer Language
Khmer ( ; , Romanization of Khmer#UNGEGN, UNGEGN: ) is an Austroasiatic language spoken natively by the Khmer people. This language is an official language and national language of Cambodia. The language is also widely spoken by Khmer people in Eastern Thailand and Isan, Thailand, as well as in the Southeast (Vietnam), Southeastern and Mekong Delta regions of Vietnam. Khmer has been influenced considerably by Sanskrit and Pali especially in the royal and religious Register (sociolinguistics), registers, through Hinduism and Buddhism, due to Old Khmer being the language of the historical empires of Chenla and Angkorian Empire, Angkor. The vast majority of Khmer speakers speak ''Central Khmer'', the dialect of the central plain where the Khmer are most heavily concentrated. Within Cambodia, regional accents exist in remote areas but these are regarded as varieties of Central Khmer. Two exceptions are the speech of the capital, Phnom Penh, and that of the Khmer Khe in Stung Treng ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Malayo–Polynesian Languages
The Malayo-Polynesian languages are a subgroup of the Austronesian languages, with approximately 385.5 million speakers. The Malayo-Polynesian languages are spoken by the Austronesian peoples outside of Taiwan, in the island nations of Southeast Asia (Indonesia and the Philippine Archipelago) and the Pacific Ocean, with a smaller number in continental Asia in the areas near the Malay Peninsula, with Cambodia, Vietnam and the Chinese island Hainan as the northwest geographic outlier. Malagasy, spoken on the island of Madagascar off the eastern coast of Africa in the Indian Ocean, is the furthest western outlier. Many languages of the Malayo-Polynesian family in insular Southeast Asia show the strong influence of Sanskrit, Tamil and Arabic, as the western part of the region has been a stronghold of Hinduism, Buddhism, and, later, Islam. Two morphological characteristics of the Malayo-Polynesian languages are a system of affixation and reduplication (repetition of all or part of a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Q With Hook Tail
Q with hook tail (majuscule: …ä, minuscule: …ã) is a letter of the extended Latin alphabet. It was introduced by Lutheran missionaries in Papua New Guinea for use in the Numanggang language in the 1930s or 1940s. In 2002, it was decided to discontinue using the letter. , Lorna A. Priest, 2004. It is still used in the K√¢te language to represent a . (Latin Q is voiceless ) The [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tenuis Consonant
In linguistics, a tenuis consonant ( or ) is an obstruent that is voiceless, unaspirated and unglottalized. In other words, it has the "plain" phonation of with a voice onset time close to zero (a zero-VOT consonant), as Spanish ''p, t, ch, k'' or English ''p, t, k'' after ''s'' (''spy, sty, sky''). For most languages, the distinction is relevant only for stops and affricates. However, a few languages have analogous series for fricatives. Mazahua, for example, has ejective, aspirated, and voiced fricatives alongside tenuis , parallel to stops alongside tenuis . Many click languages have tenuis click consonants alongside voiced, aspirated, and glottalized series. Transcription In transcription, tenuis consonants are not normally marked explicitly, and consonants written with voiceless IPA letters, such as , are typically assumed to be unaspirated and unglottalized unless otherwise indicated. However, aspiration is often left untranscribed if no contrast needs to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bilabial Click
The bilabial clicks are a family of click consonants that sound like a smack of the lips. They are found as phonemes only in the small Tuu language family (currently two languages, one down to its last speaker), in the ǂ’Amkoe language of Botswana (also moribund), and in the extinct Damin ritual jargon of Australia. However, bilabial clicks are found paralinguistically for a kiss in various languages, including integrated into a greeting in the Hadza language of Tanzania, and as allophones of labial–velar stops in some West African languages (Ladefoged 1968), as of /mw/ in some of the languages neighboring Shona, such as Ndau and Tonga. The symbol in the International Phonetic Alphabet that represents the place of articulation of these sounds is . This may be combined with a second letter to indicate the manner of articulation, though this is commonly omitted for tenuis clicks. An uncommon para-IPA letter for bilabial clicks is a turned ''b'' with hook, . Bilab ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Apostrophe
The apostrophe (, ) is a punctuation mark, and sometimes a diacritical mark, in languages that use the Latin alphabet and some other alphabets. In English, the apostrophe is used for two basic purposes: * The marking of the omission of one or more letters, e.g. the contraction (grammar), contraction of "do not" to "don't" * The marking of Possessive, possessive case of nouns (as in "the eagle's feathers", "in one month's time", "the twins' coats") It is also used in a few exceptional cases for the #Use in forming some plurals, marking of plurals, e.g. "p's and q's" or Oakland A's. The same mark is used as a single quotation mark. It is also substituted informally for other marks for example instead of the prime symbol to indicate the units of foot (unit), foot or minutes of arc. The word ''apostrophe'' comes from the Ancient Greek language, Greek (hē apóstrophos [prosōidía], '[the accent of] turning away or elision'), through Latin language, Latin and French language, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |