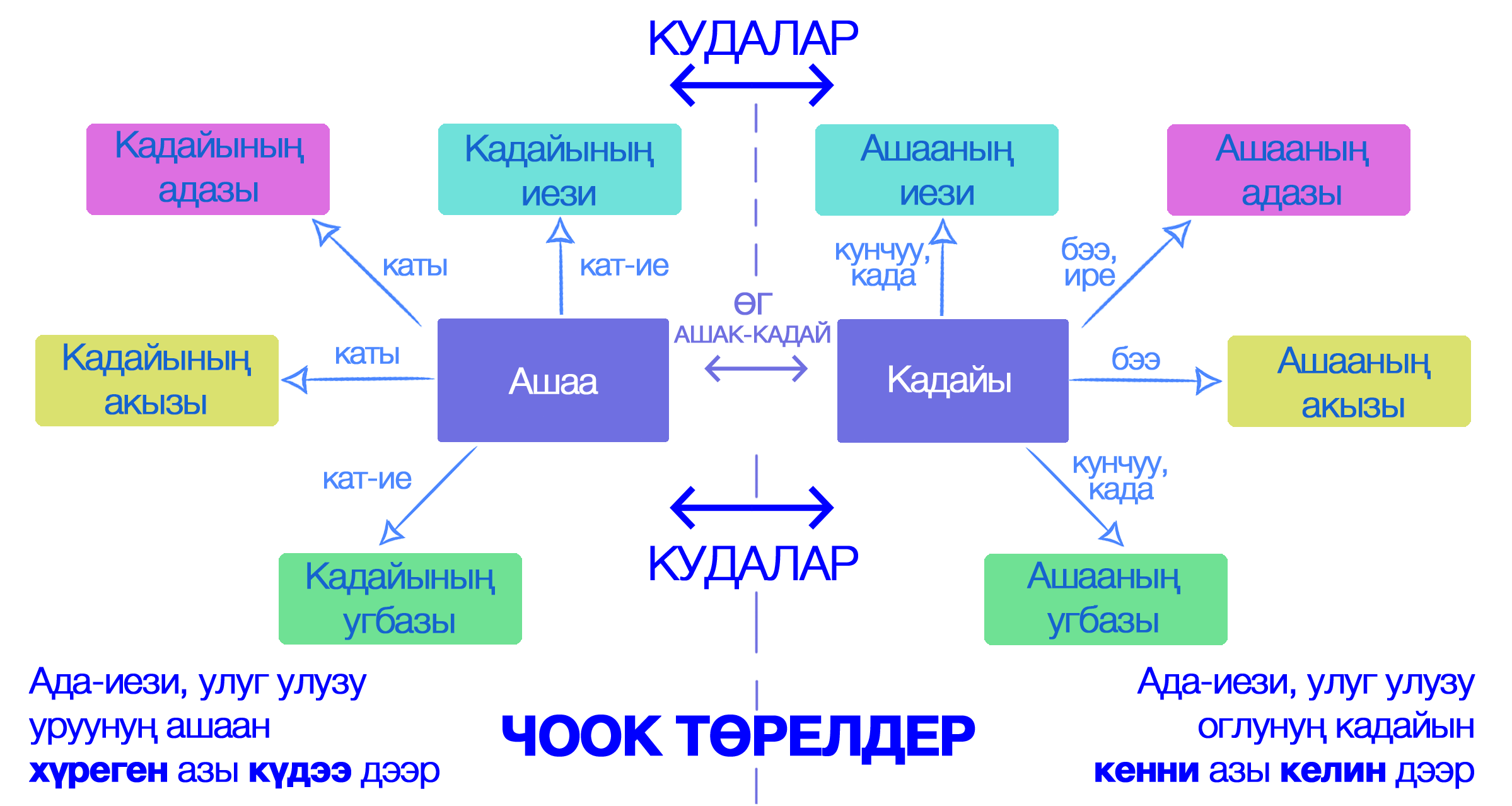
|
Cyrillic Script
The Cyrillic script ( ) is a writing system used for various languages across Eurasia. It is the designated national script in various Slavic languages, Slavic, Turkic languages, Turkic, Mongolic languages, Mongolic, Uralic languages, Uralic, Caucasian languages, Caucasian and Iranian languages, Iranic-speaking countries in Southeastern Europe, Eastern Europe, the Caucasus, Central Asia, North Asia, and East Asia, and used by many other minority languages. , around 250 million people in Eurasia use Cyrillic as the official script for their national languages, with Russia accounting for about half of them. With the accession of Bulgaria to the European Union on 1 January 2007, Cyrillic became the third official script of the Languages of the European Union#Writing systems, European Union, following the Latin script, Latin and Greek alphabet, Greek alphabets. The Early Cyrillic alphabet was developed during the 9th century AD at the Preslav Literary School in the First Bulga ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cyrillic
The Cyrillic script ( ) is a writing system used for various languages across Eurasia. It is the designated national script in various Slavic, Turkic, Mongolic, Uralic, Caucasian and Iranic-speaking countries in Southeastern Europe, Eastern Europe, the Caucasus, Central Asia, North Asia, and East Asia, and used by many other minority languages. , around 250 million people in Eurasia use Cyrillic as the official script for their national languages, with Russia accounting for about half of them. With the accession of Bulgaria to the European Union on 1 January 2007, Cyrillic became the third official script of the European Union, following the Latin and Greek alphabets. The Early Cyrillic alphabet was developed during the 9th century AD at the Preslav Literary School in the First Bulgarian Empire during the reign of Tsar Simeon I the Great, probably by the disciples of the two Byzantine brothers Cyril and Methodius, who had previously created the Gl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Buryat Language
Buryat or Buriat, known in foreign sources as the Bargu-Buryat dialect of Mongolian, and in pre-1956 Soviet sources as Buryat-Mongolian, is a variety of the Mongolic languages spoken by the Buryats and Bargas that is classified either as a language or major dialect group of Mongolian. Geographic distribution The majority of Buryat speakers live in Russia along the northern border of Mongolia. In Russia, it is an official language in the Republic of Buryatia and was an official language in the former Ust-Orda Buryatia and Aga Buryatia autonomous okrugs. In the Russian census of 2002, 353,113 people out of an ethnic population of 445,175 reported speaking Buryat (72.3%). Some other 15,694 can also speak Buryat, mostly ethnic Russians. Buryats in Russia have a separate literary standard, written in a Cyrillic alphabet. It is based on the Russian alphabet with three additional letters: Ү/ү, Ө/ө and Һ/һ. There are at least 100,000 ethnic Buryats in Mongolia and Inne ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Karakalpak Language
Karakalpak () is a Turkic language spoken by Karakalpaks in Karakalpakstan. It is divided into two dialects, Northeastern Karakalpak and Southwestern Karakalpak. It developed alongside Nogai and neighbouring Kazakh languages, being markedly influenced by both. Typologically, Karakalpak belongs to the Kipchak branch of the Turkic languages, thus being closely related to and highly mutually intelligible with Kazakh and Nogai. Classification Karakalpak is a member of the Kipchak branch of Turkic languages, which includes Kazakh, Bashkir, Tatar, Kumyk, Karachay, Nogai and Kyrgyz. Due to its proximity to Turkmen and Uzbek, some of Karakalpak's vocabulary and grammar has been influenced by Uzbek and Turkmen. Like the vast majority of Turkic languages, Karakalpak has vowel harmony, is agglutinative and has no grammatical gender. Word order is usually subject–object–verb. Geographic distribution Karakalpak is spoken mainly in the Karakalpakstan Autonomous Republic of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kalmyk Language
Kalmyk Oirat (, ), also known as the Kalmyk language () and formerly anglicized as Calmuck, is a Variety (linguistics), variety of the Oirat language, natively spoken by the Kalmyks, Kalmyk people of Kalmykia, a federal subject of Russia. In Russia, it is the standard language, standard form of the Oirat Mongolian (based on the Torgut Oirat, Torgut dialect), which belongs to the Mongolic languages, Mongolic language family. The Kalmyk people of the Northwest Caspian Sea of Russia claim descent from the Oirats from Eurasia, who have also historically settled in Mongolia and Northwest China. According to UNESCO, the language is "definitely endangered". сән /sæn/. Nevertheless, in inflected forms of such words, short vowels tend to become elongated: сән /sæn/ "good" > сәәг /sæːgə/ "good-", күн /kyn/ "man"> күүнә /kyːnæ/ "man-". Despite that, long vowels still may be pronounced in non-initial syllables. This happens if a word consists of three syllables, sec ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bashkir Language
Bashkir ( , ) or Bashkort (, ) is a Turkic languages, Turkic language belonging to the Kipchak languages, Kipchak branch. It is official language#Political alternatives, co-official with Russian language, Russian in Bashkortostan. Bashkir has approximately 750,000 native speakers. It has two dialect groups: Southern and Eastern. Bashkir has native speakers in Russia, as well as in Ukraine, Belarus, Kazakhstan, Uzbekistan, Estonia and other neighboring post-Soviet states, and among the Bashkirs, Bashkir diaspora. Speakers Speakers of Bashkir mostly live in the republic of Bashkortostan (a republic within the Russian Federation). Many speakers also live in Tatarstan, Chelyabinsk Oblast, Chelyabinsk, Orenburg Oblast, Orenburg, Tyumen Oblast, Tyumen, Sverdlovsk Oblast, Sverdlovsk and Kurgan Oblasts and other regions of Russia. Minor Bashkir groups also live in Kazakhstan and the United States. In a recent local media report in Bashkortostan, it was reported that some officials of t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tuvan Language
Tuvan, also spelt Tyvan, is a Turkic language spoken in the Republic of Tuva in South Central Siberia, Russia. There are small groups of Tuvans that speak distinct dialects of Tuvan in China and Mongolia. History The earliest record of Tuvan is from the early 19th century by ''Wūlǐyǎsūtái zhìlüè'' (), Julius Klaproth 1823, Matthias Castrén 1857, Nikolay Katanov, Vasily Radlov, etc. The name Tuva goes back as early as the publication of ''The Secret History of the Mongols''. The Tuva (as they refer to themselves) have historically been referred to as Soyons, Soyots or Uriankhais. Classification Tuvan (also spelled Tyvan) is linguistically classified as a Sayan Turkic language. Its closest relative is the moribund Tofa. Tuvan, as spoken in Tuva, is principally divided into four dialect groups; Western, Central, Northeastern, Southeastern. * Central: forms the basis of the literary language and includes Ovyur and Bii-Khem subdialects. The geographical c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Yakut Language
The Yakut language ( ), also known as the Sakha language ( ) or Yakutian, is a Siberian Turkic language spoken by around 450,000 native speakers—primarily by ethnic Yakuts. It is one of the official languages of the Sakha Republic, a republic in the Russian Federation. The Yakut language has a large number of loanwords of Mongolic origin, a layer of vocabulary of unclear origin, as well as numerous recent borrowings from Russian. Like other Turkic languages, Yakut is an agglutinative language and features vowel harmony. Classification Yakut is a member of the Northeastern Common Turkic family of languages, which also includes Shor, Tuvan and Dolgan. Like most Turkic languages, Yakut has vowel harmony, is agglutinative and has no grammatical gender. Word order is usually subject–object–verb. Yakut has been influenced by Tungusic and Mongolian languages. Historically, Yakut left the community of Common Turkic speakers relatively early. Due to this, it diverge ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Uilta Language
Uilta (, also called Ulta, Ujlta, or Orok) is a Tungusic language spoken in the Poronaysky and Nogliksky Administrative Divisions of Sakhalin Oblast, in the Russian Federation, by the Uilta people. The northern Uilta who live along the river of Tym’ and around the village of Val have reindeer herding as one of their traditional occupations. The southern Uilta live along the Poronay near the city of Poronaysk. The two dialects come from the northern and eastern groups, however, they have very few differences. Classification Uilta is closely related to Nanai, and is classified within the southern branch of the Tungusic languages. Classifications which recognize an intermediate group between the northern and southern branch of Manchu-Tungus classify Uilta (and Nanai) as Central Tungusic. Within Central Tungusic, Glottolog groups Uilta with Ulch as "Ulchaic", and Ulchaic with Nanai as "Central-Western Tungusic" (also known as the "Nanai group"), while Oroch, Kilen and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fita
Fita (Ѳ ѳ; italics: ''Ѳ ѳ'') is a letter of the Early Cyrillic alphabet. The shape and the name of the letter are derived from the Θ, Greek letter theta (Θ θ). In the ISO 9 system, Ѳ is romanized using F grave accent (F̀ f̀). In the Cyrillic numerals, Cyrillic numeral system, Fita has a numerical value of 9. Shape In traditional (Church Slavonic) typefaces, the central line is typically about twice the width of the letter's body and has serifs similar to those on the letter Te (Cyrillic), Т: . Sometimes the line is drawn as low as the baseline, which makes the letter difficult to distinguish from De (Cyrillic), Д. Usage Old Russian and Church Slavonic The traditional Russian name of the letter is ''fitá'' (or, in pre-1918 spelling, ѳита́). Fita was mainly used to write proper names and loanwords derived from or via Greek. Russians pronounced these names with the sound instead of (like the pronunciation of in "thin"), for example "Theodor ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
ISO 9
ISO 9 is an international standard establishing a system for the transliteration into Latin characters of Cyrillic characters constituting the alphabets of many Slavic and non-Slavic languages. Published on February 23, 1995 by the International Organization for Standardization, the major advantage ISO 9 has over other competing systems is its univocal system of one character for one character equivalents (by the use of diacritics), which faithfully represents the original spelling and allows for reverse transliteration, even if the language is unknown. Earlier versions of the standard, ISO/R 9:1954, ISO/R 9:1968 and ISO 9:1986, were more closely based on the international scholarly system for linguistics ( scientific transliteration), but have diverged in favour of unambiguous transliteration over phonemic representation. The edition of 1995 supersedes the edition of 1986. ISO 9:1995 The standard features three mapping tables: the first covers contemporary Slavic languages, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Yañalif
The New Turkic Alphabet or Yañalif ( Tatar: jaꞑa əlifba/yaña älifba → jaꞑalif/yañalif, , Cyrillic: Яңалиф, "new alphabet"), is the first Latin alphabet used during the latinisation in the Soviet Union in the 1930s for the Turkic languages. It replaced the Arabic script-based alphabets like Yaña imlâ used for Tatar in 1928, and was replaced by the Cyrillic alphabet in 1938–1940. After their respective independence in 1991, several former Soviet states in Central Asia switched back to Latin script, with slight modifications to the original Yañalif. There are 33 letters in Yañalif, nine of which are vowels. The apostrophe (') is used for the glottal stop (həmzə or hämzä) and is sometimes considered a letter for the purposes of alphabetic sorting. Other characters may also be used in spelling foreign names. The lowercase form of the letter B is ʙ (small caps B), to prevent confusion with Ь ь (I with bowl). Letter No. 33, similar to Zhuang Ƅ, is not ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |