|
čģčī
The following multigraphs are used in the Cyrillic script. The palatalized consonants of Russian and other languages written as C- are mostly predictable and therefore not included here unless they are irregular. Likewise, in the languages of the Caucasus, there are numerous other predictable multigraphs that are not included. These include doubled letters (or whole digraphs) that indicate ' tense' ('strong') consonants and long vowels; sequences with , , for labialized consonants; and sequences with or for ejective consonants or pharyngealized consonants and vowels. Tatar also has discontinuous digraphs. See Cyrillic digraphs for examples. ąÉ : * Archi: : * Archi: : * Dungan: : * Chechen: * Ingush: * Tabasaran: : * Archi: ąō : * Abaza: * Archi: * Lezgian: : * Tabasaran: : * Adyghe: * Kabardian: * Ossetian: * Also found in several other languages where is used for labialization (though this is a predictable effect of assimilation, and th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chechen Language
Chechen (, ) (, , ) is a Northeast Caucasian language spoken by 2 million people, mostly in the Chechen Republic and by members of the Chechen diaspora throughout Russia and the rest of Europe, Jordan, Central Asia (mainly Kazakhstan and Kyrgyzstan) and Georgia. Classification Chechen is a Northeast Caucasian language. Together with the closely related Ingush, with which there exists a large degree of mutual intelligibility and shared vocabulary, it forms the Vainakh branch. Dialects There are a number of Chechen dialects: Ehki, Chantish, Chebarloish, Malkhish, Nokhchmakhkakhoish, Orstkhoish, Sharoish, Shuotoish, Terloish, Itum-Qalish and Himoish. The Kisti dialect of Georgia is not easily understood by northern Chechens without a few days' practice. One difference in pronunciation is that Kisti aspirated consonants remain aspirated when they are doubled (fortis) or after /s/, but they then lose their aspiration in other dialects. Dialects of Chechen can be classified by t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
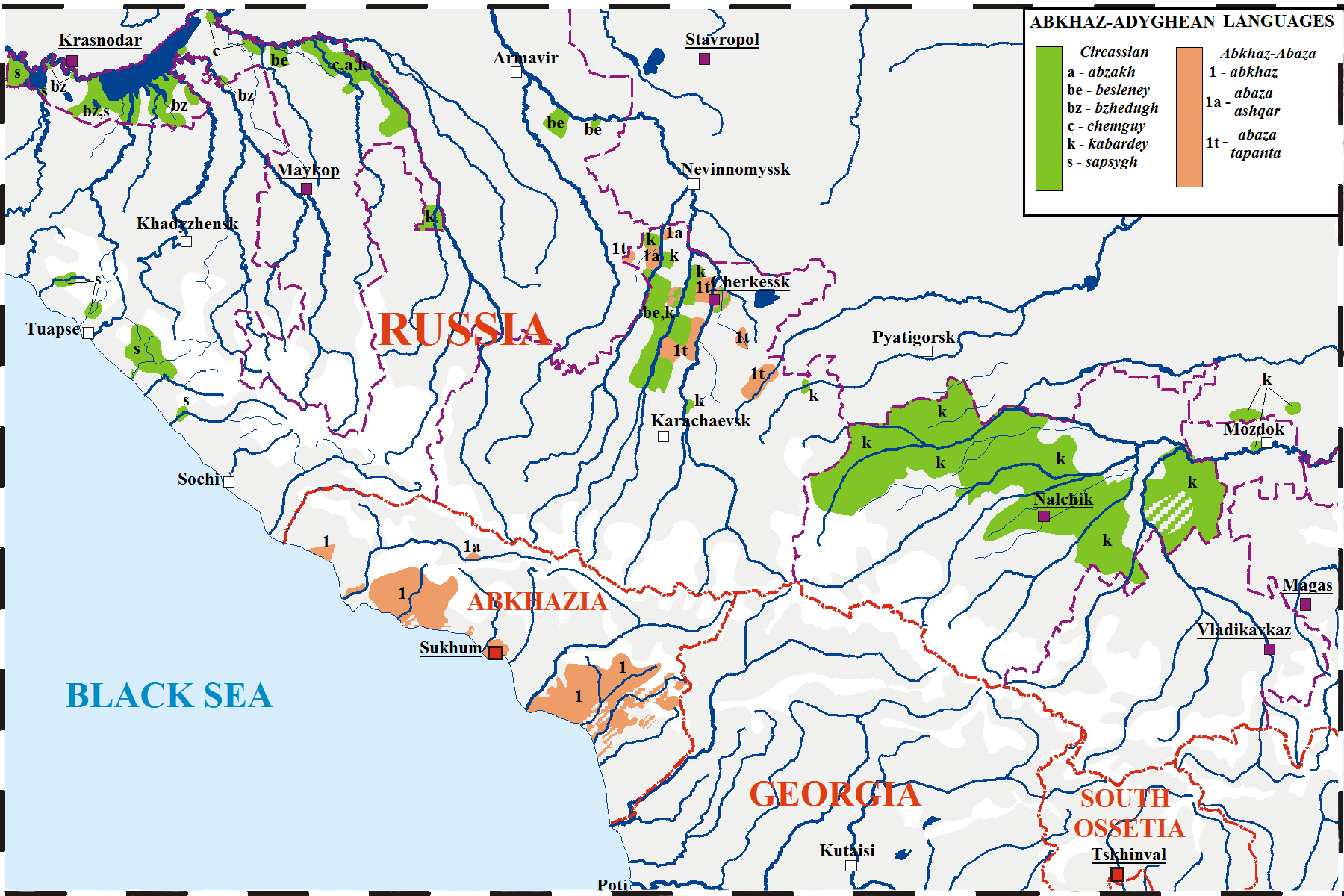
Adyghe Language
Adyghe ( or ; ady, ąÉą┤čŗą│ą░ą▒ąĘčŹ, Adygabz╔Ö, ), also known as West Circassian ( ady, link=no, ą║ėÅą░čģčŗą▒ąĘčŹ, khaxybz╔Ö), is a Northwest Caucasian language spoken by the western subgroups of Circassians. It is spoken mainly in Russia, as well as in Turkey, Jordan, Syria and Israel, where they settled after the Circassian genocide. It is closely related to the Kabardian (East Circassian) language, though some reject the distinction between the two languages in favor of both being dialects of a unitary Circassian language. The literary language is based on the Temirgoy dialect. Adyghe and Russian are the two official languages of the Republic of Adygea in the Russian Federation. There are around 128,000 speakers of Adyghe in Russia, almost all of them native speakers. In total, some 300,000 speak it worldwide. The largest Adyghe-speaking community is in Turkey, spoken by the diaspora from the RussianŌĆōCircassian War (ŌĆō1864). In addition, the Adyghe language is spoke ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cyrillic Digraphs
The Cyrillic script family contains many specially treated two-letter combinations, or digraphs, but few of these are used in Slavic languages. In a few alphabets, trigraphs and even the occasional tetragraph or pentagraph are used. In early Cyrillic, the digraphs and were used for . As with the equivalent digraph in Greek, they were reduced to a typographic ligature, , and are now written . The modern letters and started out as digraphs, and . In Church Slavonic printing practice, both historical and modern, (which is considered as a letter from the alphabet's point of view) is mostly treated as two individual characters, but is a single letter. For example, letter-spacing affects as if they were two individual letters, and never affects components of . In a context of Old Slavonic language, is a digraph that can replace a letter and vice versa. Modern Slavic languages written in the Cyrillic alphabet make little or no use of digraphs. There are only two true dig ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Abkhaz Language
Abkhaz ( ; ), sometimes spelled Abxaz and also known as Abkhazian, is a Northwest Caucasian language most closely related to Abaza. It is spoken mostly by the Abkhaz people. It is one of the official languages of Abkhazia, where around 100,000 people speak it. Furthermore, it is spoken by thousands of members of the Abkhazian diaspora in Turkey, Georgia's autonomous republic of Adjara, Syria, Jordan, and several Western countries. 27 October is the day of the Abkhazian language in Georgia. Classification Abkhaz is a Northwest Caucasian language and is thus related to Adyghe. The language of Abkhaz is especially close to Abaza, and they are sometimes considered dialects of the same language,''B. G. Hewitt Abkhaz 1979;'' page 1. Abazgi, of which the literary dialects of Abkhaz and Abaza are simply two ends of a dialect continuum. Grammatically, the two are very similar; however, the differences in phonology are substantial, it also contains elements characteristic of Kabar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Archi Language
Archi is a Northeast Caucasian language spoken by the Archis in the village of Archib, southern Dagestan, Russia, and the six surrounding smaller villages. It is unusual for its many phonemes and for its contrast between several voiceless velar lateral fricatives, , voiceless and ejective velar lateral affricates, , and a voiced velar lateral fricative, . It is an ergativeŌĆōabsolutive language with four noun classesThe Archi language tutorial, presenting an overview of the grammar of Archi and has a remarkable morphological system with irregularities on all levels. Mathematically, there are 1,502,839 possible |
Kabardian Language
Kabardian (; ; ), also known as , is a Northwest Caucasian language closely related to the Adyghe (West Circassian) language. Circassian nationalists reject the distinction between the two languages and refer to them both as " Circassian". It is spoken mainly in parts of the North Caucasus republics of Kabardino-Balkaria and Karachay-Cherkessia (Eastern Circassia), and in Turkey, Jordan and Syria (the extensive post-war diaspora). It has 47 or 48 consonant phonemes, of which 22 or 23 are fricatives, depending upon whether one counts as phonemic, but it has only 3 phonemic vowels. It is one of very few languages to possess a clear phonemic distinction between ejective affricates and ejective fricatives. The Kabardian language has two major dialects: Kabardian and Besleney. Some linguists argue that Kabardian is only one dialect of an overarching Adyghe or Circassian language, which consists of all of the dialects of Adyghe and Kabardian together, and the Kabardians ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Avar Language
Avar (, , "language of the mountains" or , , "Avar language"), also known as Avaric, is a Northeast Caucasian language of the AvarŌĆōAndic subgroup that is spoken by Avars, primarily in Dagestan. In 2010, there were approximately 1 million speakers in Dagestan and elsewhere in Russia. Geographic distribution It is spoken mainly in the western and southern parts of the Russian Caucasus republic of Dagestan, and the Balaken, Zaqatala regions of north-western Azerbaijan. Some Avars live in other regions of Russia. There are also small communities of speakers living in the Russian republics of Chechnya and Kalmykia; in Georgia, Kazakhstan, Ukraine, Jordan, and the Marmara Sea region of Turkey. It is spoken by about 762,000 people worldwide. UNESCO classifies Avar as vulnerable to extinction. Status It is one of six literary languages of Dagestan, where it is spoken not only by the Avar, but also serves as the language of communication between different ethnic groups. Dialec ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lezgian Language
Lezgin , also called Lezgi or Lezgian, is a Northeast Caucasian language. It is spoken by the Lezgins, who live in southern Dagestan (Russia); northern Azerbaijan; and to a much lesser degree Turkmenistan; Uzbekistan; Kazakhstan; Turkey, and other countries. It is a much-written literary language and an official language of Dagestan. It is classified as "vulnerable" by UNESCO's Atlas of the World's Languages in Danger. Geographic distribution In 2002, Lezgian was spoken by about 397,000 people in Russia, mainly Southern Dagestan; in 1999 it was spoken by 178,400 people in mainly the Qusar, Quba, Qabala, Oghuz, Ismailli and Khachmaz ''(Xa├¦maz)'' provinces of northeastern Azerbaijan. Lezgian is also spoken in Kazakhstan, Kyrgyzstan, Turkey, Turkmenistan, Ukraine, Germany and Uzbekistan by immigrants from Azerbaijan and Dagestan. Some speakers are in the Balikesir, Yalova, Izmir, Bursa regions of Turkey especially in Kirne (Ortaca), a village in Balikesir Province whi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aghul Language
Aghul is a Northeast Caucasian language spoken by the Aghuls in southern Dagestan, Russia and in Azerbaijan. It is spoken by about 29,300 people (2010 census). Classification Aghul belongs to the Eastern Samur group of the Lezgic branch of the Northeast Caucasian language family. Geographic distribution In 2002, Aghul was spoken by 28,300 people in Russia, mainly in Southern Dagestan, as well as 32 people in Azerbaijan. Related languages There are nine languages in the Lezgian language family, namely: Aghul, Tabasaran, Rutul, Lezgian, Tsakhur, Budukh, Kryts, Udi and Archi. Phonology Aghul has contrastive epiglottal consonants. Aghul makes, like many Northeast Caucasian languages, a distinction between tense consonants with concomitant length and weak consonants. The tense consonants are characterized by the intensiveness (tension) of articulation, which naturally leads to a lengthening of the consonant so they are traditionally transcribed with the length diacritic. The ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ingush Language
Ingush (; , , pronounced ) is a Northeast Caucasian language spoken by about 500,000 people, known as the Ingush, across a region covering the Russian republics of Ingushetia and Chechnya. Classification Ingush and Chechen, together with Bats, constitute the Nakh branch of the Northeast Caucasian language family. There is pervasive passive bilingualism between Ingush and Chechen. Geographic distribution Ingush is spoken by about 413,000 people (2002), primarily across a region in the Caucasus covering parts of Russia, primarily Ingushetia and Chechnya. Speakers can also be found in Kazakhstan, Uzbekistan, Turkmenistan, Belgium, Norway, Turkey and Jordan. Official status Ingush is, alongside Russian, an official language of Ingushetia, a federal subject of Russia. Writing system Ingush became a written language with an Arabic-based writing system at the beginning of the 20th century. After the October Revolution it first used a Latin alphabet, which was later replaced by Cyrill ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Abaza Language
Abaza (, ; ady, ą░ą▒ą░ąĘ菹▒ąĘčŹ) is a Northwest Caucasian language spoken by Abazins in Russia and many of the exiled communities in Turkey. The language has gone through several different orthographies based primarily on Arabic, Roman, and Cyrillic letters. Its consonant to vowel ratio is remarkably high; making it quite similar to many other languages from the same parent chain. The language evolved in popularity in the mid to late 1800s, but has become an endangered language. Abaza is spoken by approximately 35,000 people in Russia, where it is written in a Cyrillic alphabet, as well as another 10,000 in Turkey, where the Latin script is used. It consists of two dialects, the Ashkherewa dialect and the T'ap'anta dialect, which is the literary standard. The language also consists of five sub dialects known as Psyzh-Krasnovostok, Abazakt, Apsua, Kubin-Elburgan and Kuvin. Abaza, like its relatives in the family of Northwest Caucasian languages, is a highly agglutinative langu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tabasaran Language
Tabasaran (also written Tabassaran) is a Northeast Caucasian language of the Lezgic branch. It is spoken by the Tabasaran people in the southern part of the Russian Republic of Dagestan. There are two main dialects: North (Khanag) and South Tabasaran. It has a literary language based on the Southern dialect, one of the official languages of Dagestan. Tabasaran is an ergative language. The verb system is relatively simple; verbs agree with the subject in number, person and (in North Tabasaran) class. North Tabasaran has two noun classes (also dubbed with the term "grammatical gender"), whereas Southern Tabasaran lacks noun classes. Geographical distribution It is spoken in the basin of Upper Rubas-nir and Upper Chirakh-nir. Phonology Consonants The post-alveolar sibilants may be whistled. Vowels Vowel sounds of Tabasaran are , y, ╔ø, ├”, ╔æ, u Writing system Tabasaran is written using Cyrillic since 1938 (from 1928 to 1938 the Latin alphabet was used as a base fo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |