|
Žł Persei
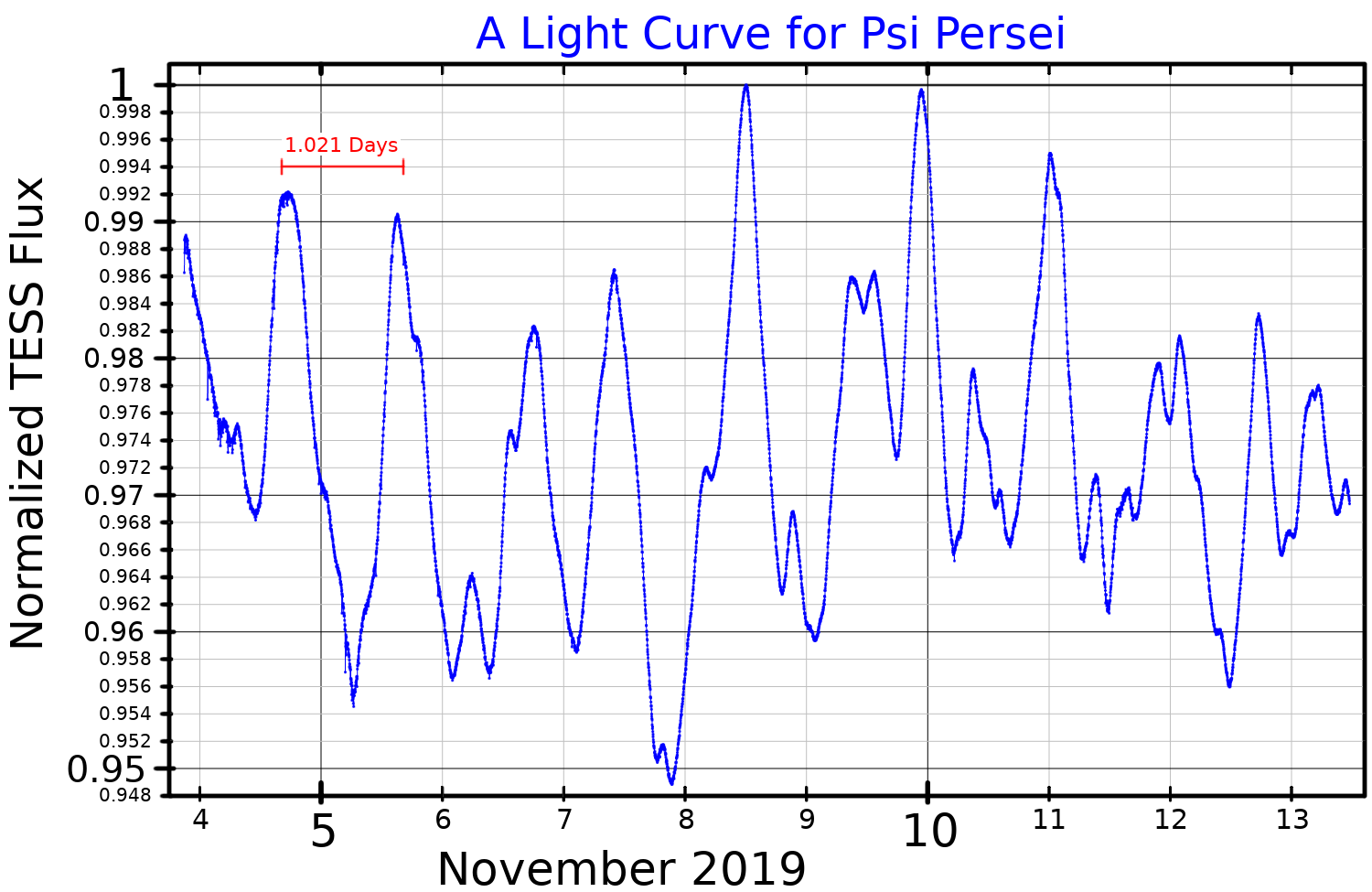
Psi Persei (Psi Per, Žł Persei, Žł Per) is a single Be star in the northern constellation of Perseus. It has an apparent visual magnitude of about 4.2, so it is visible to the naked eye at night under suitably dark skies. Based on parallax measurements, it is located at a distance of roughly from the Earth. Properties This star has a stellar classification of B5Ve, which indicates it is a B-type main sequence star that is generating energy at its core through the nuclear fusion of hydrogen. It is a shell star with a circumstellar disc of gas surrounding the equator and extending out to about 11 times the radius of the star. As a result of this disc, the spectrum of this star shows emission lines (as indicated by the 'e' in the stellar class) and its magnitude varies over a period 1.021 days. The General Catalog of Variable Stars classifies Psi Persei as a gamma Cassiopeiae variable star, whose visual band brightness varies from magnitude 4.17 to 4.28. Ps ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Perseus (constellation)
Perseus is a constellation in the Northern celestial hemisphere, northern sky, being named after the Greek mythology, Greek mythological hero Perseus. It is one of the 48 ancient constellations listed by the 2nd-century astronomer Ptolemy, and among the IAU designated constellations, 88 modern constellations defined by the International Astronomical Union (IAU). It is located near several other constellations named after ancient Greek legends surrounding Perseus, including Andromeda (constellation), Andromeda to the west and Cassiopeia (constellation), Cassiopeia to the north. Perseus is also bordered by Aries (constellation), Aries and Taurus (constellation), Taurus to the south, Auriga (constellation), Auriga to the east, Camelopardalis to the north, and Triangulum to the west. Some Celestial cartography, star atlases during the early 19th century also depicted Perseus holding the disembodied head of Medusa, whose Asterism (astronomy), asterism was named together as ''Perseus e ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
B-type Main Sequence Star
A B-type main-sequence star (B V) is a main-sequence (hydrogen-burning) star of spectral type B and luminosity class V. These stars have from 2 to 16 times the mass of the Sun and surface temperatures between 10,000 and 30,000 K. B-type stars are extremely luminous and blue. Their spectra have neutral helium, which are most prominent at the B2 subclass, and moderate hydrogen lines. Examples include Regulus and Algol A. This class of stars was introduced with the Harvard sequence of stellar spectra and published in the ''Revised Harvard photometry'' catalogue. The definition of type B-type stars was the presence of non-ionized helium lines with the absence of singly ionized helium in the blue-violet portion of the spectrum. All of the spectral classes, including the B type, were subdivided with a numerical suffix that indicated the degree to which they approached the next classification. Thus B2 is 1/5 of the way from type B (or B0) to type A. Later, however, more refined s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
APOGEE
An apsis (; ) is the farthest or nearest point in the orbit of a planetary body about its primary body. For example, the apsides of the Earth are called the aphelion and perihelion. General description There are two apsides in any elliptic orbit. The name for each apsis is created from the prefixes ''ap-'', ''apo-'' (), or ''peri-'' (), each referring to the farthest and closest point to the primary body the affixing necessary suffix that describes the primary body in the orbit. In this case, the suffix for Earth is ''-gee'', so the apsides' names are ''apogee'' and ''perigee''. For the Sun, its suffix is ''-helion'', so the names are ''aphelion'' and ''perihelion''. According to Newton's laws of motion, all periodic orbits are ellipses. The barycenter of the two bodies may lie well within the bigger bodyŌĆöe.g., the EarthŌĆōMoon barycenter is about 75% of the way from Earth's center to its surface. If, compared to the larger mass, the smaller mass is negligible (e.g., f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
GALAH
The galah (; ''Eolophus roseicapilla''), also known as the pink and grey cockatoo or rose-breasted cockatoo, is the only species within genus ''Eolophus'' of the cockatoo family. Found throughout Australia, it is among the most common of the cockatoos. With its distinctive pink and grey plumage and its bold and loud behaviour, it is a familiar sight in the wild and increasingly in urban areas. It has benefited from the change in the landscape since European colonisation, and appears to be replacing the Major Mitchell's cockatoo in parts of its range. Etymology The term galah is derived from ''gilaa'', a word from the Yuwaalaraay and neighbouring Aboriginal languages spoken in north-western New South Wales. Description The galah is about in length, and weighs . It has a pale silver to grey back, a pale grey rump, a pink face and breast, and a light pink mobile crest. It has a bone-coloured beak, and the bare skin of the eye ring is carunculated. It has grey legs. The sexes a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Proper Motion
Proper motion is the astrometric measure of the observed changes in the apparent places of stars or other celestial objects in the sky, as seen from the center of mass of the Solar System, compared to the abstract background of the more distant stars. The components for proper motion in the equatorial coordinate system (of a given epoch, often J2000.0) are given in the direction of right ascension (''╬╝''╬▒) and of declination (''╬╝''╬┤). Their combined value is computed as the ''total proper motion'' (''╬╝''). It has dimensions of angle per time, typically arcseconds per year or milliarcseconds per year. Knowledge of the proper motion, distance, and radial velocity allows calculations of an object's motion from our star system's frame of reference and its motion from the galactic frame of reference – that is motion in respect to the Sun, and by coordinate transformation, that in respect to the Milky Way. Introduction Over the course of centuries, stars appear t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Alpha Persei Cluster
The Alpha Persei Cluster, also known as Melotte 20 or Collinder 39, is an open cluster of stars in the northern constellation of Perseus. To the naked eye, the cluster consists of several blue-hued spectral type B stars. The most luminous member is the ~2nd magnitude white-yellow supergiant Mirfak, also known as Alpha Persei. Bright members also include Delta, Sigma, Psi, 29, 30, 34, and 48 Persei. The Hipparcos satellite and infrared color-magnitude diagram fitting have been used to establish a distance to the cluster of ~. The distance established via the independent analyses agree, thereby making the cluster an important rung on the cosmic distance ladder. As seen from the Earth, the extinction of the cluster due to interstellar dust is around 0.30. The cluster is centered to the northeast of Alpha Persei. It has a core radius of , a half-mass radius of , and a tidal radius of , with 517 members being identified within the latter. The cluster shows solid evidence of having un ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Oblate
In Christianity (especially in the Roman Catholic, Orthodox, Anglican and Methodist traditions), an oblate is a person who is specifically dedicated to God or to God's service. Oblates are individuals, either laypersons or clergy, normally living in general society, who, while not professed monks or nuns, have individually affiliated themselves with a monastic community of their choice. They make a formal, private promise (annually renewable or for life, depending on the monastery with which they are affiliated) to follow the Rule of the Order in their private lives as closely as their individual circumstances and prior commitments permit. Such oblates are considered an extended part of the monastic community; for example, Benedictine oblates also often include the post-nominal letters 'OblSB' or 'ObSB' after their names on documents. They are comparable to the tertiaries associated with the various mendicant orders. The term "oblate" is also used in the official name of some ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Solar Mass
The solar mass () is a standard unit of mass in astronomy, equal to approximately . It is often used to indicate the masses of other stars, as well as stellar clusters, nebulae, galaxies and black holes. It is approximately equal to the mass of the Sun. This equates to about two nonillion (short scale), two quintillion (long scale) kilograms or 2000 quettagrams: The solar mass is about times the mass of Earth (), or times the mass of Jupiter (). History of measurement The value of the gravitational constant was first derived from measurements that were made by Henry Cavendish in 1798 with a torsion balance. The value he obtained differs by only 1% from the modern value, but was not as precise. The diurnal parallax of the Sun was accurately measured during the transits of Venus in 1761 and 1769, yielding a value of (9 arcseconds, compared to the present value of ). From the value of the diurnal parallax, one can determine the distance to the Sun from the geometry o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Azimuthal
An azimuth (; from ar, ž¦┘Ä┘äž│┘Å┘æ┘ģ┘Å┘łž¬, as-sum┼½t, the directions) is an angular measurement in a spherical coordinate system. More specifically, it is the horizontal angle from a cardinal direction, most commonly north. Mathematically, the relative position vector from an observer (origin) to a point of interest is projected perpendicularly onto a reference plane (the horizontal plane); the angle between the projected vector and a reference vector on the reference plane is called the azimuth. When used as a celestial coordinate, the azimuth is the horizontal direction of a star or other astronomical object in the sky. The star is the point of interest, the reference plane is the local area (e.g. a circular area with a 5 km radius at sea level) around an observer on Earth's surface, and the reference vector points to true north. The azimuth is the angle between the north vector and the star's vector on the horizontal plane. Azimuth is usually measured in degrees ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Stellar Rotation
Stellar rotation is the angular motion of a star about its axis. The rate of rotation can be measured from the spectrum of the star, or by timing the movements of active features on the surface. The rotation of a star produces an equatorial bulge due to centrifugal force. As stars are not solid bodies, they can also undergo differential rotation. Thus the equator of the star can rotate at a different angular velocity than the higher latitudes. These differences in the rate of rotation within a star may have a significant role in the generation of a stellar magnetic field. The magnetic field of a star interacts with the stellar wind. As the wind moves away from the star its rate of angular velocity slows. The magnetic field of the star interacts with the wind, which applies a drag to the stellar rotation. As a result, angular momentum is transferred from the star to the wind, and over time this gradually slows the star's rate of rotation. Measurement Unless a star is being observ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Photometric System
In astronomy, a photometric system is a set of well-defined passbands (or optical filters), with a known sensitivity to incident radiation. The sensitivity usually depends on the optical system, detectors and filters used. For each photometric system a set of primary standard stars is provided. A commonly adopted standardized photometric system is the Johnson-Morgan or UBV photometric system (1953). At present, there are more than 200 photometric systems. Photometric systems are usually characterized according to the widths of their passbands: * broadband (passbands wider than 30 nm, of which the most widely used is Johnson-Morgan UBV system) * intermediate band (passbands between 10 and 30 nm wide) * narrow band (passbands less than 10 nm wide) Photometric letters Each letter designates a section of light of the electromagnetic spectrum; these cover well the consecutive major groups, near-ultraviolet (NUV), visible light (centered on the V band), near-infrared ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
General Catalog Of Variable Stars
The General Catalogue of Variable Stars (GCVS) is a list of variable stars. Its first edition, containing 10,820 stars, was published in 1948 by the Academy of Sciences of the USSR and edited by B. V. Kukarkin and P. P. Parenago. Second and third editions were published in 1958 and 1968; the fourth edition, in three volumes, was published 1985–1987. It contained 28,435 stars. A fourth volume of the fourth edition containing reference tables was later published, as well as a fifth volume containing variable stars outside the Galaxy. The last edition (GCVS v5.1) based on data compiled in 2015 gathers 52,011 variable stars. The most up-to-date version of the GCVS is available at the GCVS website. It contains improved coordinates for the variable stars in the printed fourth edition of the GCVS, as well as variable stars discovered too recently to be included in the fourth edition. An older version of the GCVS dating from 2004 is available from the VizieR service at the Ce ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |

.png)
