|
╬▒-Cadinol
╬▒-Cadinol or 10╬▒-hydroxy-4-cadinene is an organic compound, a sesquiterpenoid alcohol. Natural occurrence This compound is found in essential oils and extracts of many plants, such as *'' Agrotaxis selaginoides'', * ''Tabernaemontana catharinensis'' * '' Litsea acutivena'' (7.7%), * '' Salvia aratocensis'' (20%), * '' Protium giganteum'' (7%), * '' Uvaria ovata'' root bark (13ŌĆō24%), * '' Plinia trunciflora'' (19%) * '' Tanacetum sonbolii'' (35%) * ''Schisandra chinensis'' berries (5%), * ''Melia azedarach'' (11%), * ''Neolitsea parvigemma'' (10%), * ''Tetradenia riparia'' (8%) Biological activity ╬▒-Cadinol was said to act as anti-fungal and as hepatoprotective, and was proposed as a possible remedy for drug-resistant tuberculosis. See also * ╬┤-Cadinol ╬┤-Cadinol is an organic compound, a sesquiterpenoid alcohol produced by many plants as well as some animals and microorganisms. It is a white crystalline solid, soluble in isopropyl ether and ethanol. It is an epimer o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Organic Compound
In chemistry, organic compounds are generally any chemical compounds that contain carbon-hydrogen or carbon-carbon bonds. Due to carbon's ability to catenate (form chains with other carbon atoms), millions of organic compounds are known. The study of the properties, reactions, and syntheses of organic compounds comprise the discipline known as organic chemistry. For historical reasons, a few classes of carbon-containing compounds (e.g., carbonate salts and cyanide salts), along with a few other exceptions (e.g., carbon dioxide, hydrogen cyanide), are not classified as organic compounds and are considered inorganic. Other than those just named, little consensus exists among chemists on precisely which carbon-containing compounds are excluded, making any rigorous definition of an organic compound elusive. Although organic compounds make up only a small percentage of Earth's crust, they are of central importance because all known life is based on organic compounds. Living t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Schisandra Chinensis
''Schisandra chinensis'' (common name: magnolia-vine, Chinese magnolia-vine, schisandra), whose fruit is called magnolia berry or five-flavor-fruit (from Chinese õ║öÕæ│ÕŁÉ ''wŪöw├©izi''), is a vine plant native to forests of Northern China, the Russian Far East and Korea. Wild varieties are also found in Japan. It is hardy in USDA Zone 4. The fruits are red berries in dense clusters around long. Etymology, common names, and taxonomy The genus ''Schisandra'' was first published by Andr├® Michaux in 1803, the name deriving from the Greek words ''schizein'' ('to split') and ''andros'' ('man'), referring to the separate anther cells on the stamens. In the 21st century, ''Schisandra chinensis'' belongs to the family of Schisandraceae. In earlier years, it was assumed that the species belonged to the family of Magnoliaceae, hence the name ''Chinese magnolia-vine''. However, many differences in plant phenology betweenŌĆ» SchisandraŌĆ»and members of Magnoliaceae led to the formatio ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tertiary Alcohols
In chemistry, an alcohol is a type of organic compound that carries at least one hydroxyl () functional group bound to a saturated carbon atom. The term ''alcohol'' originally referred to the primary alcohol ethanol (ethyl alcohol), which is used as a drug and is the main alcohol present in alcoholic drinks. An important class of alcohols, of which methanol and ethanol are the simplest examples, includes all compounds which conform to the general formula . Simple monoalcohols that are the subject of this article include primary (), secondary () and tertiary () alcohols. The suffix ''-ol'' appears in the IUPAC chemical name of all substances where the hydroxyl group is the functional group with the highest priority. When a higher priority group is present in the compound, the prefix ''hydroxy-'' is used in its IUPAC name. The suffix ''-ol'' in non-IUPAC names (such as paracetamol or cholesterol) also typically indicates that the substance is an alcohol. However, some compound ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sesquiterpenes
Sesquiterpenes are a class of terpenes that consist of three isoprene units and often have the molecular formula C15H24. Like monoterpenes, sesquiterpenes may be cyclic or contain rings, including many unique combinations. Biochemical modifications such as oxidation or rearrangement produce the related sesquiterpenoids. Sesquiterpenes are found naturally in plants and insects, as semiochemicals, e.g. defensive agents or pheromones. Biosynthesis and examples The reaction of geranyl pyrophosphate with isopentenyl pyrophosphate results in the 15-carbon farnesyl pyrophosphate (FPP), which is an intermediate in the biosynthesis of sesquiterpenes such as farnesene. Cyclic sesquiterpenes are more common than cyclic monoterpenes because of the increased chain length and additional double bond in the sesquiterpene precursors. In addition to common six-membered ring systems such as the ones found in zingiberene and bisacurone, cyclization of one end of the chain to the other end can l ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tuberculosis
Tuberculosis (TB) is an infectious disease usually caused by '' Mycobacterium tuberculosis'' (MTB) bacteria. Tuberculosis generally affects the lungs, but it can also affect other parts of the body. Most infections show no symptoms, in which case it is known as latent tuberculosis. Around 10% of latent infections progress to active disease which, if left untreated, kill about half of those affected. Typical symptoms of active TB are chronic cough with blood-containing mucus, fever, night sweats, and weight loss. It was historically referred to as consumption due to the weight loss associated with the disease. Infection of other organs can cause a wide range of symptoms. Tuberculosis is spread from one person to the next through the air when people who have active TB in their lungs cough, spit, speak, or sneeze. People with Latent TB do not spread the disease. Active infection occurs more often in people with HIV/AIDS and in those who smoke. Diagnosis of active TB is ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
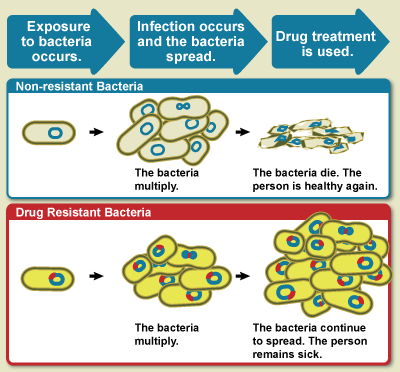
Drug Resistance
Drug resistance is the reduction in effectiveness of a medication such as an antimicrobial or an antineoplastic in treating a disease or condition. The term is used in the context of resistance that pathogens or cancers have "acquired", that is, resistance has evolved. Antimicrobial resistance and antineoplastic resistance challenge clinical care and drive research. When an organism is resistant to more than one drug, it is said to be multidrug-resistant. The development of antibiotic resistance in particular stems from the drugs targeting only specific bacterial molecules (almost always proteins). Because the drug is ''so'' specific, any mutation in these molecules will interfere with or negate its destructive effect, resulting in antibiotic resistance. Furthermore, there is mounting concern over the abuse of antibiotics in the farming of livestock, which in the European Union alone accounts for three times the volume dispensed to humans ŌĆō leading to development of super-resi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hepatoprotective
Hepatoprotection or antihepatotoxicity is the ability of a chemical substance to prevent damage to the liver. This is opposite to hepatotoxicity. Hepatoprotective molecules used in emergency medicine * Acetylcysteine is considered the hepatoprotective drug of choice when treating an overdose of acetaminophen/paracetamol. * Silymarin is given intravenously to treat poisoning from Amanita mushrooms according to the Santa Cruz protocol devised by Dr Todd Mitchell at University of California, Santa Cruz, UCSC. Herbs with potentially hepatoprotective constituents * ''Astragalus membranaceus'' * ''Curcuma longa'' * ''Brassica'' * ''Silybum marianum'' * ''Andrographis paniculata''Andrographis paniculata http://www.stuartxchange.com/Sinta.html References {{Bile and liver therapy Hepatology ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Antifungal Medication
An antifungal medication, also known as an antimycotic medication, is a pharmaceutical fungicide or fungistatic used to treat and prevent mycosis such as athlete's foot, ringworm, candidiasis (thrush), serious systemic infections such as cryptococcal meningitis, and others. Such drugs are usually yes obtained by a doctor's prescription, but a few are available over the counter (OTC). Types of antifungal There are two types of antifungals: local and systemic. Local antifungals are usually administered topically or vaginally, depending on the condition being treated. Systemic antifungals are administered orally or intravenously. Of the clinically employed azole antifungals, only a handful are used systemically. These include ketoconazole, itraconazole, fluconazole, fosfluconazole, voriconazole, posaconazole, and isavuconazole. Examples of non-azole systemic antifungals include griseofulvin and terbinafine. Classes Polyenes A polyene is a molecule with multiple conjugated ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tetradenia Riparia
''Tetradenia riparia'' is a species of flowering plant native to southern Africa. It belongs in the mint and sage family Lamiaceae. It is occasionally referred to as misty plume bush and is commonly used as a decorative garden plant due to its flowers when in full bloom. ''Tetradenia'' means 'four glands' and ''riparia'' translates to 'growing on banks of rivers'. This species was first described by botanists (Hochst.) Codd in 1983. It is also known as ginger bush, Ibozane and musk bush. Description It is a shrub that grows up to 2m high, occasionally reaching 5m. The foliage is sticky and smells pleasantly aromatic. The plant is deciduous and multi-stemmed while the branches are semi-succulent. The leaves are simple, large, heart-shaped and opposite. They are also coarsely toothed, thick-haired and sticky, and are 35ŌĆō80 mm long. Leaves that are crushed have a ginger scent. Both sides are covered with a thin dark red lint. The inflorescences are branched, large bunches at ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Neolitsea Parvigemma
''Neolitsea parvigemma'' is a species of small to medium-sized tree in the family Lauraceae. It is Endemism, endemic to Taiwan, and confined to the south central mountain regions of the island. A number of chemicals from ''N. parvigemma'' show interesting biological properties. The hydrodistillated leaf essential oil of ''N. parvigemma'' has antifungal and anti-wood-decay fungal properties Sesquiterpenes isolated from the stems have anti-inflammatory properties. References Neolitsea, parvigemma Trees of Taiwan Endemic flora of Taiwan {{Laurales-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Melia Azedarach
''Melia azedarach'', commonly known as the chinaberry tree, pride of India, bead-tree, Cape lilac, syringa berrytree, Persian lilac, Indian lilac, or white cedar, is a species of deciduous tree in the mahogany family, Meliaceae, that is native to Indomalaya and Australasia. Description The fully grown tree has a rounded crown, and commonly measures tall, exceptionally . The leaves are up to long, alternate, long-petioled, two or three times compound (odd-pinnate); the leaflets are dark green above and lighter green below, with serrate margins. The flowers are small and fragrant, with five pale purple or lilac petals, growing in clusters. The fruit is a drupe, marble-sized, light yellow at maturity, hanging on the tree all winter, and gradually becoming wrinkled and almost white. As the stem ages and grows, changes occur that transform its surface into bark. Chemistry Italo et al 2009 and Safithri and Sari 2016 report flavonoids and phenols found in ''M. azed ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |



_eating_Bakain_(Melia_Azadirachta)_berries_at_Roorkee%2C_Uttarakhand_W_IMG_9016.jpg)