|
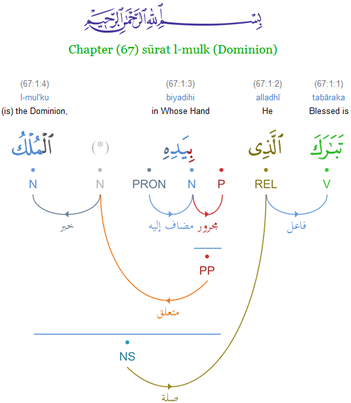
╩ŠI╩┐rab
(, ) is an Arabic term for the system of nominal, adjectival, or verbal suffixes of Classical Arabic to mark grammatical case. These suffixes are written in fully vocalized Arabic texts, notably the '' '' or texts written for children or Arabic learners, and they are articulated when a text is formally read aloud, but they do not survive in any spoken dialect of Arabic. Even in Literary Arabic, these suffixes are often not pronounced ''in pausa'' ( '); i.e. when the word occurs at the end of the sentence, in accordance with certain rules of Arabic pronunciation. (That is, the nunation suffix ''-n'' is generally dropped at the end of a sentence or line of poetry, with the notable exception of the nuniyya; the vowel suffix may or may not be, depending on the requirements of metre.) Depending on the knowledge of , some Arabic speakers may omit case endings when reading out in Modern Standard Arabic, thus making it similar to spoken dialects. Many Arabic textbooks for foreigners t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Harakat
The Arabic script has numerous diacritics, which include: consonant pointing known as (), and supplementary diacritics known as (). The latter include the vowel marks termed (; singular: , '). The Arabic script is a modified abjad, where short consonants and long vowels are represented by letters but short vowels and consonant length are not generally indicated in writing. ' is optional to represent missing vowels and consonant length. Modern Arabic is always written with the ''iŌĆśj─üm''ŌĆöconsonant pointing, but only religious texts, children's books and works for learners are written with the full ''tashk─½l''ŌĆövowel guides and consonant length. It is however not uncommon for authors to add diacritics to a word or letter when the grammatical case or the meaning is deemed otherwise ambiguous. In addition, classical works and historic documents rendered to the general public are often rendered with the full ''tashk─½l'', to compensate for the gap in understanding resultin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Arabic Grammar
Arabic grammar or Arabic language sciences ( ar, ž¦┘ä┘åžŁ┘ł ž¦┘äž╣ž▒ž©┘Ŗ ' or ar, ž╣┘Å┘ä┘Å┘ł┘ģ ž¦┘ä┘äž║┘Äž® ž¦┘äž╣┘Äž▒┘Äž©┘É┘Ŗ┘Ä┘æž® ') is the grammar of the Arabic language. Arabic is a Semitic language and its grammar has many similarities with the grammar of other Semitic languages. Classical Arabic and Modern Standard Arabic have largely the same grammar; colloquial spoken varieties of Arabic can vary in different ways. The largest differences between classical and colloquial Arabic are the loss of morphological markings of grammatical case; changes in word order, an overall shift towards a more analytic morphosyntax, the loss of the previous system of grammatical mood, along with the evolution of a new system; the loss of the inflected passive voice, except in a few relict varieties; restriction in the use of the dual number and (for most varieties) the loss of the feminine plural. Many Arabic dialects, Maghrebi Arabic in particular also have significant vowel shifts a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Varieties Of Arabic
The varieties (or dialects or vernacular languages) of Arabic, a Semitic language within the Afroasiatic family originating in the Arabian Peninsula, are the linguistic systems that Arabic speakers speak natively. There are considerable variations from region to region, with degrees of mutual intelligibility that are often related to geographical distance and some that are mutually unintelligible. Many aspects of the variability attested to in these modern variants can be found in the ancient Arabic dialects in the peninsula. Likewise, many of the features that characterize (or distinguish) the various modern variants can be attributed to the original settler dialects. Some organizations, such as SIL International, consider these approximately 30 different varieties to be different languages, while others, such as the Library of Congress, consider them all to be dialects of Arabic. In terms of sociolinguistics, a major distinction exists between the formal standardized lang ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Classical Arabic
Classical Arabic ( ar, links=no, ┘▒┘ä┘Æž╣┘Äž▒┘Äž©┘É┘Ŗ┘Ä┘æž®┘Å ┘▒┘ä┘Æ┘ü┘ÅžĄ┘ÆžŁ┘Ä┘ē┘░, al-╩┐arab─½yah al-fuß╣ŻßĖź─ü) or Quranic Arabic is the standardized literary form of Arabic used from the 7th century and throughout the Middle Ages, most notably in Umayyad and Abbasid literary texts such as poetry, elevated prose and oratory, and is also the liturgical language of Islam. The first comprehensive description of ''Al-╩┐Arabiyyah'' "Arabic", Sibawayh's ''al''-''Kit─üb'', was upon a corpus of poetic texts, in addition to the Qur╩Š─ün and Bedouin informants whom he considered to be reliable speakers of the ''╩┐arabiyya''. Modern Standard Arabic is its direct descendant used today throughout the Arab world in writing and in formal speaking, for example prepared speeches, some radio and TV broadcasts and non-entertainment content. Whilst the lexis and stylistics of Modern Standard Arabic are different from Classical Arabic, the morphology and syntax have remained basically unc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pausa
In linguistics, pausa (Latin for 'break', from Greek ŽĆ╬▒ß┐”Žā╬╣Žé, ''pausis'' 'stopping, ceasing') is the hiatus between prosodic declination units. The concept is somewhat broad, as it is primarily used to refer to allophones that occur in certain prosodic environments, and these environments vary between languages. Characteristics Some sound laws specifically operate only ''in pausa''. For example, certain phonemes may be pronounced differently at the beginning or the end of a word if no other word precedes or follows within the same prosodic unit, such as a word in the citation form. That is the case with the final-obstruent devoicing of German, Turkish, Russian, and other languages whose voiced obstruent consonants are devoiced pre-pausa and before voiceless consonants. The opposite environment is relevant in Spanish, whose voiced fricatives become stops post-pausa and after nasals. Such environments are often termed ''pre-pausal'' and ''post-pausal'', respectivel ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ta' Marbuta
Taw, tav, or taf is the twenty-second and last letter of the Semitic abjads, including Phoenician T─üw , Hebrew Tav , Aramaic Taw , Syriac Taw ▄¼, and Arabic ž¬ T─ü╩╝ (22nd in abjadi order, 3rd in modern order). In Arabic, it is also gives rise to the derived letter ß╣«─ü╩╝. Its original sound value is . The Phoenician letter gave rise to the Greek ''tau'' (╬ż), Latin T, and Cyrillic ąó. Origins of taw Taw is believed to be derived from the Egyptian hieroglyph representing a tally mark (viz. a decussate cross) Z9 Arabic t─ü╩╝ The letter is named '. It is written in several ways depending on its position in the word: Final ('' fatha'', then with a sukun on it, pronounced , though diacritics are normally omitted) is used to mark feminine gender for third-person perfective/past tense verbs, while final (, ) is used to mark past-tense second-person singular masculine verbs, final (, ) to mark past-tense second-person singular feminine verbs, and final (, ) to m ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mimation
Mimation refers to the suffixed ' (the letter mem in many Semitic abjads) which occurs in some Semitic languages. This occurs in Akkadian on singular nouns. Akkadian grammar: Noun declension It was also present in the . It is retained in the plural and the few remaining dual forms in . It corresponds to the letter [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mater Lectionis
''Matres lectionis'' (from Latin "mothers of reading", singular form: ''mater lectionis'', from he, ūÉųĄūØ ū¦ų░ū©ų┤ūÖūÉųĖūö ) are consonants that are used to indicate a vowel, primarily in the writing down of Semitic languages such as Arabic, Hebrew and Syriac. The letters that do this in Hebrew are ''aleph'' , '' he'' , '' waw'' and '' yod'' , and in Arabic, the ''matres lectionis'' (though they are much less often referred to thus) are ''╩Šalif'' , ''w─üw'' and ''y─ü╩Š'' . The yod'' and ''waw'' in particular are more often vowels than they are consonants. The original value of the ''matres lectionis'' corresponds closely to what is called in modern linguistics glides or semivowels. Overview Because the scripts used to write some Semitic languages lack vowel letters, unambiguous reading of a text might be difficult. Therefore, to indicate vowels (mostly long), consonant letters are used. For example, in the Hebrew construct-state form ''b─ōt'', meaning "the house o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Accusative Case
The accusative case (abbreviated ) of a noun is the grammatical case used to mark the direct object of a transitive verb. In the English language, the only words that occur in the accusative case are pronouns: 'me,' 'him,' 'her,' 'us,' and ŌĆśthemŌĆÖ. The spelling of those words will change depending on how they are used in a sentence. For example, the pronoun ''they'', as the subject of a sentence, is in the nominative case ("They wrote a book"); but if the pronoun is instead the object, it is in the accusative case and ''they'' becomes ''them'' ("The book was written by them"). The accusative case is used in many languages for the objects of (some or all) prepositions. It is usually combined with the nominative case (for example in Latin). The English term, "accusative", derives from the Latin , which, in turn, is a translation of the Greek . The word may also mean "causative", and this may have been the Greeks' intention in this name, but the sense of the Roman translation has ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Predicative (adjectival Or Nominal)
A predicative expression (or just predicative) is part of a clause predicate, and is an expression that typically follows a copula (or linking verb), e.g. ''be'', ''seem'', ''appear'', or that appears as a second complement of a certain type of verb, e.g. ''call'', ''make'', ''name'', etc. The most frequently acknowledged types of predicative expressions are predicative adjectives (also ''predicate adjectives'') and predicative nominals (also ''predicate nominals''). The main trait of all predicative expressions is that they serve to express a property that is assigned to a "subject", whereby this subject is usually the clause subject, but at times it can be the clause object. A primary distinction is drawn between predicative (also ''predicate'') and attributive expressions. Further, predicative expressions are typically ''not'' clause arguments, and they are also typically ''not'' clause adjuncts. There is hence a three-way distinction between predicative expressions, arguments ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |