|
≈Ývarc‚ÄìMilnor Lemma
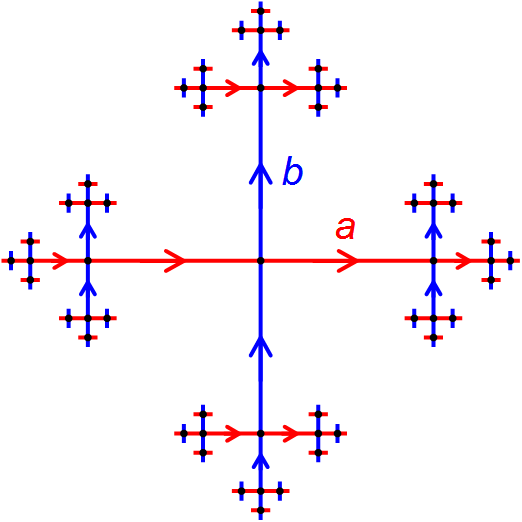
In the mathematical subject of geometric group theory, the ≈Ývarc‚ÄìMilnor lemma (sometimes also called Milnor‚Äì≈Ývarc lemma, with both variants also sometimes spelling ≈Ývarc as Schwarz) is a statement which says that a group G, equipped with a "nice" discrete isometric action on a metric space X, is quasi-isometric to X. This result goes back, in different form, before the notion of quasi-isometry was formally introduced, to the work of Albert S. Schwarz (1955) and John Milnor (1968). Pierre de la Harpe called the ≈Ývarc‚ÄìMilnor lemma "the ''fundamental observation in geometric group theory''"Pierre de la Harpe, Topics in geometric group theory'. Chicago Lectures in Mathematics. University of Chicago Press, Chicago, IL, 2000. ; p. 87 because of its importance for the subject. Occasionally the name "fundamental observation in geometric group theory" is now used for this statement, instead of calling it the ≈Ývarc‚ÄìMilnor lemma; see, for example, Theorem 8.2 in the book ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Geometric Group Theory
Geometric group theory is an area in mathematics devoted to the study of finitely generated groups via exploring the connections between algebraic properties of such groups and topological and geometric properties of spaces on which these groups can act non-trivially (that is, when the groups in question are realized as geometric symmetries or continuous transformations of some spaces). Another important idea in geometric group theory is to consider finitely generated groups themselves as geometric objects. This is usually done by studying the Cayley graphs of groups, which, in addition to the graph structure, are endowed with the structure of a metric space, given by the so-called word metric. Geometric group theory, as a distinct area, is relatively new, and became a clearly identifiable branch of mathematics in the late 1980s and early 1990s. Geometric group theory closely interacts with low-dimensional topology, hyperbolic geometry, algebraic topology, computational group ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Cocompact Group Action
In mathematics, an action of a group ''G'' on a topological space ''X'' is cocompact if the quotient space ''X''/''G'' is a compact space. If ''X'' is locally compact In topology and related branches of mathematics, a topological space is called locally compact if, roughly speaking, each small portion of the space looks like a small portion of a compact space. More precisely, it is a topological space in which e ..., then an equivalent condition is that there is a compact subset ''K'' of ''X'' such that the image of ''K'' under the action of ''G'' covers ''X''. It is sometimes referred to as ''mpact'', a tongue-in-cheek reference to dual notions where prefixing with "co-" twice would "cancel out". References * Group actions {{topology-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Horoball
In hyperbolic geometry, a horosphere (or parasphere) is a specific hypersurface in hyperbolic ''n''-space. It is the boundary of a horoball, the limit of a sequence of increasing balls sharing (on one side) a tangent hyperplane and its point of tangency. For ''n'' = 2 a horosphere is called a horocycle. A horosphere can also be described as the limit of the hyperspheres that share a tangent hyperplane at a given point, as their radii go towards infinity. In Euclidean geometry, such a "hypersphere of infinite radius" would be a hyperplane, but in hyperbolic geometry it is a horosphere (a curved surface). History The concept has its roots in a notion expressed by F. L. Wachter in 1816 in a letter to his teacher Gauss. Noting that in Euclidean geometry the limit of a sphere as its radius tends to infinity is a plane, Wachter affirmed that even if the fifth postulate were false, there would nevertheless be a geometry on the surface identical with that of the ordinary plane. The ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Lattice (discrete Subgroup)
In Lie theory and related areas of mathematics, a lattice in a locally compact group is a discrete subgroup with the property that the quotient space has finite invariant measure. In the special case of subgroups of R''n'', this amounts to the usual geometric notion of a lattice as a periodic subset of points, and both the algebraic structure of lattices and the geometry of the space of all lattices are relatively well understood. The theory is particularly rich for lattices in semisimple Lie groups or more generally in semisimple algebraic groups over local fields. In particular there is a wealth of rigidity results in this setting, and a celebrated theorem of Grigory Margulis states that in most cases all lattices are obtained as arithmetic groups. Lattices are also well-studied in some other classes of groups, in particular groups associated to Kac–Moody algebras and automorphisms groups of regular trees (the latter are known as ''tree lattices''). Lattices a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Lie Group
In mathematics, a Lie group (pronounced ) is a group (mathematics), group that is also a differentiable manifold, such that group multiplication and taking inverses are both differentiable. A manifold is a space that locally resembles Euclidean space, whereas groups define the abstract concept of a binary operation along with the additional properties it must have to be thought of as a "transformation" in the abstract sense, for instance multiplication and the taking of inverses (to allow division), or equivalently, the concept of addition and subtraction. Combining these two ideas, one obtains a continuous group where multiplying points and their inverses is continuous. If the multiplication and taking of inverses are smoothness, smooth (differentiable) as well, one obtains a Lie group. Lie groups provide a natural model for the concept of continuous symmetry, a celebrated example of which is the circle group. Rotating a circle is an example of a continuous symmetry. For an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Universal Cover
In topology, a covering or covering projection is a map between topological spaces that, intuitively, locally acts like a projection of multiple copies of a space onto itself. In particular, coverings are special types of local homeomorphisms. If p : \tilde X \to X is a covering, (\tilde X, p) is said to be a covering space or cover of X, and X is said to be the base of the covering, or simply the base. By abuse of terminology, \tilde X and p may sometimes be called covering spaces as well. Since coverings are local homeomorphisms, a covering space is a special kind of étalé space. Covering spaces first arose in the context of complex analysis (specifically, the technique of analytic continuation), where they were introduced by Riemann as domains on which naturally multivalued complex functions become single-valued. These spaces are now called Riemann surfaces. Covering spaces are an important tool in several areas of mathematics. In modern geometry, covering spaces ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Riemannian Metric
In differential geometry, a Riemannian manifold is a geometric space on which many geometric notions such as distance, angles, length, volume, and curvature are defined. Euclidean space, the N-sphere, n-sphere, hyperbolic space, and smooth surfaces in three-dimensional space, such as ellipsoids and paraboloids, are all examples of Riemannian manifold, manifolds. Riemannian manifolds are named after German mathematician Bernhard Riemann, who first conceptualized them. Formally, a Riemannian metric (or just a metric) on a smooth manifold is a choice of inner product for each tangent space of the manifold. A Riemannian manifold is a smooth manifold together with a Riemannian metric. The techniques of differential and integral calculus are used to pull geometric data out of the Riemannian metric. For example, integration leads to the Riemannian distance function, whereas differentiation is used to define curvature and parallel transport. Any smooth surface in three-dimensional Eucl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Fundamental Group
In the mathematics, mathematical field of algebraic topology, the fundamental group of a topological space is the group (mathematics), group of the equivalence classes under homotopy of the Loop (topology), loops contained in the space. It records information about the basic shape, or holes, of the topological space. The fundamental group is the first and simplest homotopy group. The fundamental group is a homotopy invariant—topological spaces that are homotopy equivalent (or the stronger case of homeomorphic) have Group isomorphism, isomorphic fundamental groups. The fundamental group of a topological space X is denoted by \pi_1(X). Intuition Start with a space (for example, a surface (mathematics), surface), and some point in it, and all the loops both starting and ending at this point—path (topology), paths that start at this point, wander around and eventually return to the starting point. Two loops can be combined in an obvious way: travel along the first loop, then alo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Euler Characteristic
In mathematics, and more specifically in algebraic topology and polyhedral combinatorics, the Euler characteristic (or Euler number, or Euler–Poincar√© characteristic) is a topological invariant, a number that describes a topological space's shape or structure regardless of the way it is bent. It is commonly denoted by \chi (Greek alphabet, Greek lower-case letter chi (letter), chi). The Euler characteristic was originally defined for polyhedron, polyhedra and used to prove various theorems about them, including the classification of the Platonic solids. It was stated for Platonic solids in 1537 in an unpublished manuscript by Francesco Maurolico. Leonhard Euler, for whom the concept is named, introduced it for convex polyhedra more generally but failed to rigorously prove that it is an invariant. In modern mathematics, the Euler characteristic arises from homology (mathematics), homology and, more abstractly, homological algebra. Polyhedra The Euler characteristic was ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Richard Schwartz (mathematician)
Richard Evan Schwartz (born August 11, 1966) is an American mathematician notable for his contributions to geometric group theory and to an area of mathematics known as billiards. Geometric group theory is a relatively new area of mathematics beginning around the late 1980sM. Gromov, ''Hyperbolic Groups'', in "Essays in Group Theory" (G. M. Gersten, ed.), MSRI Publ. 8, 1987, pp. 75–263. which explores finitely generated groups, and seeks connections between their algebraic properties and the geometric spaces on which these groups act. He has worked on what mathematicians refer to as ''billiards'', which are dynamical systems based on a convex shape in a plane. He has explored geometric iterations involving polygons, and he has been credited for developing the mathematical concept known as the pentagram map. In addition, he is author of a mathematics picture book for young children. In 2018 he is a professor of mathematics at Brown University. Career Schwartz was born in Los Angel ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Quotient Topology
In topology and related areas of mathematics, the quotient space of a topological space under a given equivalence relation is a new topological space constructed by endowing the quotient set of the original topological space with the quotient topology, that is, with the finest topology that makes continuous the canonical projection map (the function that maps points to their equivalence classes). In other words, a subset of a quotient space is open if and only if its preimage under the canonical projection map is open in the original topological space. Intuitively speaking, the points of each equivalence class are or "glued together" for forming a new topological space. For example, identifying the points of a sphere that belong to the same diameter produces the projective plane as a quotient space. Definition Let X be a topological space, and let \sim be an equivalence relation on X. The quotient set Y = X/ is the set of equivalence classes of elements of X. The equivalenc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Compact Space
In mathematics, specifically general topology, compactness is a property that seeks to generalize the notion of a closed and bounded subset of Euclidean space. The idea is that a compact space has no "punctures" or "missing endpoints", i.e., it includes all ''limiting values'' of points. For example, the open interval (0,1) would not be compact because it excludes the limiting values of 0 and 1, whereas the closed interval ,1would be compact. Similarly, the space of rational numbers \mathbb is not compact, because it has infinitely many "punctures" corresponding to the irrational numbers, and the space of real numbers \mathbb is not compact either, because it excludes the two limiting values +\infty and -\infty. However, the ''extended'' real number line ''would'' be compact, since it contains both infinities. There are many ways to make this heuristic notion precise. These ways usually agree in a metric space, but may not be equivalent in other topological spaces. One suc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |