|
Е amorГӯn
Е amorГӯn (; , ) is a small town in western Slovakia, southeast of Bratislava. Etymology The name is derived from a patron saint of a local church Sancta Maria, mentioned for the first time as ''villa Sancti Marie'' (1285). Today's name is an adaptation of the original name: ''Zent Maria вҖ“ Samaria вҖ“ Somoria вҖ“ Е amorГӯn''. Geography The town is located on the Danubian Flat in the ЕҪitnГҪ ostrov island, near the GabДҚГӯkovo dam by the Danube around southeast of Bratislava and west of DunajskГЎ Streda. Administratively, the town belongs to the Trnava Region, DunajskГЎ Streda District. History The oldest artifacts indicating the settlement of the area are dated to the Neolithic and Eneolithic Period. The settlement of the location is documented also for the Bronze Age and the Iron Age. Later archaeologic research (2008) uncovered artifacts from the Early and High Middle Ages (remnants of settlements, dwellings, farm buildings). After the Mongol invasion, the village ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
List Of Municipalities And Towns In Slovakia
This is an alphabetical list of the 2,891 (singular , "municipality") in Slovakia. They are grouped into 79 Districts of Slovakia, districts (, singular ), in turn grouped into 8 Regions of Slovakia, regions (, singular ); articles on individual districts and regions list their municipalities. The average area of Slovak municipalities is about and an average population of about 1,888 people. * ГҒbelovГЎ * Abovce * AbrahГЎm * AbrahГЎmovce, Bardejov District * AbrahГЎmovce, KeЕҫmarok District * AbramovГЎ * Abranovce * AdamovskГ© Kochanovce * Adidovce * AlekЕЎince * Andovce * AndrejovГЎ * Ardanovce * Ardovo * Arnutovce * BГЎb, Nitra District, BГЎb * Babie * BabГӯn * BabinГЎ * Babindol * Babinec, Slovakia, Babinec * BacГәch * BacГәrov * BГЎДҚ * BaДҚka, Slovakia, BaДҚka * BaДҚkov, TrebiЕЎov District, BaДҚkov * BaДҚkovГӯk * BaДҸan * BГЎdice * BadГӯn * BГЎhoЕҲ * Bajany * BajДҚ * Bajerov * Bajerovce * Bajka * Bajtava * Baka, Slovakia, Baka * BalГЎ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
ЕҪitnГҪ Ostrov
ЕҪitnГҪ ostrov (), also called VeДҫkГҪ ЕҪitnГҪ ostrov (; , ) to differentiate it from SzigetkГ¶z, MalГҪ ЕҪitnГҪ ostrov (; ; ), is a river island in southwestern Slovakia, extending from Bratislava to KomГЎrno. It lies between the Danube, its tributary Little Danube and VГЎh. The island is a major part of the Danubian Flat. It is the biggest river island in Europe, with an area of , measuring in length and in width. The main towns on the island are KomГЎrno, DunajskГЎ Streda and Е amorГӯn. Two boroughs of Bratislava, VrakuЕҲa and PodunajskГ© Biskupice, are also located on the island. The Slovnaft refinery is also located on the island. The island is the biggest drinking water reservoir in Slovakia, and one of the biggest in Europe as well. Because of its warm climate, good soils and water reservoirs it is an important agricultural region, with the best conditions for crop production. It is the most fertile region in Slovakia, causing the majority of the island to be deforested. S ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
DunajskГЎ Streda District
DunajskГЎ Streda District ( Slovak: ''Okres DunajskГЎ Streda'', Hungarian: ''Dunaszerdahelyi jГЎrГЎs'') is a district in the Trnava Region of western Slovakia. Until 1918, the district was mostly part of the county of Kingdom of Hungary of Pozsony, apart from a small area in the south, which formed part of the county of KomГЎrno, and BaloЕҲ, which formed part of the county of GyЕ‘r. The majority of the inhabitants of DunajskГЎ Streda District are Hungarians Hungarians, also known as Magyars, are an Ethnicity, ethnic group native to Hungary (), who share a common Culture of Hungary, culture, Hungarian language, language and History of Hungary, history. They also have a notable presence in former pa .... Municipalities References External links DunajskГЎ Streda Districts of the Trnava Region {{Trnava-geo-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Royal Free City
A royal free city, or free royal city (Latin: ''libera regia civitas''), was the official term for the most important cities in the Kingdom of Hungary from the late 12th centuryBГЎcskai Vera вҖ“ Nagy Lajos: PiackГ¶rzetek, piackГ¶zpontok Г©s vГЎrosok MagyarorszГЎgon 1828-ban. Budapest, 1984. to the Hungarian Revolution of 1848. The cities were granted certain privileges by the King of Hungary to prevent their control by the Hungarian nobility, hence "royal", and exercised some self-government in relation to their internal affairs and so were "free". From the late 14th century, the elected envoys of the royal free cities participated in the sessions of the Diet of Hungary, Hungarian Diet and so they became part of the legislature. This list also includes cities in the Kingdom of Croatia (other), Kingdom of Croatia and the Banate of Bosnia, which were part of the Lands of the Hungarian Crown. The term "royal free city" in the kingdom's languages is as follows: * * * * * * * ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
SMK-MKP
The Hungarian Alliance (; , SzГ¶vetsГ©gвҖ“Aliancia) is a List of political parties in Slovakia, political party in Slovakia for the Hungarian people, ethnic Hungarian Hungarians in Slovakia, minority, previously known simply as the "Alliance", it was founded when "Party of the Hungarian Community" and MostвҖ“HГӯd merged into "Hungarian Community Togetherness". It is led by LГЎszlГі GubГӯk since September 2024. History Party of the Hungarian Coalition The SMK-MKP party was founded as Party of the Hungarian Coalition (, ) in 1998 in response to an anti-coalition law passed. The law prevented parties from forming electoral cartels at election time, which small parties had used to overcome the 5% electoral threshold. Three parties representing the Hungarian minority had formed such a cartel, called 'Hungarian Coalition' in the 1994 Slovak parliamentary election, 1994 election, and had won 10.2% of the vote. To comply with the new law, the three parties вҖ“ the Hungarian Christian ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mongol Invasion Of Europe
From the 1220s to the 1240s, the Mongol Empire, Mongols conquered the Turkic peoples, Turkic states of Volga Bulgaria, Cumania and Iranian peoples, Iranian state of Alania, and various principalities in Eastern Europe. Following this, they began their invasion into Central Europe by launching a two-pronged invasion of History of Poland during the Piast dynasty, then-fragmented Poland, culminating in the Battle of Legnica (9 April 1241), and the Kingdom of Hungary (1000вҖ“1301), Kingdom of Hungary, culminating in the Battle of Mohi (11 April 1241). Invasions were also launched into the Caucasus against the Kingdom of Georgia, the Chechens, the Ingush people, Ingush, and Circassia though they Mongol invasion of Circassia, failed to fully subjugate the latter. More invasions were launched in Southeast Europe against Second Bulgarian Empire, Bulgaria, Croatia in personal union with Hungary, Croatia, and the Latin Empire. The operations were planned by General Subutai (1175вҖ“1248) and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Eneolithic Period
The Chalcolithic ( ) (also called the Copper Age and Eneolithic) was an archaeological period characterized by the increasing use of smelted copper. It followed the Neolithic and preceded the Bronze Age. It occurred at different periods in different areas, but was absent in some parts of the world, such as Russia, where there was no well-defined Copper Age between the Stone and Bronze Ages. Stone tools were still predominantly used during this period. The Chalcolithic covers both the early cold working (hammering) of near pure copper ores, as exhibited by the likes of North American Great Lakes Old Copper complex, from around 6,500 BC, through the later copper smelting cultures. The archaeological site of Belovode, on Rudnik mountain in Serbia, has the world's oldest securely dated evidence of copper smelting at high temperature, from . The transition from Copper Age to Bronze Age in Europe occurred between the late 5th and the late In the Ancient Near East the Copper Age cov ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bronze Age
The Bronze Age () was a historical period characterised principally by the use of bronze tools and the development of complex urban societies, as well as the adoption of writing in some areas. The Bronze Age is the middle principal period of the three-age system, following the Stone Age and preceding the Iron Age. Conceived as a global era, the Bronze Age follows the Neolithic, with a transition period between the two known as the Chalcolithic. The final decades of the Bronze Age in the Mediterranean basin are often characterised as a period of widespread societal collapse known as the Late Bronze Age collapse (), although its severity and scope are debated among scholars. An ancient civilisation is deemed to be part of the Bronze Age if it either produced bronze by smelting its own copper and alloying it with tin, arsenic, or other metals, or traded other items for bronze from producing areas elsewhere. Bronze Age cultures were the first to History of writing, develop writin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Iron Age
The Iron Age () is the final epoch of the three historical Metal Ages, after the Chalcolithic and Bronze Age. It has also been considered as the final age of the three-age division starting with prehistory (before recorded history) and progressing to protohistory (before written history). In this usage, it is preceded by the Stone Age (subdivided into the Paleolithic, Mesolithic and Neolithic) and Bronze Age. These concepts originated for describing Iron Age Europe and the ancient Near East. In the archaeology of the Americas, a five-period system is conventionally used instead; indigenous cultures there did not develop an iron economy in the pre-Columbian era, though some did work copper and bronze. Indigenous metalworking arrived in Australia with European contact. Although meteoric iron has been used for millennia in many regions, the beginning of the Iron Age is defined locally around the world by archaeological convention when the production of Smelting, smelted iron (espe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
SzГ©kelys
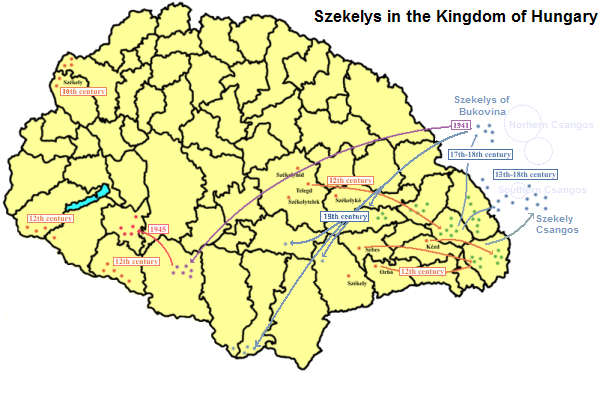
The SzГ©kelys (, Old Hungarian script, SzГ©kely runes: ), also referred to as Szeklers, are a Hungarians, Hungarian subgroup living mostly in the SzГ©kely Land in Romania. In addition to their native villages in Suceava County in Bukovina, a significant population descending from the SzГ©kelys of Bukovina currently lives in Tolna County, Tolna and Baranya County, Baranya counties in Hungary and certain districts of Vojvodina, Serbia. In the Middle Ages, the SzГ©kelys played a role in the defense of the Kingdom of Hungary#Middle Ages, Kingdom of Hungary against the Ottoman Empire, Ottomans in their posture as guards of the eastern border. With the Treaty of Trianon of 1920, Transylvania (including the SzГ©kely Land) became part of Romania, and the SzГ©kely population was a target of Romanianization efforts. In 1952, during the Socialist Republic of Romania, communist rule of Romania, the former counties with the highest concentration of SzГ©kely population вҖ“ MureИҷ County#His ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Middle Ages
In the history of Europe, the Middle Ages or medieval period lasted approximately from the 5th to the late 15th centuries, similarly to the post-classical period of global history. It began with the fall of the Western Roman Empire and transitioned into the Renaissance and the Age of Discovery. The Middle Ages is the middle period of the three traditional divisions of Western history: classical antiquity, the medieval period, and the modern period. The medieval period is itself subdivided into the Early, High, and Late Middle Ages. Population decline, counterurbanisation, the collapse of centralised authority, invasions, and mass migrations of tribes, which had begun in late antiquity, continued into the Early Middle Ages. The large-scale movements of the Migration Period, including various Germanic peoples, formed new kingdoms in what remained of the Western Roman Empire. In the 7th century, North Africa and the Middle EastвҖ”once part of the Byzantine Empireв ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pechenegs
The Pechenegs () or Patzinaks, , Middle Turkic languages, Middle Turkic: , , , , , , ka, бғһбғҗбғӯбғҗбғңбғҳбғҷбғҳ, , , ; sh-Latn-Cyrl, PeДҚenezi, separator=/, РҹРөСҮРөРҪРөР·Рё, also known as Pecheneg Turks were a semi-nomadic Turkic peoples, Turkic people from Central Asia who spoke the Pecheneg language. In the 9th and 10th centuries, the Pechenegs controlled much of the steppes of southeast Europe and the Crimean Peninsula. In the 9th century the Pechenegs began a period of wars against Kievan Rus', and for more than two centuries launched raids into the lands of Rus', which sometimes escalated into full-scale wars. Ethnonym The Pechenegs were mentioned as ''Bjnak'', ''Bjanak'' or ''Bajanak'' in medieval Arabic language, Arabic and Persian language, Persian texts, as ''Be-ДҚa-nag'' in Classical Tibetan documents, and as ''PaДҚanak-i'' in works written in Georgian language, Georgian. Anna Komnene and other Byzantine authors referred to them as ''Patzinakoi'' or ''Patzi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |