|
Ĺžebinkarahisar Castle
Şebinkarahisar Castle () is a fortification in Şebinkarahisar district of Giresun Province, northern Turkey. Şebinkarahisar Castle is located atop of a -high hill named Hacikayası southeast of Şebinkarahisar town in Giresun Province, northern Turkey. It is assumed that the castle existed during the Kingdom of Pontus before the Roman Empire period. Some parts of the castle walls in the north and southeast show traces of extensive repairs carried out during the reign of Roman emperor Justinian I (). Most of the castle walls were built during the Anatolian beyliks, Anatolian beylik of House of Mengüjek, Mengujekids. It is stated that Ruler Fahreddin Behram Shah (1162-1225) made important additions to the castle in 1184. An inscription from the Mengujekids period featuring a relief of double-headed eagle, originally situated over the castle gate, was removed in 1896 and stolen It was later found, and sent to the Governor of Sivas Province. The castle consists of two intertwined ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ĺžebinkarahisar
Şebinkarahisar is a town in Giresun Province in the Black Sea region of northeastern Turkey. It is the administrative seat of Şebinkarahisar District.İlçe Belediyesi Turkey Civil Administration Departments Inventory. Retrieved 1 March 2023. Its population is 10,695 (2022). Name The 6th-century Byzantine historian writes that the Roman general captured the then ancient fortress and renamed it Colonia, in Greek Koloneia (). A |
Byzantian Empire
The Byzantine Empire, also known as the Eastern Roman Empire, was the continuation of the Roman Empire centred on Constantinople during late antiquity and the Middle Ages. Having survived the events that caused the fall of the Western Roman Empire in the 5th centuryAD, it endured until the fall of Constantinople to the Ottoman Empire in 1453. The term 'Byzantine Empire' was coined only after its demise; its citizens used the term 'Roman Empire' and called themselves 'Romans'. During the early centuries of the Roman Empire, the western provinces were Latinised, but the eastern parts kept their Hellenistic culture. Constantine I () legalised Christianity and moved the capital to Constantinople. Theodosius I () made Christianity the state religion and Greek gradually replaced Latin for official use. The empire adopted a defensive strategy and, throughout its remaining history, experienced recurring cycles of decline and recovery. It reached its greatest extent unde ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Buildings And Structures In Giresun Province
A building or edifice is an enclosed structure with a roof, walls and windows, usually standing permanently in one place, such as a house or factory. Buildings come in a variety of sizes, shapes, and functions, and have been adapted throughout history for numerous factors, from building materials available, to weather conditions, land prices, ground conditions, specific uses, prestige, and aesthetic reasons. To better understand the concept, see ''Nonbuilding structure'' for contrast. Buildings serve several societal needs – occupancy, primarily as shelter from weather, security, living space, privacy, to store belongings, and to comfortably live and work. A building as a shelter represents a physical separation of the human habitat (a place of comfort and safety) from the ''outside'' (a place that may be harsh and harmful at times). buildings have been objects or canvasses of much artistic expression. In recent years, interest in sustainable planning and building practi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Castles In Turkey
Castles in Turkey were built in the Ancient and Medieval Times. The Turkish language, Turkish names for castle are , and . Thus the names of some castles have or suffixes. External links Castles in Turkey {{List of castles in Europe Castles in Turkey, * Lists of castles in the Middle East, Turkey Lists of castles in Asia, Turkey Lists of castles in Europe, Turkey Ancient Anatolia Lists of tourist attractions in Turkey, Castles Lists of buildings and structures in Turkey, Castles Lists of castles by country, Turkey ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Evliya Çelebi
Dervish Mehmed Zillî (25 March 1611 – 1682), known as Evliya Çelebi (), was an Ottoman Empire, Ottoman explorer who travelled through his home country during its cultural zenith as well as neighboring lands. He travelled for over 40 years, recording his commentary in a travel literature, travelogue called the ''Seyahatnâme'' ("Book of Travel"). The name Çelebi#Title, Çelebi is an honorific meaning "gentleman" or "man of God". Life Evliya Çelebi was born in Istanbul in 1611 to a wealthy family from Kütahya. Both his parents were attached to the Ottoman Empire, Ottoman court, his father, Dervish Mehmed Zilli, as a jeweller, and his mother as an Abkhazians, Abkhazian relation of the Grand Vizier of Mehmed IV Melek Ahmed Pasha. In his book, Evliya Çelebi traces his paternal genealogy back to Ahmad Yasawi, the earliest known Turkic poet and an early Sufi mystic. Evliya Çelebi received a court education from Ulama#Ottoman era, the Imperial ''ulama'' (scholars). He may have j ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Seyahatnâme
''Seyahatname'' () is the name of a literary form and tradition whose examples can be found throughout centuries in the Middle Ages around the Islamic world, starting with the Arab travellers of the Umayyad period. In a more specific sense, the name refers to the travel notes by the Ottoman Turks, Ottoman Turkish traveller Evliya Çelebi (1611–1682). The ''Seyahâtnâme'' of Evliya Çelebi is one example of this tradition. The author's personal name is Derviş Mehmed Zilli, and “Evliya” is his pen name, which he adopted in honor of his teacher, Evliya Mehmed Efendi. Evliya Çelebi's father was the chief jeweller to the courts, and thanks to the talent of his father Evliya was allowed to enjoy the favor of the court. Because of his gift in reciting the Quran, Evliya was presented to Sultan Murad IV and admitted to the palace, where he received extensive training in calligraphy, music, Arabic grammar, and tajwid. Shortly before Murad IV's expedition to Baghdad in 1638, Evliy ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ottoman Empire
The Ottoman Empire (), also called the Turkish Empire, was an empire, imperial realm that controlled much of Southeast Europe, West Asia, and North Africa from the 14th to early 20th centuries; it also controlled parts of southeastern Central Europe, between the early 16th and early 18th centuries. The empire emerged from a Anatolian beyliks, ''beylik'', or principality, founded in northwestern Anatolia in by the Turkoman (ethnonym), Turkoman tribal leader Osman I. His successors Ottoman wars in Europe, conquered much of Anatolia and expanded into the Balkans by the mid-14th century, transforming their petty kingdom into a transcontinental empire. The Ottomans ended the Byzantine Empire with the Fall of Constantinople, conquest of Constantinople in 1453 by Mehmed II. With its capital at History of Istanbul#Ottoman Empire, Constantinople (modern-day Istanbul) and control over a significant portion of the Mediterranean Basin, the Ottoman Empire was at the centre of interacti ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Seljuk Empire
The Seljuk Empire, or the Great Seljuk Empire, was a High Middle Ages, high medieval, culturally Turco-Persian tradition, Turco-Persian, Sunni Islam, Sunni Muslim empire, established and ruled by the Qiniq (tribe), Qïnïq branch of Oghuz Turks. The empire spanned a total area of from Anatolia and the Levant in the west to the Hindu Kush in the east, and from Central Asia in the north to the Persian Gulf in the south, and it spanned the time period 1037–1308, though Seljuk rule beyond the Anatolian peninsula ended in 1194. The Seljuk Empire was founded in 1037 by Tughril (990–1063) and his brother Chaghri Beg, Chaghri (989–1060), both of whom co-ruled over its territories; there are indications that the Seljuk leadership otherwise functioned as a triumvirate and thus included Seljuk dynasty, Musa Yabghu, the uncle of the aforementioned two. During the formative phase of the empire, the Seljuks first advanced from their original homelands near the Aral Sea into Greater Kho ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Shabin-Karahisar Uprising
The Shabin-Karahisar uprising (June 2–30, 1915) was a resistance effort by the Armenian militia of the Hunchaks of the Giresun Province against Ottoman troops during the Armenian genocide. They had resisted the Ottoman onslaught for the duration of a month.Simon Payaslian, "The Armenian Resistance at Shabin-Karahisar in 1915" 5th International conferences on Historic Armenian Cities and Provinces The Armenians had positioned themselves in a fort right outside the town where about 250 men fought off Turkish soldiers. Background News of the massacres in other regions of Western Armenia made the people of Shabin-Karahisar think that their "turn" was coming soon. In April, 1915, hundreds of young men were suddenly imprisoned. In June, 1915, the region's Armenian religious leader was executed. Then, 200 Armenian merchants were killed as a part of a systematic campaign of genocide by the Ottoman authorities. The able-bodied Armenians of Shabin-Karahisar thus decided to confront the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Abaza Mehmed Pasha
Abaza Mehmed Pasha (, ); 1576 – August 23, 1634) was a statesman and military commander of the Ottoman Empire, the namesake of the Abaza rebellion. He was the beylerbey of the Bosnia Eyalet in 1628–1631. He was executed by sultan Murat IV in 1634. He was involved in the Abaza and Celali rebellions. Early life Abaza was originally a slave of Abkhaz origin. The Family Lakrba is a Amista ( Lord ) Biography He started his career as the treasurer of Ali Janbulad, Pasha of Aleppo. In 1607, he was captured for his role in Janbulad rebellion by Grand Vizier Kuyucu Murad Pasha on the Amik plain. However the timely intervention of Agha Damat Halil Pasha saved his life. Abaza rose through ranks becoming Governor of Aleppo and Marash. He was later reported of becoming Governor of Erzurum. In 1617, his sponsor Damat Halil Pasha was appointed Grand Vizier, thus opening several closed doors upon him. Celali rebellion and capture Due to the constant state of war over Eastern An ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ĺžehzade Murad (son Of Ĺžehzade Ahmed)
Şehzade Murad (; 1495 Amasya – 16 October 1519, Kashan or Isfahan) was an Ottoman prince (''şehzade''), a son of Şehzade Ahmed and a grandson of Sultan Bayezid II. He was involved in the chaos that surrounded the succession to Sultan Bayezid II (1481–1512). Murad's father, Ahmed, had fought against his half-brother Şehzade Selim (later Selim I) for their father throne; during this struggle, Ahmed received support from Shah Ismail I (1501–1524) of the neighboring Safavid Empire. When Ahmed was put to death by the victorious Selim, Şehzade Murad was subsequently given support by Ismail I as claimant to the throne. Ismail I wanted to use Murad to mobilize opposition against Selim. In 1512, during Nur-Ali Khalifa's large-scale campaign in Anatolia, Murad joined his campaign, and even "girded the Qizilbash crown". According to information Selim received from his spies (December 1512/January 1513), Ismail I allegedly wanted to conquer Anatolia, give the Rum beylerbeylik ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
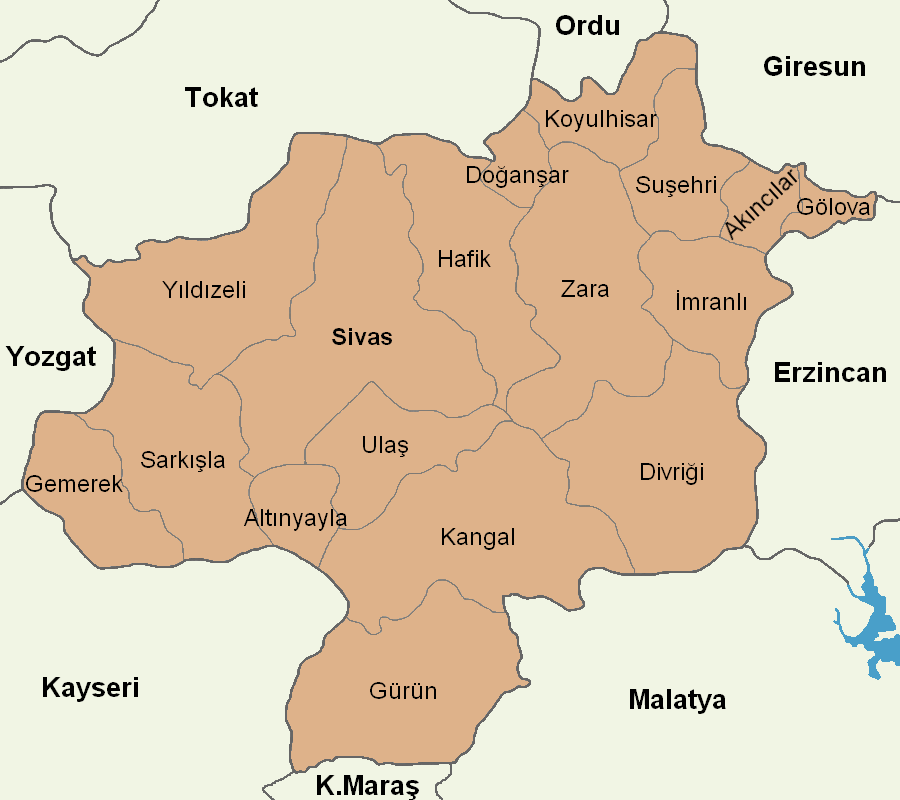
Sivas Province
Sivas Province () is a province of Turkey. It is located in the eastern part of the Central Anatolia region of Turkey. Its area is 28,164 km2 (the second largest province after Konya), and its population is 634,924 (2022). Its adjacent provinces are Yozgat to the west, Kayseri to the southwest, KahramanmaraĹź to the south, Malatya to the southeast, Erzincan to the east, Giresun to the northeast, and Ordu to the north. Its capital is Sivas. Most of Sivas Province has the typical continental climate of the Central Anatolian Region, in which summer months are hot and dry, while winter months are cold and snowy. However, the northern part of the province shows some features of the oceanic/ humid subtropical Black Sea climate, while the eastern portion has influences of the Eastern Anatolian highland climate. This province is noted for its thermal springs. Districts Sivas province is divided into 17 districts (capital district in bold): History The route of the Silk R ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |