|
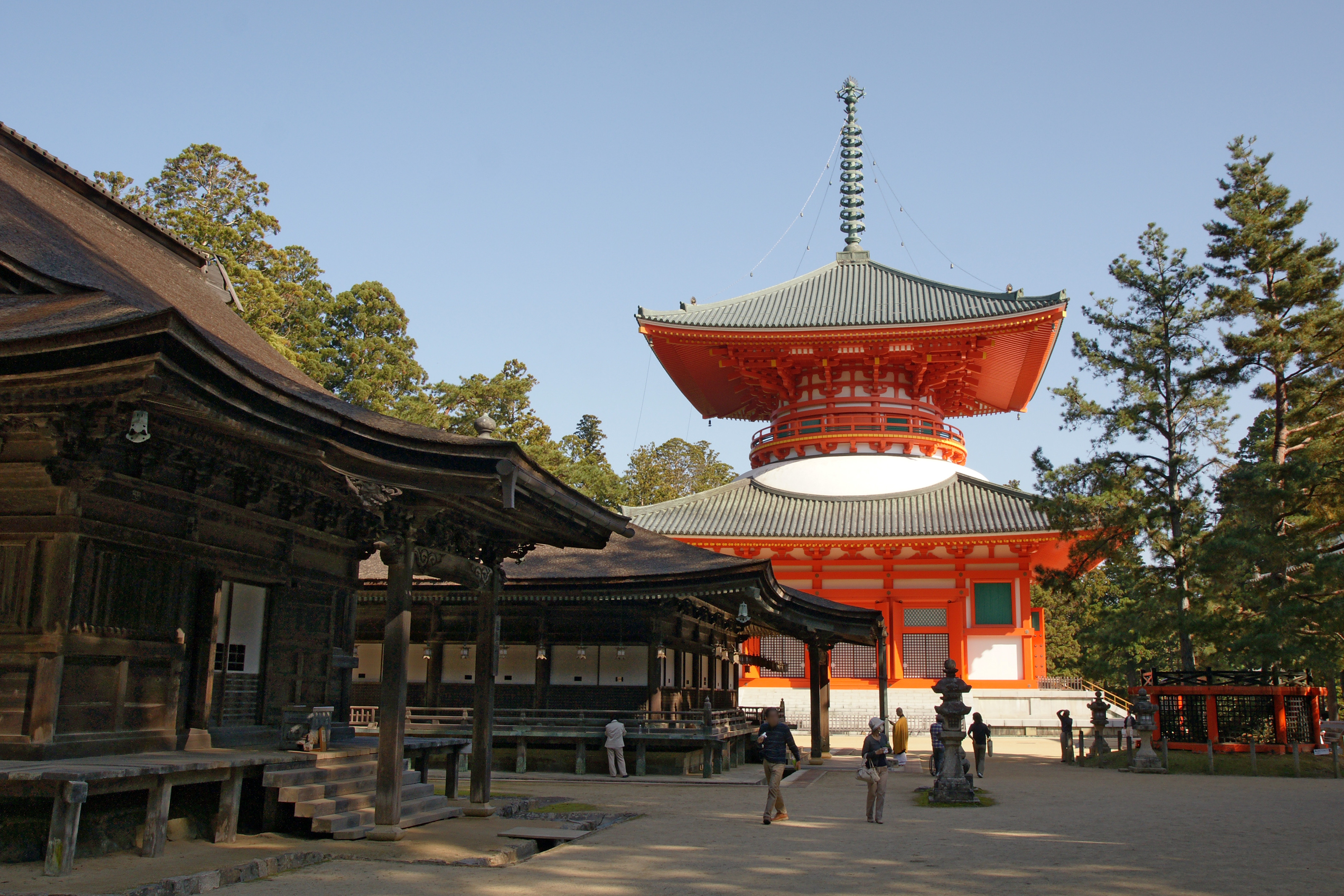
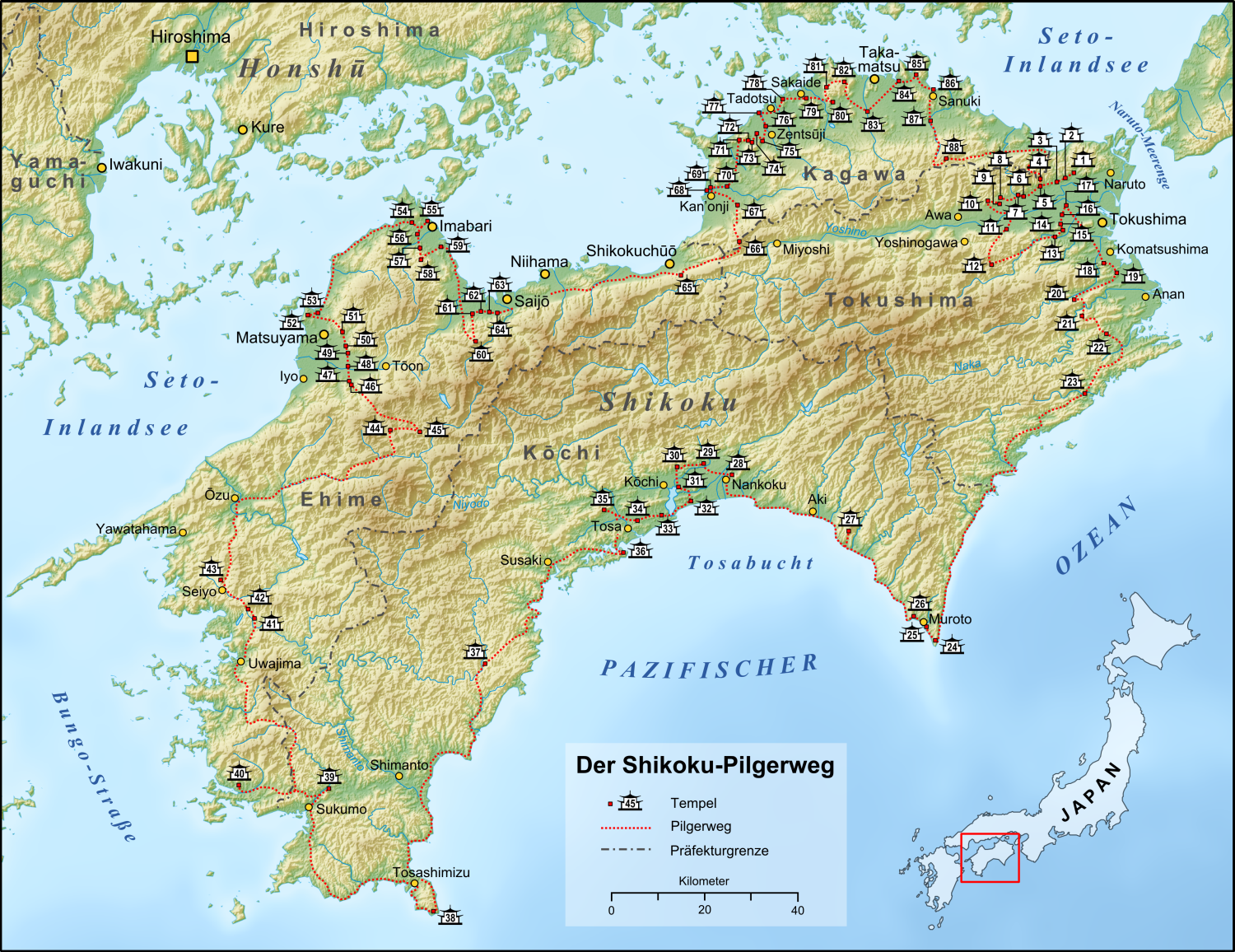
┼īkubo-ji
is a Shingon temple in Sanuki, Kagawa Prefecture, Japan. It is Temple 88 on the Shikoku 88 temple pilgrimage. Pilgrims leave their kong┼Ź-zue at the temple when completing the circuit. The ┼īkubo-ji temple bell and pilgrim bells have been selected by the Ministry of the Environment as one of the 100 Soundscapes of Japan. The temple's grounds feature a repository for walking sticks dedicated by pilgrims, symbolizing the completion of their spiritual journey. These sticks are ritually disposed of by burning them every spring and summer. Additionally, the temple offers a unique experience through a miniature pilgrimage under the Daishi Hall, where visitors can step on bags of sand representing the 88 temples, receiving the same blessings as if they visited each one. Okuboji is situated about 450 meters above sea level and is known for its beautiful autumn foliage, making it a popular spot for visitors in November. The temple is accessible by a 60-minute bus ride from JR Shido S ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kong┼Ź-zue
The is a wooden staff carried by ''yamabushi'' and pilgrims on the Shikoku Pilgrimage in Japan. The ''kong┼Ź-zue'' is said to represent the body of K┼½kai and to support the pilgrim along the way; as such it is treated with respect, having its "feet" washed and being brought inside at the end of each day's journey. It is inscribed with the chant ''Namu-Daishi-Henj┼Ź-Kong┼Ź'' and ''D┼Źgy┼Ź-Ninin'' or "We two pilgrims together". By another tradition, it is carried aloft when crossing a bridge so that it does not touch the ground and wake K┼Źb┼Ź Daishi. Pilgrims leave their ''kong┼Ź-zue'' at ┼īkubo-ji, the final temple, upon completion of the circuit. There is an occasional funerary practice in Shikoku and other parts of Japan whereby the decedent is dressed as a pilgrim and placed in the casket along with a staff and pilgrim's stamp book (''n┼Źky┼Źch┼Ź'') for their final journey. See also Oizuru (garment) is one of the sacred garments of the traditional dress of Japanese Japanese ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Shikoku Pilgrimage
The or is a multi-site pilgrimage of 88 temples associated with the Buddhist monk K┼½kai (''K┼Źb┼Ź Daishi'') on the island of Shikoku, Japan. A popular and distinctive feature of the island's cultural landscape, and with a long history, large numbers of pilgrims, known as , still undertake the journey for a variety of ascetic, pious, and tourism-related purposes. The pilgrimage is traditionally completed on foot, but modern pilgrims use cars, taxis, buses, bicycles, or motorcycles, and often augment their travels with public transportation. The standard walking course is approximately long and can take anywhere from 30 to 60 days to complete. In addition to the 88 "official" temples of the pilgrimage, there are 20 ''bekkaku'' (ÕłźµĀ╝) temples, which are officially associated with the Shikoku Pilgrimage (and hundreds more ''bangai'' (ńĢ¬Õż¢) temples, simply meaning "outside the numbers," which are not considered part of the official 88). To complete the pilgrimage, it ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sanuki, Kagawa
is a Cities of Japan, city in Kagawa Prefecture, Japan. , the city had an estimated population of 46,016 in 20847 households and a population density of and a population density of 290 persons per km2. The total area of the city is . Geography Sanuki is located in northeast Kagawa Prefecture, on the island of Shikoku, facing the Seto Inland Sea to the north, and the Sanuki Mountains to the south. The city lies just east of the prefecture capital, Takamatsu. Neighbouring municipalities Kagawa Prefecture *Higashikagawa, Kagawa, Higashikagawa *Miki, Kagawa, Miki *Takamatsu, Kagawa, Takamatsu Tokushima Prefecture * Awa, Tokushima , Awa *Mima, Tokushima , Mima Climate Sanuki has a humid subtropical climate (K├Čppen ''Cfa'') characterized by warm summers and cool winters with light snowfall. The average annual temperature in Sanuki is 15.5 ┬░C. The average annual rainfall is 1606 mm with September as the wettest month. The temperatures are highest on average in Januar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
100 Soundscapes Of Japan
The are a number of noises selected by the Ministry of the Environment (Japan), Ministry of the Environment as particularly representative of the country. They were chosen in 1996, as part of government efforts to combat noise pollution and to protect and promote protection of the Environment of Japan, environment. There were 738 submissions received from all over the country and the 100 "best" were selected after examination by the Japan Soundscape Study Group. These soundscapes are intended to function as symbols for local people and to promote the rediscovery of the sounds of everyday life. The follow-up Sixth National Assembly on Soundscape Conservation was held in Matsuyama in 2002. See also * Soundscape ecology * Ecoacoustics * Biophony * World Soundscape Project * 100 Landscapes of Japan (Heisei era) References External links * {{in lang, ja}Ministry of the Environment - 100 Soundscapes of Japan*100 Soundscapes of Japan - List in English with map (6G) Culture of Jap ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
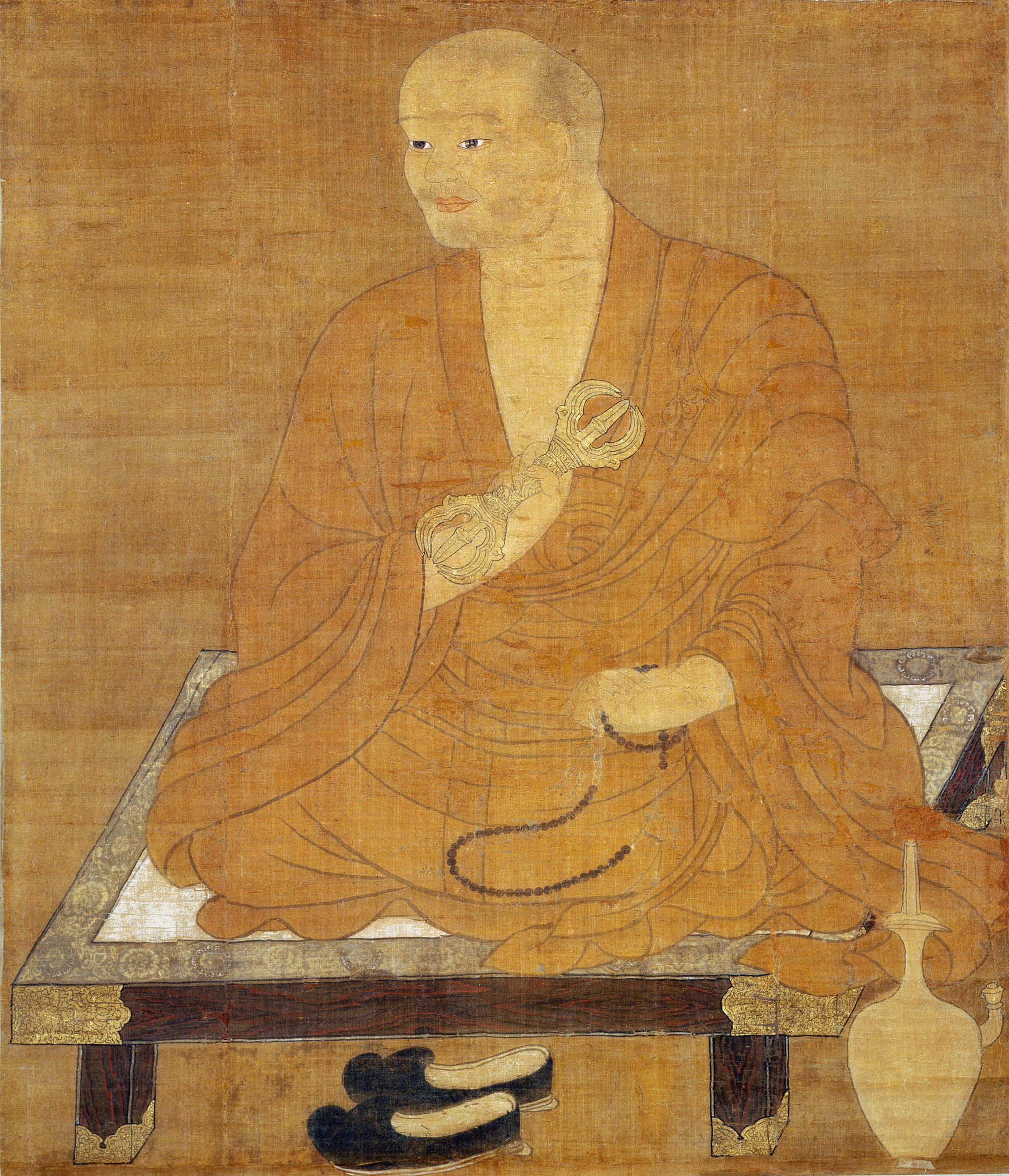
Shingon
is one of the major schools of Buddhism in Japan and one of the few surviving Vajrayana lineages in East Asian Buddhism. It is a form of Japanese Esoteric Buddhism and is sometimes called "T┼Źmitsu" (µØ▒Õ»å lit. "Esoteric [Buddhism] of T┼Ź-ji"). The word ''shingon'' is the Kan-on, Japanese reading of the Traditional Chinese characters, Chinese word ('), which is the translation of the Sanskrit word mantra. The Chinese Esoteric Buddhism, Zh─ōny├Īn lineage was founded in China (c. 7thŌĆō8th centuries) by Indian Vajracharya, vajr─üc─üryas (esoteric masters) like ┼Üubhakarasiß╣āha, Vajrabodhi and Amoghavajra. These esoteric teachings would later flourish in Japan under the auspices of a Buddhist monk named K┼½kai (, 774ŌĆō835), who traveled to Tang dynasty, Tang China and received these esoteric transmissions from a Chinese master named Huiguo (746ŌĆō805). K┼½kai established his tradition at Mount K┼Źya (in Wakayama Prefecture), which remains the central pilgrimage center of Sh ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kagawa Prefecture
is a Prefectures of Japan, prefecture of Japan located on the island of Shikoku. Kagawa Prefecture has a population of 949,358 (as of 2020) and is the List of Japanese prefectures by area, smallest prefecture by geographic area at . Kagawa Prefecture borders Ehime Prefecture to the southwest and Tokushima Prefecture to the south. Takamatsu, Kagawa, Takamatsu is the capital and largest city of Kagawa Prefecture, with other major cities including Marugame, Kagawa, Marugame, Mitoyo, Kagawa, Mitoyo, and Kan'onji, Kagawa, Kan'onji. Kagawa Prefecture is located on the Seto Inland Sea across from Okayama Prefecture on the island of Honshu, which is connected by the Great Seto Bridge. Kagawa Prefecture includes Sh┼Źdoshima, the second-largest island in the Seto Inland Sea, and the prefecture's southern land border with Tokushima Prefecture is formed by the Sanuki Mountains. History Kagawa was formerly known as Sanuki Province. For a brief period between August 1876 and December ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Japan
Japan is an island country in East Asia. Located in the Pacific Ocean off the northeast coast of the Asia, Asian mainland, it is bordered on the west by the Sea of Japan and extends from the Sea of Okhotsk in the north to the East China Sea in the south. The Japanese archipelago consists of four major islandsŌĆöHokkaido, Honshu, Shikoku, and KyushuŌĆöand List of islands of Japan, thousands of smaller islands, covering . Japan has a population of over 123 million as of 2025, making it the List of countries and dependencies by population, eleventh-most populous country. The capital of Japan and List of cities in Japan, its largest city is Tokyo; the Greater Tokyo Area is the List of largest cities, largest metropolitan area in the world, with more than 37 million inhabitants as of 2024. Japan is divided into 47 Prefectures of Japan, administrative prefectures and List of regions of Japan, eight traditional regions. About three-quarters of Geography of Japan, the countr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ministry Of The Environment (Japan)
The is a Cabinet-level ministry of the government of Japan responsible for global environmental conservation, pollution control, and nature conservation. The ministry was formed in 2001 from the sub-cabinet level Environmental Agency established in 1971. The Minister of the Environment is a member of the Cabinet of Japan and is chosen by the Prime Minister, usually from among members of the Diet. In March 2006, the then-Minister of the Environment Yuriko Koike, created a '' furoshiki'' cloth to promote its use in the modern world. In August 2011, the Cabinet of Japan approved a plan to establish a new energy watchdog under the Environment Ministry, and the Nuclear Regulation Authority was founded on September 19, 2012. Organization * Minister's Secretariat (Õż¦ĶćŻÕ«śµł┐) * (ńĘÅÕÉłńÆ░Õóāµö┐ńŁ¢ńĄ▒µŗ¼Õ«ś) * Global Environment Bureau (Õ£░ńÉāńÆ░ÕóāÕ▒Ć) * Environment Management Bureau (µ░┤Ńā╗Õż¦µ░ŚńÆ░ÕóāÕ▒Ć) * Nature Conservation Bureau (Ķć¬ńäČńÆ░ÕóāÕ▒Ć) * (ńÆ░ÕóāÕåŹńö¤Ńā╗Ķ│ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Buddhist Temples In Kagawa Prefecture
Buddhism, also known as Buddhadharma and Dharmavinaya, is an Indian religion and philosophical tradition based on teachings attributed to the Buddha, a wandering teacher who lived in the 6th or 5th century BCE. It is the world's fourth-largest religion, with about 500 million followers, known as Buddhists, who comprise four percent of the global population. It arose in the eastern Gangetic plain as a movement in the 5th century BCE, and gradually spread throughout much of Asia. Buddhism has subsequently played a major role in Asian culture and spirituality, eventually spreading to the West in the 20th century. According to tradition, the Buddha instructed his followers in a path of development which leads to awakening and full liberation from '' dukkha'' (). He regarded this path as a Middle Way between extremes such as asceticism or sensual indulgence. Teaching that ''dukkha'' arises alongside attachment or clinging, the Buddha advised meditation practices and ethic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Shingon Buddhism
is one of the major schools of Buddhism in Japan and one of the few surviving Vajrayana lineages in East Asian Buddhism. It is a form of Japanese Esoteric Buddhism and is sometimes called "T┼Źmitsu" (µØ▒Õ»å lit. "Esoteric uddhismof T┼Ź-ji"). The word ''shingon'' is the Japanese reading of the Chinese word ('), which is the translation of the Sanskrit word mantra. The Zh─ōny├Īn lineage was founded in China (c. 7thŌĆō8th centuries) by Indian vajr─üc─üryas (esoteric masters) like ┼Üubhakarasiß╣āha, Vajrabodhi and Amoghavajra. These esoteric teachings would later flourish in Japan under the auspices of a Buddhist monk named K┼½kai (, 774ŌĆō835), who traveled to Tang China and received these esoteric transmissions from a Chinese master named Huiguo (746ŌĆō805). K┼½kai established his tradition at Mount K┼Źya (in Wakayama Prefecture), which remains the central pilgrimage center of Shingon Buddhism. The practice of the Shingon school stresses that one is able to atta ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Buddhist Pilgrimage Sites In Japan
Buddhism, also known as Buddhadharma and Dharmavinaya, is an Indian religion and philosophical tradition based on teachings attributed to the Buddha, a wandering teacher who lived in the 6th or 5th century BCE. It is the world's fourth-largest religion, with about 500 million followers, known as Buddhists, who comprise four percent of the global population. It arose in the eastern Gangetic plain as a movement in the 5th century BCE, and gradually spread throughout much of Asia. Buddhism has subsequently played a major role in Asian culture and spirituality, eventually spreading to the West in the 20th century. According to tradition, the Buddha instructed his followers in a path of development which leads to awakening and full liberation from '' dukkha'' (). He regarded this path as a Middle Way between extremes such as asceticism or sensual indulgence. Teaching that ''dukkha'' arises alongside attachment or clinging, the Buddha advised meditation practices and e ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |