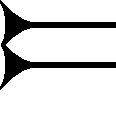
|
Ù (cuneiform)
The cuneiform ├╣ sign ('u, no. 3'), is found in both the 14th century BC Amarna letters and the ''Epic of Gilgamesh''. Its use is as a conjunction, (translated as for example: ''and, but, else, until,'' etc.), but rarely it is substituted for ''alphabetic u'', but that vowel ''u'' is typically represented by 'u, no. 2', (u prime), ├║; occasionally 'u, no. 1', (u (cuneiform)), , (mostly used for a conjunction, and ''numeral 10''), is also substituted for the "alphabetic u". The use of ''├╣'' is often as a "stand-alone" conjunction, for example between two listed items, but it is used especially as a segue in text, (example Amarna letters), when changing topics, or when inserting segue-pausing positions. In the Amarna letters, it is also commonly immediately followed by a preposition: '' a- na'', or '' i- na'', used as ''"...And, to...."'', or ''"...And, in...."''; also ''"...But, for...."'', etc. This usage with a preposition is also a better example of the segue usage. Of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
B001ellst
B, or b, is the second Letter (alphabet), letter of the Latin alphabet, used in the English alphabet, modern English alphabet, the alphabets of other western European languages and others worldwide. Its name in English is ''English alphabet#Letter names, bee'' (pronounced ), plural ''bees''. It represents the voiced bilabial stop in many languages, including English. In some other languages, it is used to represent other bilabial consonants. History The Roman derived from the Greek alphabet, Greek capital beta (letter), beta via its Old Italic script, Etruscan and Archaic Greek alphabets#Euboean, Cumaean variants. The Greek letter was an adaptation of the Phoenician alphabet, Phoenician letter bet (letter), b─ōt . The Ancient Egypt, Egyptian Egyptian hieroglyphs, hieroglyph for the consonant voiced bilabial plosive, /b/ had been an image of a foot (hieroglyph), foot and calf , but b─ōt (Phoenician for "house") was a modified form of a Proto-Sinaitic script, Proto-Sinait ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ú (cuneiform)
The cuneiform sign ├║ is a common-use sign of the Amarna letters, the ''Epic of Gilgamesh,'' and other cuneiform texts (for example Hittite texts). It has a secondary sub-use in the Epic of Gilgamesh for ┼Īam. Linguistically, it has the alphabetical usage in texts for ''u'', but can replace any of the four vowels, so also used for ''a'', or ''e'', or ''i''. ''Epic of Gilgamesh'' usage The ''├║'' sign usage in the ''Epic of Gilgamesh'' is as follows: (''┼Īam'', 45 times, ''├║'', 493, ''K├Ü┼Ā'', 2, and ''├Ü'', 4 times).Parpola, 1971. ''The Standard Babylonian Epic of Gilgamesh'', Sign List, pp. 155-165, sign no. 318, p. 160. ''├Ü'' is logogram, for Akkadian "tullal", a ''soapwort''. ┼Īam syllabic use in the Epic of Gilgamesh The following words use the syllabic '' ┼Īam'' as the first syllable in the word entries under ''┼Ī'' in the glossary. #''┼Īamhatu'', for English, ''"harlot"''. #''┼Īamhi┼Ī'', ''"proudly, stoutly",''. #''┼Īammmu'', ''"drug, plant, grass"''. Reference ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ar (cuneiform)
The cuneiform Ar sign, .—is a cuneiform sign that is a combined sign, containing ┼Āi (cuneiform), and Ri (cuneiform). It is used in one prominent name in the '' Amarna letters'', for ┼Āuwardata, as well as in a number of Amarna letters. "Ar" is also used in the ''Epic of Gilgamesh'', and other texts. ''Epic of Gilgamesh'' usage The ''Ar'' sign usage in the ''Epic of Gilgamesh'' is as follows: ''ar''-(21 times). References * Moran, William L. 1987, 1992. ''The Amarna Letters.'' Johns Hopkins University Press, 1987, 1992. 393 pages.(softcover, ) * Parpola, 1971. ''The Standard Babylonian Epic of Gilgamesh'', Parpola, Simo, Neo-Assyrian Text Corpus Project The Neo-Assyrian Text Corpus Project is an international scholarly project aimed at collecting and publishing ancient Assyrian texts of the Neo-Assyrian Empire and studies based on them. Its headquarters are in Helsinki in Finland. State Archives ..., c 1997, Tablet I thru Tablet XII, Index of Names, Sign List, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Di (cuneiform)
The cuneiform di sign, also de, ß╣Łe, ß╣Łi, and sumerograms DI and S├ü is a common-use sign of the ''Epic of Gilgamesh'', the 1350 BC Amarna letters, and other cuneiform texts. In the Akkadian language for forming words, it can be used syllabically for: ''de, di, ß╣Łe, and ß╣Łi''; also alphabetically for letters ''d'', ''ß╣Ł'', ''e'', or ''i''. (All the four vowels in Akkadian are interchangeable for forming words (''a, e, i, u''), thus the many choices of scribes is apparent for composing actual 'dictionary-entry' words.) Some consonant-pairs (d/t), are also interchangeable (for example the ''d'', ''t'', and ''ß╣Ł''). ''Epic of Gilgamesh'' usage The usage numbers for ''di/de'' in the ''Epic of Gilgamesh'' are as follows: ''de''-(8) times, ''di''-(161), ''ß╣Łe''-(7), ''ß╣Łi''-(19), ''DI''-(1), ''S├ü''-(2) times. Besides ''┼Īa'' usage in word components of verbs, nouns, etc., it has a major usage between words. In Akkadian, for English language ''"who"'', it is an interrogative ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
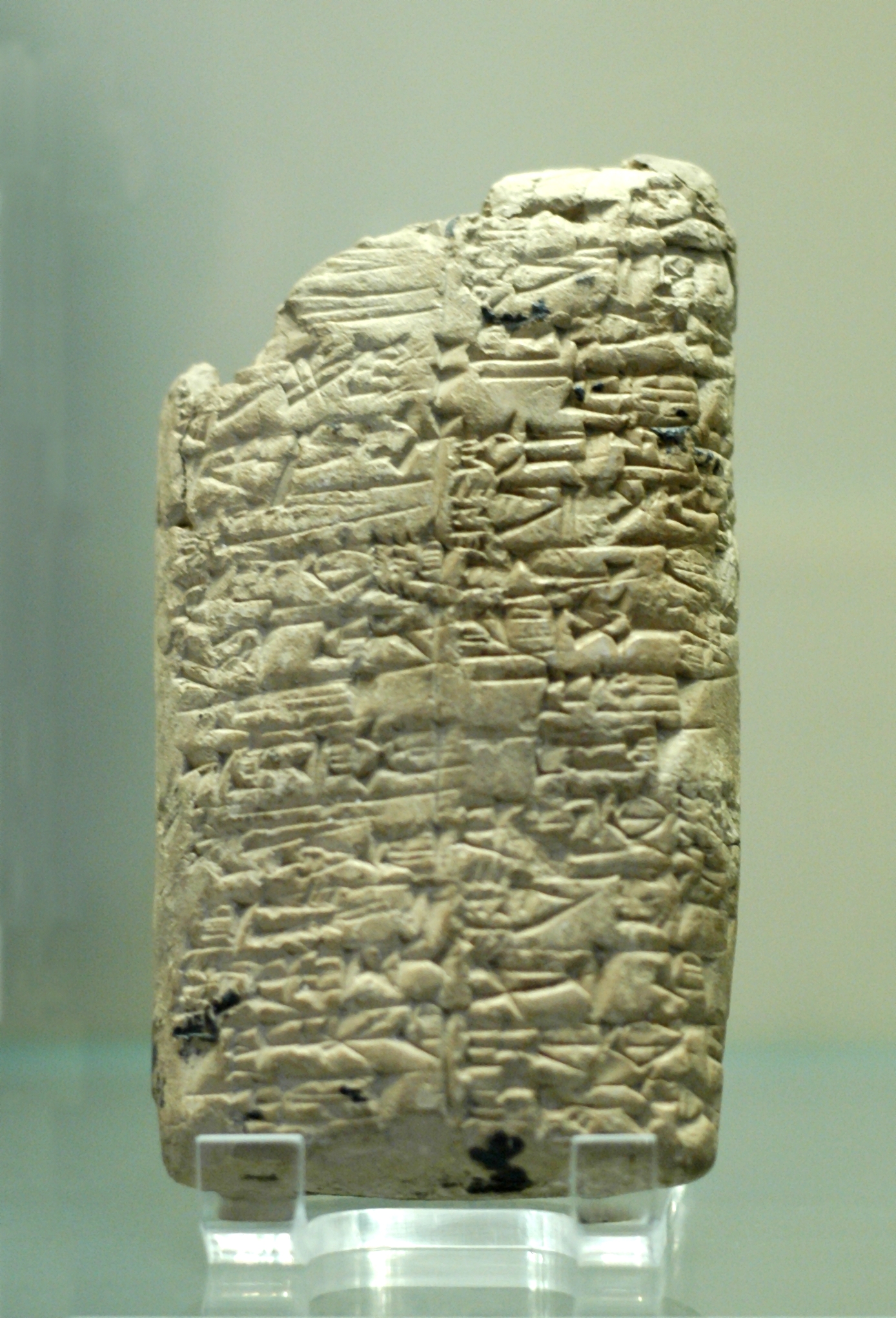
Clay Tablet
In the Ancient Near East, clay tablets (Akkadian language, Akkadian ) were used as a writing medium, especially for writing in cuneiform, throughout the Bronze Age and well into the Iron Age. Cuneiform characters were imprinted on a wet clay tablet with a stylus often made of Reed (plant), reed (reed pen). Once written upon, many tablets were dried in the sun or air, remaining fragile. Later, these unfired clay tablets could be soaked in water and recycled into new clean tablets. Other tablets, once written, were either deliberately fired in hot kilns, or inadvertently fired when buildings were burnt down by accident or during conflict, making them hard and durable. Collections of these clay documents made up the first archives. They were at the root of the first library, libraries. Tens of thousands of written tablets, including many fragments, have been found in the Middle East. Most of the documents on tablets that survive from the Minoan civilization, Minoan and Mycenaean ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Um (cuneiform)
The cuneiform alphabetic um sign, also dup, tup, ß╣Łup, and DUB, the Sumerogram (logogram), for Akkadian language "ß╣Łuppu",Parpola, 1971. ''The Standard Babylonian Epic of Gilgamesh'', Glossary, pp. 119-145, ß╣Łuppu, p. 144. (= the clay tablet), is found in both the 14th century BC Amarna letters and the Epic of Gilgamesh. In the Amarna letters as ''um'', it is found as ''um-ma'' in the introduction of the letters as ''"Message (thus)"''...(and then the PN (personal name) of the individual sending, or authoring the letter). In specific texts with dialogue, for example Amarna letter EA 19, ''Love and Gold'', an extensive discussion is made by the king of Babylon about his father, ancestry, friendship between kings, envoys, women (for the harem, or wife), etc., and consequently the dialogue is preceded by ''um-ma'' ("quote"), then the dialogue by the messenger, (or the king). References * Moran, William L. 1987, 1992. ''The Amarna Letters.'' Johns Hopkins University Press, 19 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Endaruta
Endaruta was the ruler of Achshaph-(''Ak┼Īapa'' of the letters), in the 1350- 1335 BC Amarna letters correspondence. Endaruta was the author of EA 223 ( EA for 'el Amarna') of the letters. He is only referenced in two other letters EA 366 and 367, but EA 367, entitled: '' "From the Pharaoh to a vassal" '' is addressed to Endaruta, with instructions to guard his city. Pharaoh states Hanni–''Khanni'', is en route with the "archer-army force", and to prepare for their needs. Tablet-letter 367 is an undamaged, twenty-five line letter. The Amarna letters involving Endaruta EA 367--title: ''"From the Pharaoh to a vassal"'' Say to ''Endaruta'', the ruler of Ak┼Īapa: Thus the king-(pharaoh). He herewith dispatches to you this tablet, (i.e. tablet-letter), saying to you, "Be on your guard. You are to guard the place of the king where you are. The king herewith sends to you Hanni, the ''son of Maireya'', the stable overseer of the king in Canaan. And what he tells you heed ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Amarna Letter EA 367
Amarna letter EA 367, titled ''From the Pharaoh to a Vassal,'' is a medium-small, square clay tablet Amarna letter to Endaruta of Achshaph, (Ak┼Īapa of the letters), one of only about 10 letters of the el-Amarna corpus, that is from the Pharaoh of Egypt to his correspondent. (Two of the Pharaonic letters are lists, and not a 'letter' per se.) The letter is distinctive in that, 1- there are basically no spaces between the Akkadian language cuneiform signs, (lines 3, 4, 5 (end Para I scribe-line), and lines 6, 7, and 8), on the letter, and, 2- only a few segue-spaces (sections with no signs, except at the end of some text lines ŌĆō no segue spaces in the middle of the text, tablet obverse). And, some text extends to the right (the cuneiform starts at the left margin) into the right side of the clay tablet's pillow shaped thickness, and further into the reverse side, which would appear upside down in the text of the reverse. (See photo of Amarna letter EA 9, bottom right of rever ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |