|
Г“ Maol FГЎbhail
Г“ Maol FГЎbhail, anglicised as Lavelle is an Irish surname. It can also be found as O'Mullawill, or rarely, as Mulfall or Mac Fall. Lavelle of Connacht The surname Lavelle is found mainly in Connacht, particularly in County Mayo, where Griffith's Valuation of 1857 recorded 286 ''Lavelle'' households. Many were located on Achill Island. It is found sparsely elsewhere in Ireland. The Lavelles of Mayo and elsewhere in Connacht are believed by MacLysaght to be descendants of the clan Г“ Maol FГЎbhail, a surname phonetically anglicised as Lavelle. On page 370 of RuaidhrГӯ Г“ Flaithbheartaigh's ''Iar Connacht'', James Hardiman quotes the manuscript called Crichaireacht cinedach nduchasa Muintiri Murchada, which states that ''O'Maelampaill of Donaghpatrick is the brehon of O'Flaherty.'' Hardiman notes concerning this family states: * ''O'Maelampaill. This name is written Г“ Maol FГЎbhail in Dubhaltach Mac Fhirbhisigh's copy of this tract. The name is still extant, but pronounced ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Anglicised
Anglicisation is the process by which a place or person becomes influenced by English culture or British culture, or a process of cultural and/or linguistic change in which something non-English becomes English. It can also refer to the influence of English culture and business on other countries outside England or the United Kingdom, including their media, cuisine, popular culture, technology, business practices, laws, or political systems. Linguistic anglicisation is the practice of modifying foreign words, names, and phrases to make them easier to spell, pronounce or understand in English. The term commonly refers to the respelling of foreign words, often to a more drastic degree than that implied in, for example, romanisation. One instance is the word "dandelion", modified from the French ''dent-de-lion'' ("lion's tooth", a reference to the plant's sharply indented leaves). The term can also refer to phonological adaptation without spelling change: ''spaghetti'', for example ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Clare (barony)
Clare may refer to: Places Antarctica * Clare Range, a mountain range in Victoria Land Australia * Clare, South Australia, a town in the Clare Valley * Clare Valley, South Australia Canada * Clare (electoral district), an electoral district * Clare, Nova Scotia, a municipal district Republic of Ireland * County Clare, one of the 32 counties of Ireland * Clare, County Westmeath, a townland in Killare civil parish, barony of Rathconrath * Clare Island, County Mayo * Clarecastle, a village in County Clare * Clare (DГЎil constituency) (since 1921) * Clare (UK Parliament constituency) (1801вҖ“1885) * Clare (Parliament of Ireland constituency) (until 1800) * River Clare, County Galway South Africa *Clare, Mpumalanga, a town in Mpumalanga province United Kingdom * Clare, County Antrim, a townland in County Antrim, Northern Ireland * Clare (Ballymore), a townland in County Armagh, Northern Ireland * Clare, County Down, a townland in County Down, Northern Ireland * Clare, Cou ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Conall Gulban
Conall Gulban (died c. 464) was an Irish king and eponymous ancestor of the ''CenГ©l Conaill'', who founded the kingdom of ''TГӯr Chonaill'' in the 5th century, comprising much of what is now County Donegal in Ulster. He was the son of Niall NoГӯgiallach. His by-name Gulban derives from '' Benn Ghulbain'' in County Sligo, from which centre the sons of Niall set out upon their conquest of the North. King Conall Gulban was murdered by the Masraige at ''Magh SlГ©cht'' (located in the west of modern County Cavan) in 464, on a Friday. He was buried by Saint Caillin at Fenagh, County Leitrim. He is important in the history of Irish Christianity as he was the first nobleman baptised by St. Patrick, thus opening the way for the conversion of the ruling classes of Ireland. He appears as a host and companion of CaГӯlte mac RГіnГЎin, one of the central Fianna figures in the tale ''Acallam na SenГіrach'' (''Colloquy of the Ancients'') who survive into Christian times and recounts tales ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
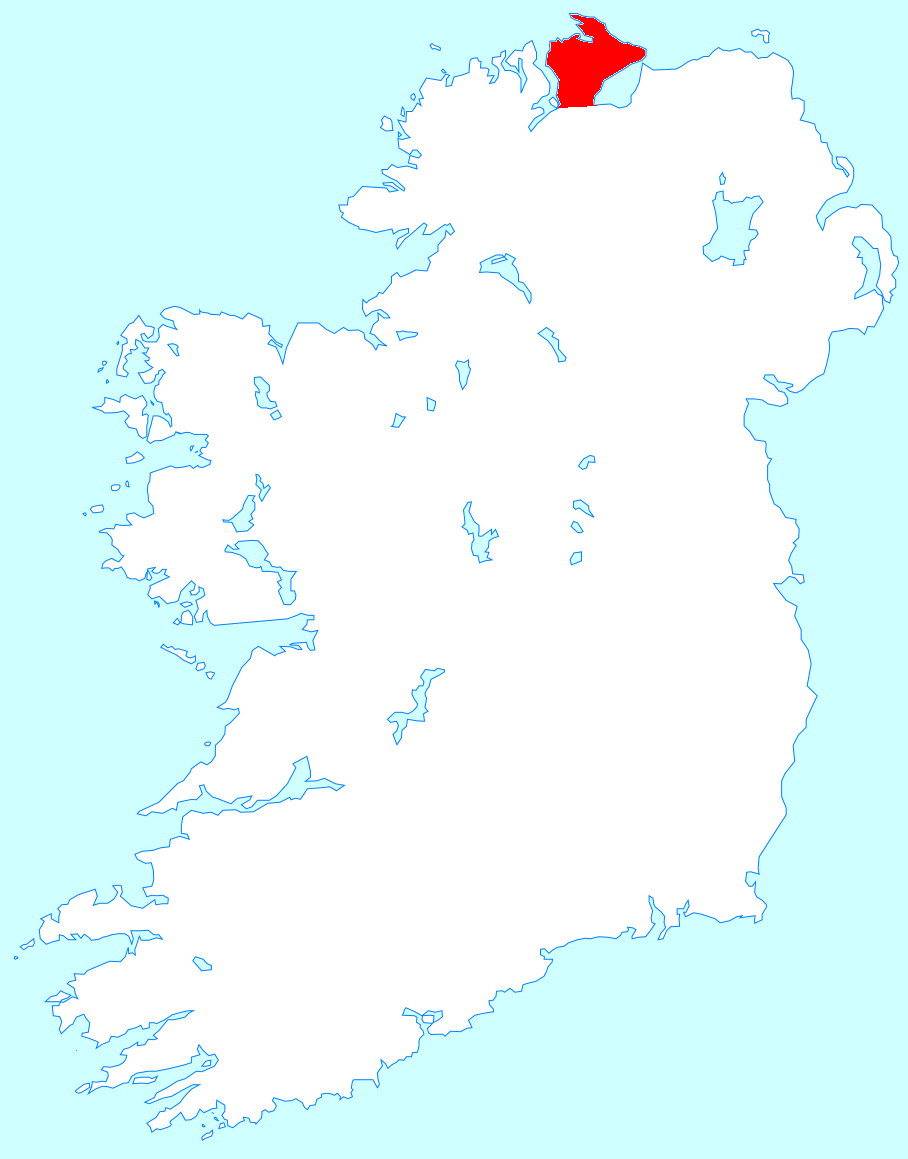
Inishowen
Inishowen () is a peninsula in the north of County Donegal in Ireland. Inishowen is the largest peninsula on the island of Ireland. The Inishowen peninsula includes Ireland's most northerly point, Malin Head. The Grianan of Aileach, a ringfort that served as the royal seat of the over-kingdom of Ailech, stands at the entrance to the peninsula. Towns and villages The main towns and villages of Inishowen are: * Ballyliffin, Buncrana, Bridgend, Burnfoot, Burt * Carndonagh, Carrowmenagh, Clonmany, Culdaff * Dunaff * Fahan * Glengad, Gleneely, Greencastle * Malin, Malin Head, Moville, Muff * Redcastle * Shrove * Quigley's Point * Urris Geography Inishowen is a peninsula of 884.33 square kilometres (218,523 acres), situated in the northernmost part of the island of Ireland. It is bordered to the north by the Atlantic Ocean, to the east by Lough Foyle, and to the west by Lough Swilly. It is joined at the south to the rest of the island and is mostly in County Donegal in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cairrge Brachaidhe
Cairrge Brachaidhe, aka Carrickbraghy or Carrichbrack, was a Gaelic- Irish medieval territory located in Inishowen, County Donegal, Ireland. Overview Thought to have been named after, or by, Brachaidi mac Diarmata of the CenГ©l Fergusa (see List of Irish clans in Ulster), a clan who held the territory from the early medieval period. The family of Г“ Maol FГЎbhail were its kings. In the early modern era it was part of the barony of Inishowen West, in County Donegal. Cairrge Brachaidhe in the Irish annals * ''721: Snedgus Dearg Ua Brachaidhe, was slain in battle on the side of Aedh Allan, son of Fearghal, and the Cinel Eoghain.'' * ''834, Fearghus son of Badhbhchadh, lord of Carraig (Cairge or Cairrge) Brach Aidhe, was slain by the Munstermen.'' * ''857, SeghonnГЎn, son of Conang, lord of Carraig Brachaidhe, died.'' * ''859, Sechonnan filius Conaing, rex Cairgi Brachaide, died.'' * ''878/81, Maelfabhaill, son of Loingseach, lord of Carraig Brachaighe (or Chairrge Brachaighe), ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Niall Of The Nine Hostages
Niall ''NoГӯgГӯallach'' (; Old Irish "having nine hostages"), or Niall of the Nine Hostages, was a legendary, semi-historical Irish king who was the ancestor of the UГӯ NГ©ill dynasties that dominated Ireland from the 6th to the 10th centuries. Irish annalistic and chronicle sources place his reign in the late 4th and early 5th centuries, although modern scholars, through critical study of the annals, date him about half a century later. Historicity and dates Niall is presumed, on the basis of the importance of his sons and grandsons, to have been a historical person,Francis J. Byrne, ''Irish Kings and High-Kings'', Second Edition, Dublin: Four Courts Press, 2001, but the early Irish annals say little about him. The ''Annals of Inisfallen'' date his death before 382, and the ''Chronicon Scotorum'' to 411.Kathleen Hughes, "The church in Irish society, 400вҖ“800, in DГЎibhГӯ Г“ CrГіinГӯn (ed.), ''A New History of Ireland Vol I: Prehistoric and Early Ireland'', Oxford University ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hearth Money Rolls
A hearth () is the place in a home where a fire is or was traditionally kept for home heating and for cooking, usually constituted by at least a horizontal hearthstone and often enclosed to varying degrees by any combination of reredos (a low, partial wall behind a hearth), fireplace, oven, smoke hood, or chimney. Hearths are usually composed of masonry such as brick or stone. For centuries, the hearth was such an integral part of a home, usually its central and most important feature, that the concept has been generalized to refer to a homeplace or household, as in the terms "hearth and home" and "keep the home fires burning". In the modern era, since the advent of central heating, hearths are usually less central to most people's daily life because the heating of the home is instead done by a furnace or a heating stove, and cooking is instead done with a kitchen stove/range (combination cooktop and oven) alongside other home appliances; thus many homes built in the 20t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
County Armagh
County Armagh (, named after its county town, Armagh) is one of the six counties of Northern Ireland and one of the traditional thirty-two counties of Ireland. Adjoined to the southern shore of Lough Neagh, the county covers an area of and has a population of about 175,000. County Armagh is known as the "Orchard County" because of its many apple orchards. The county is part of the historic province of Ulster. Etymology The name "Armagh" derives from the Irish word ' meaning "height" (or high place) and '. is mentioned in '' The Book of the Taking of Ireland'', and is also said to have been responsible for the construction of the hill site of (now Navan Fort near Armagh City) to serve as the capital of the kings (who give their name to Ulster), also thought to be 's ''height''. Geography and features From its highest point at Slieve Gullion, in the south of the county, Armagh's land falls away from its rugged south with Carrigatuke, Lislea and Camlough mountains, to rollin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Annals Of Inisfallen
Annals ( la, annДҒles, from , "year") are a concise historical record in which events are arranged chronologically, year by year, although the term is also used loosely for any historical record. Scope The nature of the distinction between annals and history is a subject based on divisions established by the ancient Romans. Verrius Flaccus is quoted by Aulus Gellius as stating that the etymology of ''history'' (from Greek , , equated with Latin , "to inquire in person") properly restricts it to primary sources such as Thucydides's which have come from the author's own observations, while annals record the events of earlier times arranged according to years. White distinguishes annals from chronicles, which organize their events by topics such as the reigns of kings, and from histories, which aim to present and conclude a narrative implying the moral importance of the events recorded. Generally speaking, annalists record events drily, leaving the entries unexplained and equally ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Leabhar Na NGenealach
''Leabhar na nGenealach'' ("Book of Genealogies") is a massive genealogical collection written mainly in the years 1649 to 1650, at the college-house of St. Nicholas' Collegiate Church, Galway, by Dubhaltach MacFhirbhisigh. He continued to add material until at least 1666, five years before he was murdered in 1671. The original 17th century manuscript was bequeathed to University College Dublin (UCD), by Dublin solicitor Arthur Cox in 1929, and can be consulted iUCD Library Special Collections The manuscript can be viewed online at ', which is available i and i Leabhar na nGenealach, was reprinted, and published in a five volume edition in Dublin in 2004 as ''The Great Book of Irish Genealogies''. Description and compilation Described by Eoin MacNeill ''"by far the largest and fullest body of Irish genealogical lore"'', it contains roughly twice as much material as found in the Book of Ballymote and the Book of Lecan. It preserves notes on families from all parts of Ireland, G ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nollaig Г“ MuraГӯle
Nollaig Г“ MuraГӯle is an Irish scholar. He published an acclaimed edition of Dubhaltach Mac Fhirbhisigh's ''Leabhar na nGenealach'' in 2004. He was admitted to the Royal Irish Academy in 2009. Life and career A native of Knock, County Mayo, Г“ MuraГӯle attended National University of Ireland, Maynooth where he was a postgraduate student enrolled for a PhD. He was Placenames Officer with the Ordnance Survey of Ireland 1972вҖ“1993. He was Reader in Irish and Celtic Studies at Queen's University Belfast to 2004 and Senior Lecturer at the Department of Irish, National University of Ireland, Galway from 2005вҖ“2014. He is married to Tresa NГӯ ChianГЎin and has two children, RГіisГӯn and PГЎdraic. He lives in Dublin. Г“ MuraГӯle and Mac Fhirbhisigh In 1971, at the suggestion of TomГЎs Г“ Fiaich, then Professor of Modern History at Maynooth, Г“ MuraГӯle began work on Dubhaltach Mac Fhirbhisigh's ''Leabhar na nGenealach''. This was continued under the direction of Professor of Old and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |