|
Émile Benveniste
Émile Benveniste (; 27 May 1902 – 3 October 1976) was a French structural linguist and semiotician. He is best known for his work on Indo-European languages and his critical reformulation of the linguistic paradigm established by Ferdinand de Saussure. Biography Benveniste was born in Aleppo, Aleppo Vilayet, Ottoman Syria to a Sephardi family. His father sent him to Paris to undertake rabbinical studies, but he left the Rabbinical School after receiving his baccalauréat, and enrolled in the École pratique des hautes études. There he studied under Antoine Meillet, a former student of Saussure, and Joseph Vendryes, completing his degree in 1920. He would return to the École pratique des hautes études in 1927 as a director of studies, and would receive his doctorate there in 1935, with his major thesis on the formation of noun roots, and his secondary thesis on the Avestan infinitive. Following Meillet's death in 1936, he was elected to the Chair of Comparative Grammar in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aleppo
)), is an adjective which means "white-colored mixed with black". , motto = , image_map = , mapsize = , map_caption = , image_map1 = , mapsize1 = , map_caption1 = , pushpin_map = Syria#Mediterranean east#Asia#Syria Aleppo , pushpin_label_position = left , pushpin_relief = yes , pushpin_mapsize = , pushpin_map_caption = Location of Aleppo in Syria , coordinates = , subdivision_type = Country , subdivision_name = , subdivision_type1 = Governorate , subdivision_type2 = District , subdivision_type3 = Subdistrict , subdivision_name1 = Aleppo Governorate , subdivision_name2 = Mount Simeon (Jabal Semaan) , subdivision_name3 = Mount Simeon ( ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aphasia
Aphasia is an inability to comprehend or formulate language because of damage to specific brain regions. The major causes are stroke and head trauma; prevalence is hard to determine but aphasia due to stroke is estimated to be 0.1–0.4% in the Global North. Aphasia can also be the result of brain tumors, brain infections, or neurodegenerative diseases (such as dementias). To be diagnosed with aphasia, a person's speech or language must be significantly impaired in one (or more) of the four aspects of communication following acquired brain injury. Alternatively, in the case of progressive aphasia, it must have significantly declined over a short period of time. The four aspects of communication are auditory comprehension, verbal expression, reading and writing, and functional communication. The difficulties of people with aphasia can range from occasional trouble finding words, to losing the ability to speak, read, or write; intelligence, however, is unaffected. Expressive lan ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
François Jullien
François Jullien (born 2 June 1951 in Embrun, France) is a French philosopher, Hellenist, and sinologist. Biography An alumnus of the École Normale Supérieure, École Normale Supérieure (Paris) and holder (since 1974) of the ''agrégation'', France's professorial degree, François Jullien studied Chinese language and thought at Peking University and Shanghai University from 1975 to 1977. He received his French university doctorate (''doctorat de troisième'' cycle) in 1978 and his French research doctorate (''doctorat d'État'') in Far East studies in 1983. Since then Jullien has been head of the Antenne Française de Sinologie in Hong Kong (1978–1981), a guest of the Maison Franco-Japonaise in Tokyo (1985–1987), president of the Association Française d'Etudes Chinoises (1988–1990), director of the East Asia department (UFR) of Paris Diderot University, Paris Diderot University–Paris VII (1990–2000), president of the Collège International de Philosophie (1995†... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Philippe-Joseph Salazar
Philippe-Joseph Salazar (), a French rhetorician and philosopher, was born on 10 February 1955 in Casablanca, then part of French Morocco. Salazar attended the Lycée Louis-le-Grand a prestigious secondary-school in Paris (founded 1563) before studying philosophy, politics and literature at the École Normale Supérieure. Since 1999 Salazar is a Distinguished Professor in Rhetoric in the Faculty of Law at the University of Cape Town, South Africa. Salazar's lifelong achievements made him the recipient of Africa's premier research award in 2008, the Harry Oppenheimer Fellowship Award. In 2015 he received a prestigious French literary prize for political non-fiction, , for his book on the rhetoric of jihadism: ''Paroles armées'' (2015), translated in four languages (in English, Words are Weapons. Inside ISIS's Rhetoric of Terror', Yale UP, 2017). From voice to rhetoric Salazar's advisor at Ecole Normale Supérieure was Louis Althusser. While at ENS he joined the Conférence O ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nicole Loraux
Nicole Loraux (26 April 1943 – 6 April 2003) was a French historian of classical Athens. Biography She was born in Paris and died in Argenteuil. She graduated in Classics at the École normale supérieure des filles (1962). In 1965, she obtained the agrégation de lettres classiques (examination equivalent to the Postgraduate Higher Education Teaching Certificate, but more competitive), before writing a PhD thesis under the supervision of Pierre Vidal-Naquet Pierre Emmanuel Vidal-Naquet (; 23 July 1930 – 29 July 2006) was a French historian who began teaching at the ''École des hautes études en sciences sociales'' (EHESS) in 1969. Vidal-Naquet was a specialist in the study of Ancient Greece, but .... Her doctoral thesis ''Athènes imaginaire. Histoire de l'oraison funèbre athénienne et de sa fonction dans la cité classique'' (1977) became Loraux's best known work, ''The Invention of Athens: the Funeral Oration in the Classical City'' (Cambridge, MA 1986; New York 2006; ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Barbara Cassin
Barbara Cassin (; born 24 October 1947) is a French philologist and philosopher. She was elected to the Académie française on 4 May 2018. Cassin is the recipient of the Grand Prize of Philosophy of the Académie française. She is an Emeritus Research Director at the National Center for Scientific Research (CNRS) in Paris. Cassin is a program Director at the International College of Philosophy and the director of its Scientific Council and member of its Board of Directors. She was a director of Collège international de philosophie established by Jacques Derrida. In 2006 she succeeded Jonathan Barnes to the directorship of the leading centre of excellence in Ancient philosophy, Centre Leon-Robin, at the Sorbonne. In recent years she has been teaching seminars and writing books in partnership with Alain Badiou. Work Her work centers on Sophism and rhetoric, and their relation to philosophy. In a footnote in 2007's ''Logic of Worlds'', Alain Badiou portrays her work as a synt ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Romance Languages
The Romance languages, sometimes referred to as Latin languages or Neo-Latin languages, are the various modern languages that evolved from Vulgar Latin. They are the only extant subgroup of the Italic languages in the Indo-European language family. The five most widely spoken Romance languages by number of native speakers are Spanish (489 million), Portuguese (283 million), French (77 million), Italian (67 million) and Romanian (24 million), which are all national languages of their respective countries of origin. By most measures, Sardinian and Italian are the least divergent from Latin, while French has changed the most. However, all Romance languages are closer to each other than to classical Latin. There are more than 900 million native speakers of Romance languages found worldwide, mainly in the Americas, Europe, and parts of Africa. The major Romance languages also have many non-native speakers and are in widespread use as linguae francae.M. Paul Lewis,Summary by l ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Les Éditions De Minuit
Les Éditions de Minuit (, ''Midnight Press'') is a French publishing house. It was founded in 1941, during the French Resistance of World War II, and is still publishing books today. History Les Éditions de Minuit was founded by writer and illustrator Jean Bruller and writer Pierre de Lescure (1891–1963) in 1941 in Paris, during the German occupation of northern France (by November 1942, German forces occupied all of France). At the time, the media and all forms of publishing were controlled and censored by the Nazi occupiers. ''Les Éditions de Minuit'' was started to circumvent the censorship. It was an underground publisher until the liberation of Paris on 25 August 1944. ''Le Silence de la mer'' ''(The Silence of the Sea)'' (1942) by co-founder Bruller (who wrote under the pseudonym Vercors) was the first book published. Distribution, as with other Resistance texts, was based on being passed from person to person. ''Le Silence de la mer'' was followed in 1943 by '' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pierre Bourdieu
Pierre Bourdieu (; 1 August 1930 – 23 January 2002) was a French sociologist and public intellectual. Bourdieu's contributions to the sociology of education, the theory of sociology, and sociology of aesthetics have achieved wide influence in several related academic fields (e.g. anthropology, media and cultural studies, education, popular culture, and the arts). During his academic career he was primarily associated with the School for Advanced Studies in the Social Sciences in Paris and the Collège de France. Bourdieu's work was primarily concerned with the dynamics of power in society, especially the diverse and subtle ways in which power is transferred and social order is maintained within and across generations. In conscious opposition to the idealist tradition of much of Western philosophy, his work often emphasized the corporeal nature of social life and stressed the role of practice and embodiment in social dynamics. Building upon and criticizing the theories of Kar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Roland Barthes
Roland Gérard Barthes (; ; 12 November 1915 – 26 March 1980) was a French literary theorist, essayist, philosopher, critic, and semiotician. His work engaged in the analysis of a variety of sign systems, mainly derived from Western popular culture. His ideas explored a diverse range of fields and influenced the development of many schools of theory, including structuralism, anthropology, literary theory, and post-structuralism. Barthes is perhaps best known for his 1957 essay collection ''Mythologies'', which contained reflections on popular culture, and 1967 essay "The Death of the Author," which critiqued traditional approaches in literary criticism. During his academic career he was primarily associated with the École des Hautes Études en Sciences Sociales (EHESS) and the Collège de France. Biography Early life Roland Barthes was born on 12 November 1915 in the town of Cherbourg in Normandy. His father, naval officer Louis Barthes, was killed in a battle during ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Structuralism
In sociology, anthropology, archaeology, history, philosophy, and linguistics, structuralism is a general theory of culture and methodology that implies that elements of human culture must be understood by way of their relationship to a broader system. It works to uncover the structures that underlie all the things that humans do, think, perceive, and feel. Alternatively, as summarized by philosopher Simon Blackburn, structuralism is: Blackburn, Simon, ed. 2008. "Structuralism." In '' Oxford Dictionary of Philosophy'' (2nd rev. ed.). Oxford: Oxford University Press. . p. 353. e belief that phenomena of human life are not intelligible except through their interrelations. These relations constitute a structure, and behind local variations in the surface phenomena there are constant laws of abstract structure.Structuralism in Europe developed in the early 20th century, mainly in France and the Russian Empire, in the structural linguistics of Ferdinand de Saussure and the subsequ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
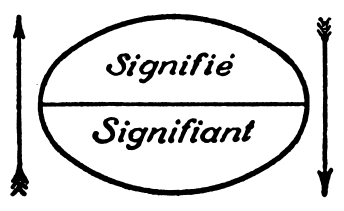
Signified And Signifier
In semiotics, signified and signifier ( French: ''signifié'' and ''signifiant'') stand for the two main components of a sign, where ''signified'' pertains to the "plane of content", while ''signifier'' is the "plane of expression". The idea was first proposed in the work of Swiss linguist Ferdinand de Saussure, one of the two founders of semiotics. Concept of signs The concept of signs has been around for a long time, having been studied by many classic philosophers such as Plato, Aristotle, Augustine, William of Ockham, and Francis Bacon, among others. The term ''semiotics'' derives from the Greek root ''seme'', as in ''semeiotikos'' (an 'interpreter of signs'). Berger, Arthur Asa. 2012. ''Media Analysis Techniques''. Beverly Hills: Sage Publications. It was not until the early part of the 20th century, however, that Saussure and American philosopher Charles Sanders Peirce brought the term into more common use. While both Saussure and Peirce contributed greatly to the concep ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |