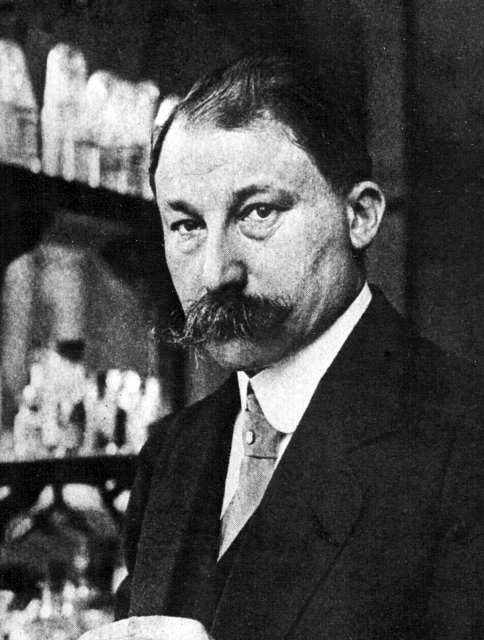|
École Supérieure De Chimie Physique Électronique De Lyon
or CPE Lyon is a French located in Villeurbanne, near Lyon. Degrees CPE Lyon offers two ''diplôme d'ingénieur'' () and two Master's level degrees, in two disciplines and three diplomas. The chemistry and chemical engineering degrees involve the conception, synthesis and manufacture of new and valuable molecules that can be "first on the market". They also involve a focus on environmental issues, sustainability and management. The electronics, telecommunications, maths and computer science degrees include a global education in electronics, microelectronics, computer science, image and signal processing, telecommunications, applied math and management. CPE Lyon also conducts research in organic chemistry, analytical sciences, chemical and process engineering, microelectronics and image processing. Selected students can prepare a PhD in one of the research laboratories (50 new students per year on average). History In 1883, the ''École Supérieure de Chimie Industriell ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Grande école
A ''grande école'' () is a specialised university that is separate from, but parallel and often connected to, the main framework of the French public university system. The grandes écoles offer teaching, research and professional training in single academic fields such as engineering, architecture, business administration, academic research, or public policy and administration. The schools only admit students through an extremely competitive examination process; a significant proportion of their graduates occupy senior positions in French business, academia, civil service and civil society. Grandes écoles primarily admit students based on their national ranking in competitive written and oral exams called ''concours,'' which are organised annually by the French central government. While anyone can register for ''concours'', successful candidates have almost always completed two or three years of dedicated preparatory classes (''classes preparatoires'') prior to admission. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Telecommunications
Telecommunication is the transmission of information by various types of technologies over wire, radio, optical, or other electromagnetic systems. It has its origin in the desire of humans for communication over a distance greater than that feasible with the human voice, but with a similar scale of expediency; thus, slow systems (such as postal mail) are excluded from the field. The transmission media in telecommunication have evolved through numerous stages of technology, from beacons and other visual signals (such as smoke signals, semaphore telegraphs, signal flags, and optical heliographs), to electrical cable and electromagnetic radiation, including light. Such transmission paths are often divided into communication channels, which afford the advantages of multiplexing multiple concurrent communication sessions. ''Telecommunication'' is often used in its plural form. Other examples of pre-modern long-distance communication included audio messages, such as coded drumb ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jean Dercourt
Jean may refer to: People * Jean (female given name) * Jean (male given name) * Jean (surname) Fictional characters * Jean Grey, a Marvel Comics character * Jean Valjean, fictional character in novel ''Les Misérables'' and its adaptations * Jean Pierre Polnareff, a fictional character from ''JoJo's Bizarre Adventure'' Places * Jean, Nevada, USA; a town * Jean, Oregon, USA Entertainment * Jean (dog), a female collie in silent films * Jean (song), "Jean" (song) (1969), by Rod McKuen, also recorded by Oliver * Jean Seberg (musical), ''Jean Seberg'' (musical), a 1983 musical by Marvin Hamlisch Other uses * JEAN (programming language) * USS Jean (ID-1308), USS ''Jean'' (ID-1308), American cargo ship c. 1918 * Sternwheeler Jean, a 1938 paddleboat of the Willamette River See also *Jehan * * Gene (other) * Jeanne (other) * Jehanne (other) * Jeans (other) * John (other) {{disambiguation ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Minister (government)
A minister is a politician who heads a ministry, making and implementing decisions on policies in conjunction with the other ministers. In some jurisdictions the head of government is also a minister and is designated the ‘prime minister’, ‘premier’, ‘chief minister’, ‘chancellor’ or other title. In Commonwealth realm jurisdictions which use the Westminster system of government, ministers are usually required to be members of one of the houses of Parliament or legislature, and are usually from the political party that controls a majority in the lower house of the legislature. In other jurisdictions—such as Belgium, Mexico, Netherlands, Philippines, Slovenia, and Nigeria—the holder of a cabinet-level post or other government official is not permitted to be a member of the legislature. Depending on the administrative arrangements in each jurisdiction, ministers are usually heads of a government department and members of the government's ministry, cabinet and p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
CERN
The European Organization for Nuclear Research, known as CERN (; ; ), is an intergovernmental organization that operates the largest particle physics laboratory in the world. Established in 1954, it is based in a northwestern suburb of Geneva, on the France–Switzerland border. It comprises 23 member states, and Israel (admitted in 2013) is currently the only non-European country holding full membership. CERN is an official United Nations General Assembly observer. The acronym CERN is also used to refer to the laboratory; in 2019, it had 2,660 scientific, technical, and administrative staff members, and hosted about 12,400 users from institutions in more than 70 countries. In 2016, CERN generated 49 petabytes of data. CERN's main function is to provide the particle accelerators and other infrastructure needed for high-energy physics research — consequently, numerous experiments have been constructed at CERN through international collaborations. CERN is the site of the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
European Space Agency
, owners = , headquarters = Paris, Île-de-France, France , coordinates = , spaceport = Guiana Space Centre , seal = File:ESA emblem seal.png , seal_size = 130px , image = Views in the Main Control Room (12052189474).jpg , size = , caption = , acronym = , established = , employees = 2,200 , administrator = Director General Josef Aschbacher , budget = €7.2 billion (2022) , language = English and French (working languages) , website = , logo = European Space Agency logo.svg , logo_caption = Logo , image_caption = European Space Operations Centre (ESOC) Main Control Room The European Space Agency (ESA; french: Agence spatiale européenne , it, Agenzia Spaziale Europea, es, Agencia Espacial Europea ASE; german: Europäische Weltraumorganisation) is an intergovernmental organisation of 22 member states dedicated to the exploration of space. Established in 1975 and headquartered i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hubert Curien
Hubert Curien (30 October 1924 – 6 February 2005) was a French physicist and a key figure in European science politics, as the President of CERN Council (1994–1996), the first chairman of the European Space Agency (ESA) (1981–1984), and second President of the Academia Europæa and a President of Fondation de France. Biography Born in Cornimont, Vosges in Lorraine, Curien enlisted in the French resistance during World War II. After the war he studied physics at the École normale supérieure in Paris. Curien became the director general of the Centre National de la Recherche Scientifique (CNRS) in 1969, and was one of the founders of the European Science Foundation and chairman from 1979 to 1984. He was also head of the French space agency from 1976 to 1984, and first chairman of the board of ESA from 1981 to 1984. Curien was the Minister of Research of France from 1984 to 1986 and from 1988 to 1993. He entered the French Academy of Sciences in 1994. Curien was the Pres ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Légion D'Honneur
The National Order of the Legion of Honour (french: Ordre national de la Légion d'honneur), formerly the Royal Order of the Legion of Honour ('), is the highest French order of merit, both military and civil. Established in 1802 by Napoleon Bonaparte, it has been retained (with occasional slight alterations) by all later French governments and regimes. The order's motto is ' ("Honour and Fatherland"); its seat is the Palais de la Légion d'Honneur next to the Musée d'Orsay, on the left bank of the Seine in Paris. The order is divided into five degrees of increasing distinction: ' (Knight), ' (Officer), ' (Commander), ' (Grand Officer) and ' (Grand Cross). History Consulate During the French Revolution, all of the French orders of chivalry were abolished and replaced with Weapons of Honour. It was the wish of Napoleon Bonaparte, the First Consul, to create a reward to commend civilians and soldiers. From this wish was instituted a , a body of men that was not an order of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Victor Grignard
Francois Auguste Victor Grignard (6 May 1871 – 13 December 1935) was a French chemist who won the Nobel Prize for Chemistry, Nobel Prize for his discovery of the eponymously named Grignard reagent and Grignard reaction, both of which are important in the formation of carbon–carbon bonds. Biography Grignard was the son of a sail maker. His character was described as having humble and friendly attitude. After attempting to major in mathematics, Grignard failed his entrance exams before being drafted into the army in 1892. After one year of service, he went back to pursue mathematics at the University of Lyon and finally obtained his degree Licencié ès Sciences Mathématiques in 1894. In December of the same year, he transferred to chemistry and began working with Professors Philippe Barbier (1848–1922) and Louis Bouveault (1864–1909). After working with stereochemistry and enines, Grignard was not impressed with the subject matter and asked Barbier about a new directio ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nobel Prize In Chemistry
) , image = Nobel Prize.png , alt = A golden medallion with an embossed image of a bearded man facing left in profile. To the left of the man is the text "ALFR•" then "NOBEL", and on the right, the text (smaller) "NAT•" then "MDCCCXXXIII" above, followed by (smaller) "OB•" then "MDCCCXCVI" below. , awarded_for = Outstanding contributions in chemistry , presenter = Royal Swedish Academy of Sciences , location = Stockholm, Sweden , reward = 9 million SEK (2017) , year = 1901 , holder = Carolyn R. Bertozzi, Morten P. Meldal and Karl Barry Sharpless (2022) , most_awards = Frederick Sanger and Karl Barry Sharpless (2) , website nobelprize.org, previous = 2021 , year2=2022, main=2022, next=2023 The Nobel Prize in Chemistry is awarded annually by the Royal Swedish Academy of Sciences to scientists in the various fields of chemistry. It is one of the five Nobel Prizes established by the will of Alfred Nobel in 1895, awarded for ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Louis Pasteur
Louis Pasteur (, ; 27 December 1822 – 28 September 1895) was a French chemist and microbiologist renowned for his discoveries of the principles of vaccination, microbial fermentation and pasteurization, the latter of which was named after him. His research in chemistry led to remarkable breakthroughs in the understanding of the causes and preventions of diseases, which laid down the foundations of hygiene, public health and much of modern medicine. His works are credited to saving millions of lives through the developments of vaccines for rabies and anthrax. He is regarded as one of the founders of modern bacteriology and has been honored as the "father of bacteriology" and the "father of microbiology" (together with Robert Koch; the latter epithet also attributed to Antonie van Leeuwenhoek). Pasteur was responsible for disproving the doctrine of spontaneous generation. Under the auspices of the French Academy of Sciences, his experiment demonstrated that in sterilized ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jules Raulin
Jules is the French form of the Latin "Julius" (e.g. Jules César, the French name for Julius Caesar). It is the given name of: People with the name *Jules Aarons (1921–2008), American space physicist and photographer *Jules Abadie (1876–1953), French politician and surgeon *Jules Accorsi (born 1937), French football player and manager *Jules Adenis (1823–1900), French playwright and opera librettist *Jules Adler 1865–1952), French painter *Jules Asner (born 1968), American television personality *Jules Aimé Battandier (1848–1922), French botanist *Jules Bernard (born 2000), American basketball player *Jules Bianchi (1989–2015), French Formula One driver *Jules Breton (1827–1906), French Realist painter *Jules-André Brillant (1888–1973), Canadian entrepreneur *Jules Brunet (1838–1911), French Army general *Jules Charles-Roux (1841–1918), French businessman and politician *Jules Dewaquez (1899–1971), French footballer *Jules Marie Alphonse Jacques de Dixmu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |