|
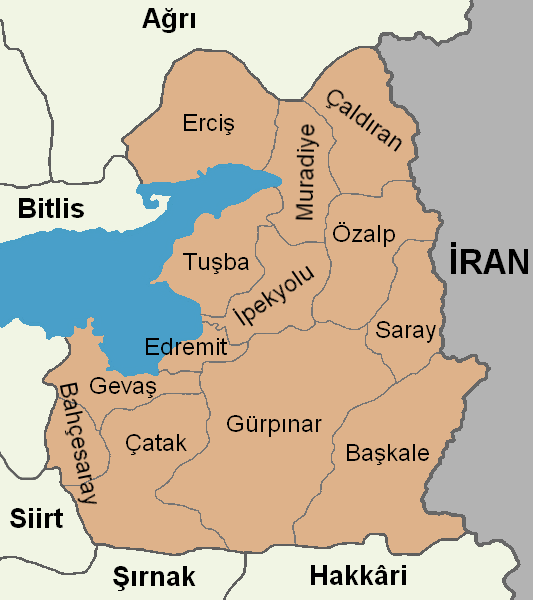
√áavuŇütepe
Sardurihinilli, also known as Haykaberd () or √áavuŇütepe Kalesi, is an ancient Urartian fortified site located on a ridge on the northeastern edge of the village of √áavuŇütepe in the G√ľrpńĪnar district of Van Province in eastern Turkey. It is located approximately 25 kilometers southeast of Van along the road leading to the city of Hakk√Ęri, in a valley once known as Hayots Dzor in historic Armenia. It was founded by the Urartian king Sarduri II () some time during his reign in the 8th century BC and is believed to be identical with the fortress of Sardurihurda mentioned in the same king's cuneiform inscriptions. In Armenian folklore it is identified with Haykaberd or Hayk Ľ, the fortress built by Hayk, the legendary founder of the Armenian nation, close to the site where he slew the invading Babylonian king Bel. Site Sardurihinilli has a linear plan, perched upon a ridge overlooking the G√ľrpńĪnar Plain called Bol DańüńĪ. It is composed of fortification walls as ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Van Province
Van Province (, , Armenian: ’é’°’∂’ę ’ī’°÷Ä’¶) is a province and metropolitan municipality in the Eastern Anatolian region of Turkey, between Lake Van and the Iranian border. Its area is 20,921 km2, and its population is 1,128,749 (2022). Its adjacent provinces are Bitlis to the west, Siirt to the southwest, ŇěńĪrnak and Hakk√Ęri to the south, and AńürńĪ to the north. The capital of the province is the city of Van, with a population of 525,016 at the end of 2022. The second-largest city is ErciŇü, with 92,945 inhabitants at end 2022. The province was part of ancient province of Vaspurakan and is considered to be one of the cradles of Armenian civilization. Before the Armenian genocide, Van Province was one of the six Armenian vilayets. A majority of the population of the province is Kurdish. Demographics The province is mainly populated by Kurds and considered part of Turkish Kurdistan. The province had a significant Christian Armenian population until the genocide ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Eruandunik
Hayots Dzor (, literally "the valley of the Armenians") or Eruandunik/Yervandunik (, from the name of the Orontid dynasty) was a canton (''gavar'') of the province of Vaspurakan of historical Armenia encompassing the area to the southeast of Lake Van, namely the valley of the Khoshab ( HoŇüap River). It was bordered by the cantons of Rshtunik to the southwest, Tosp to the north, and Kughanovit to the east. Armenian folk tradition holds the region to be the site of the legendary battle between the Armenian patriarch Hayk and the Babylonian ruler Bel. Hayk is said to have founded the fortress of Hayk Ľ or Haykaberd (traditionally identified with the ruins of the Urartian fortress of Sardurihinili) at the site of the battle, in honor of which Hayots Dzor was named. The inhabitants of region irrigated their fields using the Khoshab River and the Shamiram Canal, which was built during the time of the Kingdom of Urartu. Hayots Dzor was populated almost entirely by Armenians until ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
HoŇüap River
The HoŇüap River or G√ľzelsu River () is a river in the Van Province of Turkey. Its catchment area approximately coincides with the G√ľrpńĪnar District. Geography From its source in the ńįspiriz Mountains near BaŇükale on the southeast borders of Van Province, the river tends to the northwest. It is cut by the Zernek Dam in the G√ľrpńĪnar Plain and feeds into lake Van near D√∂neme√ß. The part of the river flowing out of the dam is also called ''D√∂neme√ß River''. At the end of the river there is the D√∂neme√ß Delta that extends into lake Van. The delta is used by birds during migration and is a breeding area of the endangered White-headed duck and Caspian tern. The river regime of the HoŇüap is nival. The lowest flow is 1.3 m¬≥/sec in August, September and October. The highest flow is 12.6 m¬≥/sec in May due to the rains and melting of snow. The total annual flow of the river is 334,106 m¬≥/year. History Historically, the HoŇüap River is known as the ''Khoshab'' or ''Anggh'' R ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hayk
Hayk (, ), also known as Hayk Nahapet (, , ), is the legendary patriarch and founder of the Armenian nation. His story is told in the ''History of Armenia'' attributed to the Armenian historian Movses Khorenatsi and in the ''Primary History'' traditionally attributed to Sebeos. Fragments of the legend of Hayk are also preserved in the works of other authors, as well as in Armenian folk tradition. Etymology The name of the patriarch, ''Hayk'' (), is not exactly homophonous with the Armenian name for "Armenia," ''Hayk Ľ'' (). In Classical Armenian, ''Hayk Ľ'' is the nominative plural of ''hay'' ( ’į’°’Ķ), the Armenian word for "Armenian." While Robert W. Thomson considers the etymology of ''Hayk Ľ'' (’Ä’°’Ķ÷Ą) from ''Hayk'' (’Ä’°’Ķ’Į) to be impossible, other scholars consider the connection between the two to be obvious and derive ''Hayk'' from ''hay''/''Hayk Ľ'' via the suffix ''-ik''. Martirosyan, Hrach (2010). ''Etymological Dictionary of the Armenian Inherited Lexicon'' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lraber Hasarakakan Gitutyunneri
''Lraber Hasarakakan Gitutyunneri'' ( "Bulletin/Review of Social Sciences") is a triannual peer-reviewed academic journal published by the Armenian Academy of Sciences covering Armenian studies. The journal's archives have undergone digitalization. See also * '' Patma-Banasirakan Handes'' * '' Bazmavep'' * '' Haigazian Armenological Review'' * '' Handes Amsorya'' * ''Revue des √Čtudes Arm√©niennes ''Revue des √Čtudes Arm√©niennes'' is a peer-reviewed academic journal that publishes articles relating to Classical and medieval Armenian history, art history, philology, linguistics, and literature.History journals Armenian studies journals [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Research On Armenian Architecture
Research on Armenian Architecture (RAA) () is a non-governmental organization established in Aachen, Germany, in 1969 by Dr. Armen Hakhnazarian and was registered as a non-profit public organization in 1982. In 1996, RAA USA was founded, followed by RAA Armenia in 1998. Until his death in 2020, Samvel Karapetian was the director of RAA Armenia. Jora Manucharian is currently the chairman of the board of trustees of the foundation, and RAA Armenia is governed by a board of directors: Emma Abrahamian (Samvel's wife), managing director; Raffi Kortoshian, co-director of administration and publications; Ashot Hakobyan, co-director of architectural activities; Armen Gevorgyan, co-director of computers and technology. The RAA maintains its headquarters in Yerevan, while RAA USA is based in Los Angeles. Activities Research on Armenian Architecture investigates and documents Armenian monuments located outside the borders of present-day Armenia, namely in historical Armenia (the Armeni ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Carl Friedrich Lehmann-Haupt
Carl may refer to: *Carl, Georgia, city in USA *Carl, West Virginia, an unincorporated community *Carl (name), includes info about the name, variations of the name, and a list of people with the name *Carl¬≤, a TV series * "Carl", an episode of television series ''Aqua Teen Hunger Force'' * An informal nickname for a student or alum of Carleton College CARL may refer to: *Canadian Association of Research Libraries *Colorado Alliance of Research Libraries See also *Carle (other) *Charles *Carle, a surname *Karl (other) *Karle (other) Karle may refer to: Places * Karle (Svitavy District), a municipality and village in the Czech Republic * Karli, India, a town in Maharashtra, India ** Karla Caves, a complex of Buddhist cave shrines * Karle, Belgaum, a settlement in Belgaum ... {{disambig ja:„āę„Éľ„Éę zh:Ść°ŚįĒ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hermitage Museum
The State Hermitage Museum ( rus, –ď–ĺ—Ā—É–ī–į—Ä—Ā—ā–≤–Ķ–Ĺ–Ĺ—č–Ļ –≠—Ä–ľ–ł—ā–į–∂, r=Gosudarstvennyj ErmitaŇĺ, p=…°…ôs äňądarstv ≤…™n(ňź)…®j …™rm ≤…™ňąta ā, links=no) is a museum of art and culture in Saint Petersburg, Russia, and holds the largest collection of paintings in the world. It was founded in 1764 when Empress Catherine the Great acquired a collection of paintings from the Berlin merchant Johann Ernst Gotzkowsky. The museum celebrates the anniversary of its founding each year on 7 December, Saint Catherine's Day. It has been open to the public since 1852. ''The Art Newspaper'' ranked the museum 10th in their list of the List of most visited art museums, most visited art museums, with 2,812,913 visitors in 2022. Its collections, of which only a small part is on permanent display, comprise over three million items (the numismatics, numismatic collection accounting for about one-third of them). The collections occupy a large complex of six historic buildings along Palace ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Joseph Orbeli
Joseph Orbeli (, Hovsep Abgari Orbeli; ; 20 March ( O.S. 8 March) 1887 ‚Äď 2 February 1961) was a Soviet-Armenian orientalist, public figure and academician who specialized in medieval history of Transcaucasia and administered the Hermitage Museum in Leningrad from 1934 to 1951. He was the founder and first president of the Armenian National Academy of Sciences (1943‚Äď47). Yuzbashyan, Karen ''¬ę’ē÷Ä’Ę’•’¨’ę, ’Ä’ł’ĺ’Ĺ’•÷É ‘Ī’Ę’£’°÷Ēꬼ'' rbeli, Hovsep AbgariArmenian Soviet Encyclopedia. Yerevan: Armenian Academy of Sciences, 1986, vol. 12, pp. 584‚Äď585. Biography Early life and education Born into the Orbeli family in Kutaisi, Russian Georgia in 1887, Joseph Orbeli completed his secondary education at a classical gymnasium in Tbilisi. Anon. "’Ä’ł’ĺ’Ĺ’•÷É ’ē÷Ä’Ę’•’¨’ę" ovsep Orbeli '' Patma-Banasirakan Handes'' 12/1 (1961), pp. 229‚Äď234. In 1904, he was accepted to Saint Petersburg University. He studied history and philology (with a particular emphasis in Latin and Gree ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Argishti I Of Urartu
Argishti I, was the sixth known king of Urartu, reigning from 786 BC to 764 BC. He founded the citadel of Erebuni in 782 BC, which is the present capital of Armenia, Yerevan. Alternate transliterations of the name include ''Argishtis'', ''Argisti'', ''ArgiŇ°ti'', and ''Argishtish''. Although the name is usually rendered as ''ArgiŇ°ti'' (read: ''Argishti''), some scholars argue that ''Argisti'' is the most likely pronunciation. This is due to the belief that the Urartians used the cuneiform symbol ''Ň°'' to voice an ''s''-sound, as opposed to representing the digraph ''sh''. A son and the successor of Menua, he continued the series of conquests initiated by his predecessors, apparently campaigning every year of his reign. He was involved in a number of inconclusive conflicts with the Assyrian king Shalmaneser IV. He conquered the northern part of Syria and made Urartu the most powerful state in post- Hittite Asia Minor. He also expanded his kingdom north to Lake Sevan, conquering ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nikolai Marr
Nikolai Yakovlevich Marr (, ''Nikolay Yakovlevich Marr''; , ''Nikoloz Iak'obis dze Mari''; ‚ÄĒ 20 December 1934) was a Georgian-born historian and linguist who gained a reputation as a scholar of the Caucasus during the 1910s before embarking on his " Japhetic theory" on the origin of language (from 1924), now considered as pseudo-scientific, and related speculative linguistic hypotheses. Marr's hypotheses were used as a rationale in the campaign during the 1920‚Äď30s in the Soviet Union of introduction of Latin alphabets for smaller ethnicities of the country. In 1950, the "Japhetic theory" fell from official favour, with Joseph Stalin denouncing it as anti-Marxist. Biography Marr was born on in Kutaisi, Georgia (then part of the Russian Empire). His father, James Montague Marr (1793‚Äď1874), was an Englishman of possible Scottish descent who moved to the Caucasus in 1822 to work as a trader, before moving into horticulture, and worked with the Gurieli family of Guria. His ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |