|
ĂstandiĂ°
ĂstandiĂ° ( Icelandic: "the condition" or "the situation") is a term used in Iceland to refer to the influence Allied troops had on Icelandic women during the Second World War. At its peak the number of Allied soldiers equaled almost 50% of the native male population. Many of the foreign soldiers would court Icelandic women and estimates of the number of local women who married foreign soldiers goes into the hundreds. Such interaction between Icelandic women and foreign troops was not always well received and the women involved were often accused of prostitution and betraying their home country. Children born from such unions are known in Icelandic as ''ĂĄstandsbörn'' ("children of the condition/situation"). When the British military invaded Iceland in 1940, people gathered on the streets to see the troops and the fact that many Icelandic women were captivated by them did not go unnoticed. Immediately discussions began over what effect this would have and minimal interact ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Iceland In World War II
At the beginning of World War II, Iceland was a sovereign kingdom in personal union with Denmark, with King Christian X as head of state. Iceland officially remained neutral throughout World War II. However, the British invaded Iceland on 10 May 1940. On 7 July 1941, the defence of Iceland was transferred from Britain to the United States, which was still a neutral country until five months later. On 17 June 1944, Iceland dissolved its union with Denmark and the Danish monarchy and declared itself a republic, which remains to this day. Background The British government was alarmed by Germany's growing interest in Iceland over the course of the 1930s. The Third Reich's overtures began with friendly competition between German and Icelandic football teams. When war began, Denmark and Iceland declared neutrality and limited visits to the island by military vessels and aircraft of the belligerents. Neutrality During the German occupation of Denmark, contact between the countrie ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
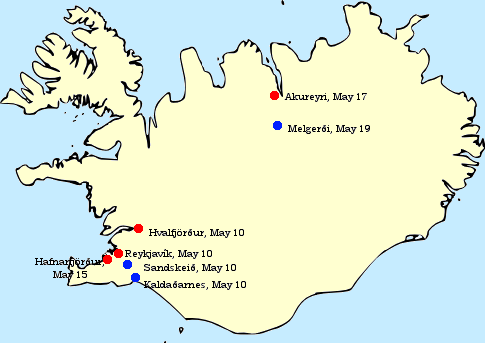
Invasion Of Iceland
The invasion of Iceland (codenamed Operation Fork) by the Royal Navy and Royal Marines occurred on 10 May 1940, during World War II. The invasion took place because the British government feared that Iceland would be used by the Germans, who had recently overrun Denmark, which was in personal union with Iceland and which had previously been largely responsible for Iceland's foreign policy. The Government of Iceland issued a protest, charging that its neutrality had been "flagrantly violated" and "its independence infringed". At the start of the war, the UK imposed strict export controls on Icelandic goods, preventing profitable shipments to Germany, as part of its naval blockade. The UK offered assistance to Iceland, seeking co-operation "as a belligerent and an ally", but the Icelandic government refused and reaffirmed its neutrality. The German diplomatic presence in Iceland, along with the island's strategic importance, alarmed the UK government. After failing to persuade ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cold War
The Cold War is a term commonly used to refer to a period of geopolitical tension between the United States and the Soviet Union and their respective allies, the Western Bloc and the Eastern Bloc. The term '' cold war'' is used because there was no large-scale fighting directly between the two superpowers, but they each supported major regional conflicts known as proxy wars. The conflict was based around the ideological and geopolitical struggle for global influence by these two superpowers, following their temporary alliance and victory against Nazi Germany and Imperial Japan in 1945. Aside from the nuclear arsenal development and conventional military deployment, the struggle for dominance was expressed via indirect means such as psychological warfare, propaganda campaigns, espionage, far-reaching embargoes, rivalry at sports events, and technological competitions such as the Space Race. The Western Bloc was led by the United States as well as a number of other First W ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
IcelandâUnited States Relations
The United States has maintained diplomatic relations with Iceland since the mid-1800s. Overview In 1868, the U.S. Department of State under William H. Seward authored a report that contemplated the purchase of Iceland from Denmark. The United States military established a presence in Iceland and around its waters after the Nazi occupation of Denmark (even before the U.S. entered World War II) in order to deny Nazi Germany access to its strategically important location (which would have been considered a threat to the Western Hemisphere). The United States was the first country to recognize Icelandic independence from Denmark in June 1944, union with Denmark under a common king, and German and British occupation during World War II. Iceland is a member of the North Atlantic Treaty Organization (NATO) but has no standing military of its own. The United States and Iceland signed a bilateral defense agreement in 1951, which stipulated that the U.S. would make arrangements for Icelan ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
IcelandâUnited Kingdom Relations
IcelandicâBritish relations are foreign relations between Iceland and the United Kingdom. Before independence, Iceland had been an independent part of the Kingdom of Denmark since 1918. Fearing an Axis move against Iceland following the Nazi occupation of Denmark, British forces landed on Iceland in 1940. On 17 June 1944, 200 days after the 25-year DanishâIcelandic Act of Union had expired and following a referendum, Iceland was declared an independent republic with this being recognised by London as well as the King of Denmark. From Iceland's independence until the mid-1970s, bilateral relations were difficult due to the 'Cod Wars' (a series of disputes over fishing rights in the 1950s and 1970s). Since then relations have improved, mainly because both countries have common interests including free trade, defence, environmental protection and international peace. Both countries are members of NATO. Queen Elizabeth II of the United Kingdom paid a state visit to Icela ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Euphemisms
A euphemism () is an innocuous word or expression used in place of one that is deemed offensive or suggests something unpleasant. Some euphemisms are intended to amuse, while others use bland, inoffensive terms for concepts that the user wishes to downplay. Euphemisms may be used to mask profanity or refer to topics some consider taboo such as disability, sex, excretion, or death in a polite way. Etymology ''Euphemism'' comes from the Greek word () which refers to the use of 'words of good omen'; it is a compound of (), meaning 'good, well', and (), meaning 'prophetic speech; rumour, talk'. '' Eupheme'' is a reference to the female Greek spirit of words of praise and positivity, etc. The term ''euphemism'' itself was used as a euphemism by the ancient Greeks; with the meaning "to keep a holy silence" (speaking well by not speaking at all). Purpose Avoidance Reasons for using euphemisms vary by context and intent. Commonly, euphemisms are used to avoid directly addressing subj ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Women In Iceland
Women in Iceland generally enjoy good gender equality. As of 2018, 88% of working-age women were employed, 65% of students attending university were female, and 41% of members of Althing, parliament were women. Nevertheless, women still earn about 14% less than men, though these statistics do not take into account the hours worked, over-time, and choices of employment. Iceland has the world's highest proportion of women in the labour market, significant child care allocations for working women. It has gender neutral parental leave, with a quota for each parent, and a transferable part. Iceland is arguably one of the world's most feminist countries, having been awarded this status in 2011 for the second year in a row. Iceland was the first country to have a female president, VigdĂs FinnbogadĂłttir, elected in 1980. It also has the world's first female and openly gay head of government, JĂłhanna SigurĂ°ardĂłttir, who was elected prime minister in 2009. Iceland enjoys the smallest ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sexuality In Iceland
Human sexuality is the way people experience and express themselves sexually. This involves biological, psychological, physical, erotic, emotional, social, or spiritual feelings and behaviors. Because it is a broad term, which has varied with historical contexts over time, it lacks a precise definition. The biological and physical aspects of sexuality largely concern the human reproductive functions, including the human sexual response cycle. Someone's sexual orientation is their pattern of sexual interest in the opposite or same sex. Physical and emotional aspects of sexuality include bonds between individuals that are expressed through profound feelings or physical manifestations of love, trust, and care. Social aspects deal with the effects of human society on one's sexuality, while spirituality concerns an individual's spiritual connection with others. Sexuality also affects and is affected by cultural, political, legal, philosophical, moral, ethical, and religious aspec ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Battle Of The Atlantic
The Battle of the Atlantic, the longest continuous military campaign in World War II, ran from 1939 to the defeat of Nazi Germany in 1945, covering a major part of the naval history of World War II. At its core was the Allied naval blockade of Germany, announced the day after the declaration of war, and Germany's subsequent counter-blockade. The campaign peaked from mid-1940 through to the end of 1943. The Battle of the Atlantic pitted U-boats and other warships of the German '' Kriegsmarine'' (Navy) and aircraft of the ''Luftwaffe'' (Air Force) against the Royal Navy, Royal Canadian Navy, United States Navy, and Allied merchant shipping. Convoys, coming mainly from North America and predominantly going to the United Kingdom and the Soviet Union, were protected for the most part by the British and Canadian navies and air forces. These forces were aided by ships and aircraft of the United States beginning September 13, 1941. Carney, Robert B., Admiral, USN. "Comment and Discu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
British Occupation Of The Faroe Islands
The British occupation of the Faroe Islands during World War II, also known as Operation Valentine, was implemented immediately following the German invasion of Denmark and Norway. It was a small component of the roles of Nordic countries in World War II. In April 1940, the United Kingdom occupied the strategically important Faroe Islands (which belonged to Denmark) to forestall a German invasion. British troops left shortly after the end of the war. Occupation At the time of the occupation, the Faroe Islands had the status of an amt (county) of Denmark. Following the invasion and occupation of Denmark on 9 April 1940, British forces launched Operation Valentine to occupy the Faroe Islands. On 11 April, Winston Churchill â then First Lord of the Admiralty â announced to the House of Commons that the Faroe Islands would be occupied: We are also at this moment occupying the Faroe Islands, which belong to Denmark and which are a strategic point of high importance, and whose ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |

.png)



