|
.dex
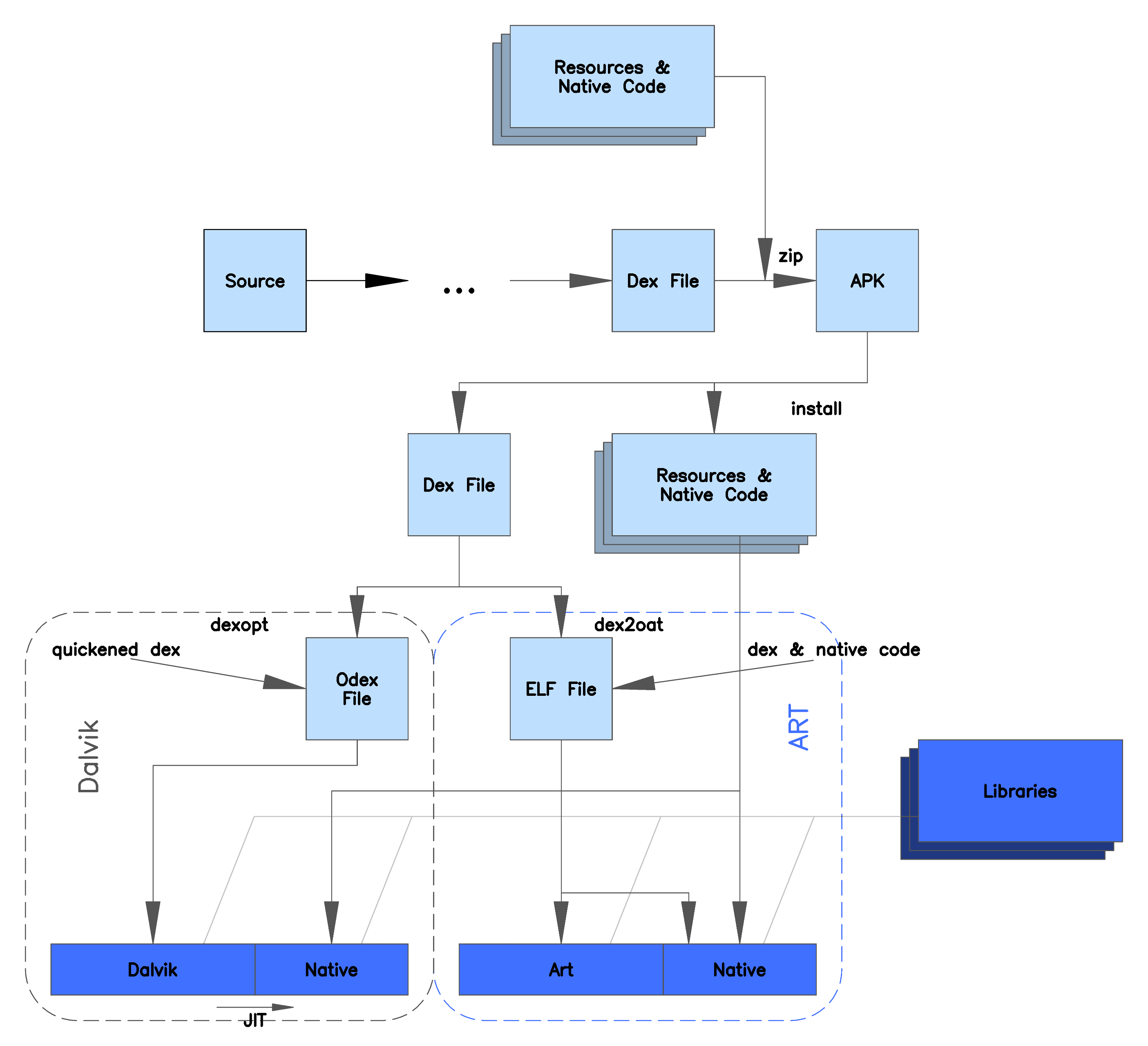
Dalvik is a discontinued process virtual machine (VM) in the Android operating system that executes applications written for Android. (Dalvik bytecode format is still used as a distribution format, but no longer at runtime in newer Android versions.) Dalvik was an integral part of the Android software stack in the (now unsupported) Android versions 4.4 "KitKat" and earlier, which were commonly used on mobile devices such as mobile phones and tablet computers, and more in some devices such as smart TVs and wearables. Dalvik is open-source software, originally written by Dan Bornstein, who named it after the fishing village of Dalvík in Eyjafjörður, Iceland. Programs for Android are commonly written in Java and compiled to bytecode for the Java Virtual Machine, which is then translated to Dalvik bytecode and stored in .dex (''Dalvik EXecutable'') and .odex (''Optimized Dalvik EXecutable'') files; related terms ''odex'' and ''de-odex'' are associated with respective bytecod ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Android Runtime
Android Runtime (ART) is an application runtime environment used by the Android (operating system), Android operating system. Replacing Dalvik (software), Dalvik, the process virtual machine originally used by Android, ART performs the Translator (computing), translation of the application's bytecode into native instructions that are later executed by the device's runtime environment. Overview Android Froyo, Android 2.2 "Froyo" brought Tracing just-in-time compilation, trace-based just-in-time (JIT) compilation into Dalvik, optimizing the execution of applications by continually Profiling (computer programming), profiling applications each time they run and dynamically Compiler (computing), compiling frequently executed short segments of their bytecode into native machine code. While Dalvik Interpreter (computing), interprets the rest of application's bytecode, native execution of those short bytecode segments, called "traces", provides significant performance improvements. Un ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dalvík
Dalvík () is the main village of the Icelandic municipality of Dalvíkurbyggð. Its population is approximately 1,400.Hagstofa Íslands ''Statistics Iceland'' Website The town's name means " ." Geography Dalvík is on the western shore of in the valley of[...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Linux Kernel
The Linux kernel is a free and open-source, monolithic, modular, multitasking, Unix-like operating system kernel. It was originally authored in 1991 by Linus Torvalds for his i386-based PC, and it was soon adopted as the kernel for the GNU operating system, which was written to be a free (libre) replacement for Unix. Linux is provided under the GNU General Public License version 2 only, but it contains files under other compatible licenses. Since the late 1990s, it has been included as part of a large number of operating system distributions, many of which are commonly also called Linux. Linux is deployed on a wide variety of computing systems, such as embedded devices, mobile devices (including its use in the Android operating system), personal computers, servers, mainframes, and supercomputers. It can be tailored for specific architectures and for several usage scenarios using a family of simple commands (that is, without the need of manually editing its source c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bytecode
Bytecode (also called portable code or p-code) is a form of instruction set designed for efficient execution by a software interpreter. Unlike human-readable source code, bytecodes are compact numeric codes, constants, and references (normally numeric addresses) that encode the result of compiler parsing and performing semantic analysis of things like type, scope, and nesting depths of program objects. The name bytecode stems from instruction sets that have one-byte opcodes followed by optional parameters. Intermediate representations such as bytecode may be output by programming language implementations to ease Interpreter (computer software), interpretation, or it may be used to reduce hardware and operating system dependence by allowing the same code to run cross-platform, on different devices. Bytecode may often be either directly executed on a virtual machine (a p-code machine, i.e., interpreter), or it may be further compiled into machine code for better performance. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Class (computer Science)
In object-oriented programming, a class is an extensible program-code-template for creating objects, providing initial values for state ( member variables) and implementations of behavior (member functions or methods). In many languages, the class name is used as the name for the class (the template itself), the name for the default constructor of the class (a subroutine that creates objects), and as the type of objects generated by instantiating the class; these distinct concepts are easily conflated. Although, to the point of conflation, one could argue that is a feature inherent in a language because of its polymorphic nature and why these languages are so powerful, dynamic and adaptable for use compared to languages without polymorphism present. Thus they can model dynamic systems (i.e. the real world, machine learning, AI) more easily. When an object is created by a constructor of the class, the resulting object is called an instance of the class, and the member variabl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Class (file Format)
A Java class file is a file (with the filename extension) containing Java bytecode that can be executed on the Java Virtual Machine (JVM). A Java class file is usually produced by a Java compiler from Java programming language source files ( files) containing Java classes (alternatively, other JVM languages can also be used to create class files). If a source file has more than one class, each class is compiled into a separate class file. JVMs are available for many platforms, and a class file compiled on one platform will execute on a JVM of another platform. This makes Java applications platform-independent. History On 11 December 2006, the class file format was modified under Java Specification Request (JSR) 202. File layout and structure Sections There are 10 basic sections to the Java class file structure: * Magic Number: 0xCAFEBABE * Version of Class File Format: the minor and major versions of the class file * Constant Pool: Pool of constants for the class * ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Application Programming Interface
An application programming interface (API) is a way for two or more computer programs to communicate with each other. It is a type of software interface, offering a service to other pieces of software. A document or standard that describes how to build or use such a connection or interface is called an ''API specification''. A computer system that meets this standard is said to ''implement'' or ''expose'' an API. The term API may refer either to the specification or to the implementation. In contrast to a user interface, which connects a computer to a person, an application programming interface connects computers or pieces of software to each other. It is not intended to be used directly by a person (the end user) other than a computer programmer who is incorporating it into the software. An API is often made up of different parts which act as tools or services that are available to the programmer. A program or a programmer that uses one of these parts is said to ''call'' tha ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Register Machine
In mathematical logic and theoretical computer science a register machine is a generic class of abstract machines used in a manner similar to a Turing machine. All the models are Turing equivalent. Overview The register machine gets its name from its use of one or more " registers". In contrast to the tape and head used by a Turing machine, the model uses multiple, uniquely addressed registers, each of which holds a single positive integer. There are at least four sub-classes found in literature, here listed from most primitive to the most like a computer: * Counter machine – the most primitive and reduced theoretical model of a computer hardware. Lacks indirect addressing. Instructions are in the finite state machine in the manner of the Harvard architecture. * Pointer machine – a blend of counter machine and RAM models. Less common and more abstract than either model. Instructions are in the finite state machine in the manner of the Harvard architecture. * Random-access ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Stack Machine
In computer science, computer engineering and programming language implementations, a stack machine is a computer processor or a virtual machine in which the primary interaction is moving short-lived temporary values to and from a push down stack. In the case of a hardware processor, a hardware stack is used. The use of a stack significantly reduces the required number of processor registers. Stack machines extend push-down automata with additional load/store operations or multiple stacks and hence are Turing-complete. Design Most or all stack machine instructions assume that operands will be from the stack, and results placed in the stack. The stack easily holds more than two inputs or more than one result, so a rich set of operations can be computed. In stack machine code (sometimes called p-code), instructions will frequently have only an opcode commanding an operation, with no additional fields identifying a constant, register or memory cell, known as a zero address fo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
ART View
Art is a diverse range of human activity, and resulting product, that involves creative or imaginative talent expressive of technical proficiency, beauty, emotional power, or conceptual ideas. There is no generally agreed definition of what constitutes art, and its interpretation has varied greatly throughout history and across cultures. In the Western tradition, the three classical branches of visual art are painting, sculpture, and architecture. Theatre, dance, and other performing arts, as well as literature, music, film and other media such as interactive media, are included in a broader definition of the arts. Until the 17th century, ''art'' referred to any skill or mastery and was not differentiated from crafts or sciences. In modern usage after the 17th century, where aesthetic considerations are paramount, the fine arts are separated and distinguished from acquired skills in general, such as the decorative or applied arts. The nature of art and related concepts, s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Android Lollipop
Android Lollipop ( codenamed Android L during development) is the fifth major version of the Android mobile operating system developed by Google and the 12th version of Android, spanning versions between 5.0 and 5.1.1. Unveiled on June 25, 2014 at the Google I/O 2014 conference, it became available through official over-the-air (OTA) updates on November 12, 2014, for select devices that run distributions of Android serviced by Google (such as Nexus and Google Play edition devices). Its source code was made available on November 3, 2014. The first phone with Android Lollipop was Nexus 6. One of the most prominent changes in the Lollipop release is a redesigned user interface built around a design language known as Material Design, which was made to retain a paper-like feel to the interface. Other changes include improvements to the notifications, which can be accessed from the lockscreen and displayed within applications as top-of-the-screen banners. Google also made internal ch ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Engadget
''Engadget'' ( ) is a multilingual technology blog network with daily coverage of gadgets and consumer electronics. ''Engadget'' manages ten blogs four of which are written in English and six have international versions with independent editorial staff. It has been operated by Yahoo since September 2021. History ''Engadget'' was founded by former '' Gizmodo'' technology weblog editor and co-founder Peter Rojas. ''Engadget'' was the largest blog in Weblogs, Inc., a blog network with over 75 weblogs, including '' Autoblog'' and '' Joystiq,'' which formerly included '' Hackaday''. Weblogs Inc. was purchased by AOL in 2005. Launched in March 2004, ''Engadget'' is updated multiple times a day with articles on gadgets and consumer electronics. It also posts rumors about the technological world, frequently offers opinion within its stories, and produces the weekly Engadget Podcast that covers tech and gadget news stories that happened during the week. On December 30, 2009, ''En ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |