|
(5407) 1992 AX
, provisional designation ', is a stony asteroid and a synchronous binary Mars-crosser from the innermost region of the asteroid belt, approximately in diameter. It was discovered on 4 January 1992, by Japanese astronomers Seiji Ueda and Hiroshi Kaneda at the Kushiro Observatory on Hokkaidō, Japan. The S-type asteroid has a short rotation period of 2.5 hours. Its sub-kilometer satellite was discovered in 1997. As of 2018, the binary system has not been named. Orbit and classification ' a member of the Mars-crossing asteroids, a dynamically unstable group between the main belt and the near-Earth populations, crossing the orbit of Mars at 1.66 AU. It orbits the Sun at a distance of 1.3–2.3 AU once every 2 years and 6 months (910 days; semi-major axis of 1.84 AU). Its orbit has an eccentricity of 0.28 and an inclination of 11 ° with respect to the ecliptic. The asteroid makes occasional close approaches to Mars. Its next close approach, on 22 January 2027, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Seiji Ueda
is a Japanese astronomer. He is a prolific discoverer of minor planets. Between 1987 and 2000, Ueda (in collaboration with Hiroshi Kaneda) discovered 705 asteroids. He holds an MD and Ph.D. from Stanford University and is on the staff at the Graduate University for Advanced Study in Japan. (pdf). Retrieved October 30, 2006. The inner main-belt
The asteroid belt is a torus-shaped region in the Solar System, located roughly between the orbits of the planets Jupiter and Mars. It contains a great many solid, irregularly shaped bodies, of many sizes, but much smaller than planets, called ... asteroid [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Asteroid
An asteroid is a minor planet of the inner Solar System. Sizes and shapes of asteroids vary significantly, ranging from 1-meter rocks to a dwarf planet almost 1000 km in diameter; they are rocky, metallic or icy bodies with no atmosphere. Of the roughly one million known asteroids the greatest number are located between the orbits of Mars and Jupiter, approximately 2 to 4 AU from the Sun, in the main asteroid belt. Asteroids are generally classified to be of three types: C-type, M-type, and S-type. These were named after and are generally identified with carbonaceous, metallic, and silicaceous compositions, respectively. The size of asteroids varies greatly; the largest, Ceres, is almost across and qualifies as a dwarf planet. The total mass of all the asteroids combined is only 3% that of Earth's Moon. The majority of main belt asteroids follow slightly elliptical, stable orbits, revolving in the same direction as the Earth and taking from three to six years to comple ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Orbital Inclination
Orbital inclination measures the tilt of an object's orbit around a celestial body. It is expressed as the angle between a reference plane and the orbital plane or axis of direction of the orbiting object. For a satellite orbiting the Earth directly above the Equator, the plane of the satellite's orbit is the same as the Earth's equatorial plane, and the satellite's orbital inclination is 0°. The general case for a circular orbit is that it is tilted, spending half an orbit over the northern hemisphere and half over the southern. If the orbit swung between 20° north latitude and 20° south latitude, then its orbital inclination would be 20°. Orbits The inclination is one of the six orbital elements describing the shape and orientation of a celestial orbit. It is the angle between the orbital plane and the plane of reference, normally stated in degrees. For a satellite orbiting a planet, the plane of reference is usually the plane containing the planet's equator. For pla ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Orbital Eccentricity
In astrodynamics, the orbital eccentricity of an astronomical object is a dimensionless parameter that determines the amount by which its orbit around another body deviates from a perfect circle. A value of 0 is a circular orbit, values between 0 and 1 form an elliptic orbit, 1 is a parabolic escape orbit (or capture orbit), and greater than 1 is a hyperbola. The term derives its name from the parameters of conic sections, as every Kepler orbit is a conic section. It is normally used for the isolated two-body problem, but extensions exist for objects following a rosette orbit through the Galaxy. Definition In a two-body problem with inverse-square-law force, every orbit is a Kepler orbit. The eccentricity of this Kepler orbit is a non-negative number that defines its shape. The eccentricity may take the following values: * circular orbit: ''e'' = 0 * elliptic orbit: 0 < ''e'' < 1 * [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Semi-major Axis
In geometry, the major axis of an ellipse is its longest diameter: a line segment that runs through the center and both foci, with ends at the two most widely separated points of the perimeter. The semi-major axis (major semiaxis) is the longest semidiameter or one half of the major axis, and thus runs from the centre, through a focus, and to the perimeter. The semi-minor axis (minor semiaxis) of an ellipse or hyperbola is a line segment that is at right angles with the semi-major axis and has one end at the center of the conic section. For the special case of a circle, the lengths of the semi-axes are both equal to the radius of the circle. The length of the semi-major axis of an ellipse is related to the semi-minor axis's length through the eccentricity and the semi-latus rectum \ell, as follows: The semi-major axis of a hyperbola is, depending on the convention, plus or minus one half of the distance between the two branches. Thus it is the distance from the center ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mars
Mars is the fourth planet from the Sun and the second-smallest planet in the Solar System, only being larger than Mercury (planet), Mercury. In the English language, Mars is named for the Mars (mythology), Roman god of war. Mars is a terrestrial planet with a thin atmosphere (less than 1% that of Earth's), and has a crust primarily composed of elements similar to Earth's crust, as well as a core made of iron and nickel. Mars has surface features such as impact craters, valleys, dunes and polar ice caps. It has two small and irregularly shaped moons, Phobos (moon), Phobos and Deimos (moon), Deimos. Some of the most notable surface features on Mars include Olympus Mons, the largest volcano and List of tallest mountains in the Solar System, highest known mountain in the Solar System and Valles Marineris, one of the largest canyons in the Solar System. The North Polar Basin (Mars), Borealis basin in the Northern Hemisphere covers approximately 40% of the planet and may be a la ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Near-Earth Object
A near-Earth object (NEO) is any small Solar System body whose orbit brings it into proximity with Earth. By convention, a Solar System body is a NEO if its closest approach to the Sun (perihelion) is less than 1.3 astronomical units (AU). If a NEO's orbit crosses the Earth's orbit, and the object is larger than across, it is considered a potentially hazardous object (PHO). Most known PHOs and NEOs are asteroids, but a small fraction are comets. There are over 30,503 known near-Earth asteroids (NEAs) and over a hundred known short-period near-Earth comets (NECs). A number of solar-orbiting meteoroids were large enough to be tracked in space before striking the Earth. It is now widely accepted that collisions in the past have had a significant role in shaping the geological and biological history of the Earth. Asteroids as small as in diameter can cause significant damage to the local environment and human populations. Larger asteroids penetrate the atmosphere to the surf ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Main Belt
The asteroid belt is a torus-shaped region in the Solar System, located roughly between the orbits of the planets Jupiter and Mars. It contains a great many solid, irregularly shaped bodies, of many sizes, but much smaller than planets, called asteroids or minor planets. This asteroid belt is also called the main asteroid belt or main belt to distinguish it from other asteroid populations in the Solar System such as near-Earth asteroids and trojan asteroids. The asteroid belt is the smallest and innermost known circumstellar disc in the Solar System. About 60% of its mass is contained in the four largest asteroids: Ceres, Vesta, Pallas, and Hygiea. The total mass of the asteroid belt is calculated to be 3% that of the Moon. Ceres, the only object in the asteroid belt large enough to be a dwarf planet, is about 950 km in diameter, whereas Vesta, Pallas, and Hygiea have mean diameters less than 600 km. The remaining bodies range down to the size of a dust particle. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
List Of Minor-planet Groups
A minor-planet group is a population of minor planets that share broadly similar orbits. Members are generally unrelated to each other, unlike in an asteroid family, which often results from the break-up of a single asteroid. It is customary to name a group of asteroids after the first member of that group to be discovered, which is often the largest. Groups out to the orbit of Earth There are relatively few asteroids that orbit close to the Sun. Several of these groups are hypothetical at this point in time, with no members having yet been discovered; as such, the names they have been given are provisional. * Vulcanoid asteroids are hypothetical asteroids that orbit entirely within the orbit of Mercury (have an aphelion of less than 0.3874 AU). A few searches for vulcanoids have been conducted but none have been discovered so far. * ꞌAylóꞌchaxnim asteroids (previously named Vatira) are asteroids that orbit entirely within the orbit of Venus (have an aphelion of less ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mars-crossing Asteroid
A Mars-crossing asteroid (MCA, also Mars-crosser, MC) is an asteroid whose orbit crosses that of Mars. Some Mars-crossers Minor planet designation, numbered below 100000 are listed here. They include the two numbered Mars trojans 5261 Eureka and . Many databases, for instance the JPL Small-Body Database (JPL SBDB), only list asteroids with a perihelion greater than 1.3 Astronomical Unit, AU as Mars-crossers. An asteroid with a perihelion less than this is classed as a near-Earth object even though it is crossing the orbit of Mars as well as crossing (or coming near to) that of Earth. Nevertheless, these objects are listed on this page. A grazer is an object with a perihelion below the aphelion of Mars (1.67 AU) but above the Martian perihelion (1.38 AU). The JPL SBDB lists 13,500 Mars-crossing asteroids. Only 18 MCAs are brighter than Absolute magnitude#Solar System bodies (H), absolute magnitude (H) 12.5, which typically makes these asteroids with H<12.5 more than 13 km in d ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
List Of Named Minor Planets
This is a list of named minor planets in an alphabetical, case-insensitive order grouped by the first letter of their name. New namings, typically proposed by the discoverer and approved by the Working Group Small Body Nomenclature (WGSBN) of the International Astronomical Union, are published nowadays in their ''WGSBN Bulletin'' and summarized in a dedicated list several times a year. Over the last four decades, the list has grown significantly with an average rate of 492 new namings published every year (or 1.35 namings per day). While in March 1979, only 1924 minor planets had received a name and completed the designation process, , the list contains 23,542 named objects. This, however, only accounts for of all numbered bodies, as there are over 600,000 minor planets with a well established orbit which is a precondition for receiving a name. Of all these minor-planet names, 1266 contain diacritical marks. See also * List of minor planet discoverers * List of minor p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
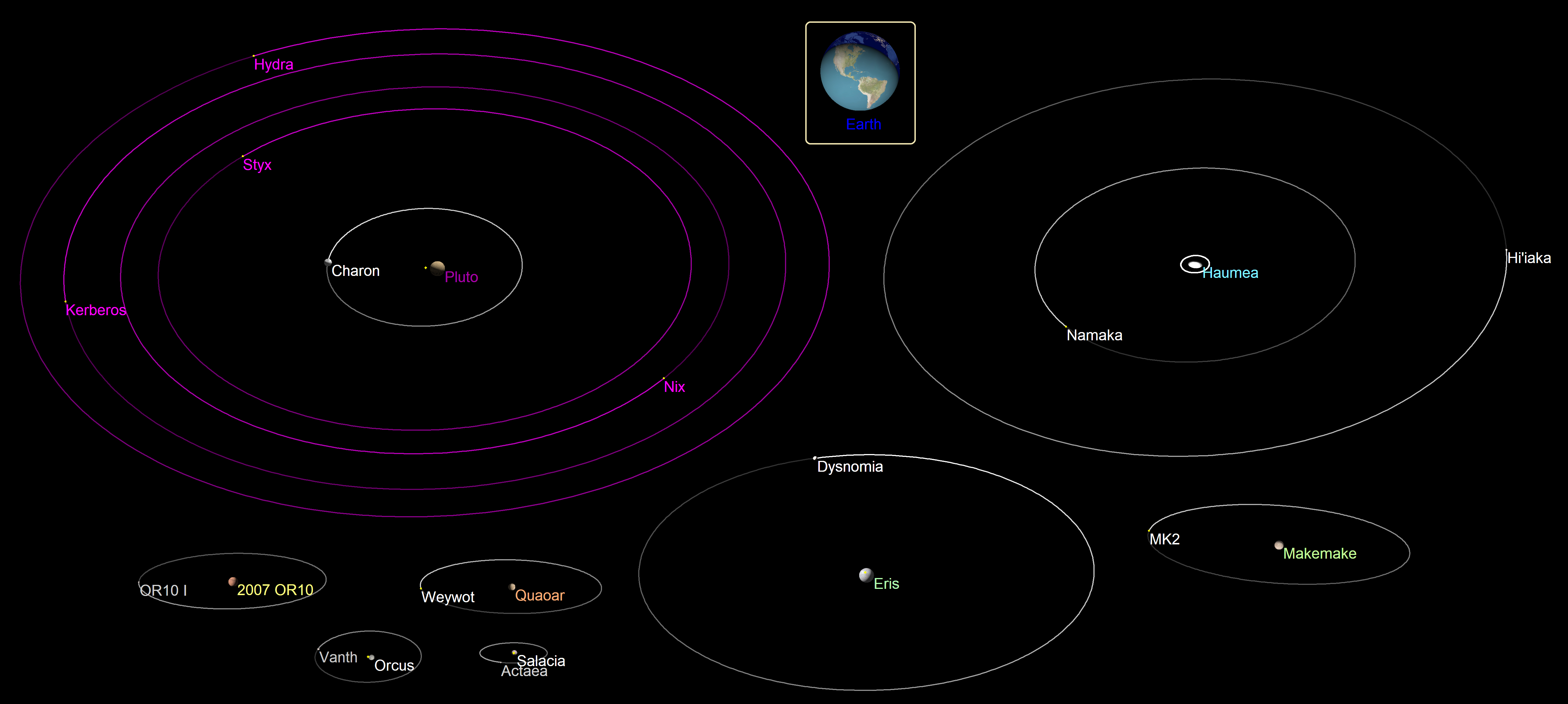
Minor-planet Moon
A minor-planet moon is an astronomical object that orbits a minor planet as its natural satellite. , there are 457 minor planets known or suspected to have moons. Discoveries of minor-planet moons (and binary objects, in general) are important because the determination of their orbits provides estimates on the mass and density of the primary, allowing insights into their physical properties that are generally not otherwise accessible. Several of the moons are quite large compared to their primaries: 90 Antiope, Mors–Somnus and Sila–Nunam (95%), Patroclus–Menoetius, Altjira and Lempo–Hiisi (90%, with Lempo–Paha at 50%). The largest known minor-planet moon in ''absolute'' size is Pluto's largest moon Charon, which itself has about half the diameter of Pluto. The first modern era mention of the possibility of an asteroid satellite was in connection with an occultation of the bright star Gamma Ceti by the asteroid 6 Hebe in 1977. The observer ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |