|
(2Z,4Z,6Z,8Z)-Thionine
(2''Z'',4''Z'',6''Z'',8''Z'')-Thionine or Thionine is an unsaturated heterocycle of nine atoms, with a sulfur replacing a carbon at one position. Thionine is a partially aromatic compound. D. O. Tymoshenko See also * * * * |
Heterocycle
A heterocyclic compound or ring structure is a cyclic compound that has atoms of at least two different chemical element, elements as members of its ring(s). Heterocyclic chemistry is the branch of organic chemistry dealing with the synthesis, properties, and applications of these heterocycles. Examples of heterocyclic compounds include all of the nucleic acids, the majority of drugs, most biomass (cellulose and related materials), and many natural and synthetic dyes. More than half of known compounds are heterocycles. 59% of US FDA-approved drugs contain nitrogen heterocycles. Classification The study of heterocyclic chemistry focuses especially on unsaturated derivatives, and the preponderance of work and applications involves unstrained 5- and 6-membered rings. Included are pyridine, thiophene, pyrrole, and furan. Another large class of heterocycles refers to those fused to benzene rings. For example, the fused benzene derivatives of pyridine, thiophene, pyrrole, and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Heterocyclic Compounds With 1 Ring
A heterocyclic compound or ring structure is a cyclic compound that has atoms of at least two different elements as members of its ring(s). Heterocyclic chemistry is the branch of organic chemistry dealing with the synthesis, properties, and applications of these heterocycles. Examples of heterocyclic compounds include all of the nucleic acids, the majority of drugs, most biomass (cellulose and related materials), and many natural and synthetic dyes. More than half of known compounds are heterocycles. 59% of US FDA-approved drugs contain nitrogen heterocycles. Classification The study of heterocyclic chemistry focuses especially on unsaturated derivatives, and the preponderance of work and applications involves unstrained 5- and 6-membered rings. Included are pyridine, thiophene, pyrrole, and furan. Another large class of heterocycles refers to those fused to benzene rings. For example, the fused benzene derivatives of pyridine, thiophene, pyrrole, and furan are quinol ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Azonine
Azonine is an unsaturated heterocycle of nine atoms, with a nitrogen replacing a carbon at one position. A variety of derivatives have been synthesised. It is considered to possess a considerable amount of aromatic stability. It and C9H9– are the largest monocyclic all-''cis'' ring systems to be aromatic and close to planar. Due to a balance between angle strain (~20°) and aromaticity, a planar conformation and distorted conformation are very close in energy and the two are observable as an equilibrium mixture in the solution phase in acetone. Furthermore, the presence of substituents or nearby cations strongly influences the conformation. See also * Azepine * Pyrrole * Cyclononatetraene * (2Z,4Z,6Z,8Z)-Thionine * Oxonine Oxonine is an unsaturated heterocycle of nine atoms, with an oxygen replacing a carbon at one position. Oxonine is a nonaromatic compound. [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Oxonine
Oxonine is an unsaturated heterocycle of nine atoms, with an oxygen replacing a carbon Carbon () is a chemical element with the symbol C and atomic number 6. It is nonmetallic and tetravalent In chemistry, the valence (US spelling) or valency (British spelling) of an element is the measure of its combining capacity with o ... at one position. Oxonine is a nonaromatic compound. D. O. Tymoshenko See also * Azonine * Furan * Cyclononatetraene * Oxepin * (2Z,4Z,6Z,8Z)-ThionineReferences Oxygen heterocycles Heterocyclic compounds with 1 ring Fully conjugated nonaromatic rings Nine-membered rings {{Heterocyclic-stub ...[...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sulfur
Sulfur (or sulphur in British English) is a chemical element with the symbol S and atomic number 16. It is abundant, multivalent and nonmetallic. Under normal conditions, sulfur atoms form cyclic octatomic molecules with a chemical formula S8. Elemental sulfur is a bright yellow, crystalline solid at room temperature. Sulfur is the tenth most abundant element by mass in the universe and the fifth most on Earth. Though sometimes found in pure, native form, sulfur on Earth usually occurs as sulfide and sulfate minerals. Being abundant in native form, sulfur was known in ancient times, being mentioned for its uses in ancient India, ancient Greece, China, and ancient Egypt. Historically and in literature sulfur is also called brimstone, which means "burning stone". Today, almost all elemental sulfur is produced as a byproduct of removing sulfur-containing contaminants from natural gas and petroleum.. Downloahere The greatest commercial use of the element is the production o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Carbon
Carbon () is a chemical element with the symbol C and atomic number 6. It is nonmetallic and tetravalent In chemistry, the valence (US spelling) or valency (British spelling) of an element is the measure of its combining capacity with other atoms when it forms chemical compounds or molecules. Description The combining capacity, or affinity of an ...—its atom making four electrons available to form covalent bond, covalent chemical bonds. It belongs to group 14 of the periodic table. Carbon makes up only about 0.025 percent of Earth's crust. Three Isotopes of carbon, isotopes occur naturally, Carbon-12, C and Carbon-13, C being stable, while Carbon-14, C is a radionuclide, decaying with a half-life of about 5,730 years. Carbon is one of the Timeline of chemical element discoveries#Ancient discoveries, few elements known since antiquity. Carbon is the 15th Abundance of elements in Earth's crust, most abundant element in the Earth's crust, and the Abundance of the c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aromatic
In chemistry, aromaticity is a chemical property of cyclic ( ring-shaped), ''typically'' planar (flat) molecular structures with pi bonds in resonance (those containing delocalized electrons) that gives increased stability compared to saturated compounds having single bonds, and other geometric or connective non-cyclic arrangements with the same set of atoms. Aromatic rings are very stable and do not break apart easily. Organic compounds that are not aromatic are classified as aliphatic compounds—they might be cyclic, but only aromatic rings have enhanced stability. The term ''aromaticity'' with this meaning is historically related to the concept of having an aroma, but is a distinct property from that meaning. Since the most common aromatic compounds are derivatives of benzene (an aromatic hydrocarbon common in petroleum and its distillates), the word ''aromatic'' occasionally refers informally to benzene derivatives, and so it was first defined. Nevertheless, many ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Thiepine
In organic chemistry, thiepine (or thiepin) is an unsaturated seven-membered heterocyclic compound, with six carbon atoms and one sulfur atom. The parent compound, C6H6S is unstable and is predicted to be antiaromatic. Bulky derivatives have been isolated and shown by X-ray crystallography to have nonplanar C6S ring. Theoretical studies suggest that thiepine would eliminate a sulfur atom to form benzene. The intermediate is this process is the bicycle thianorcaradiene. In the complex with (η4-C6H6S)Fe(CO)3, the ring is stable.Nishino, K.; Takagi, M.; Kawata, T.; Murata, I.; Inanaga, J.; Nakasuji, K., "Thiepine-iron tricarbonyl: stabilization of thermally labile parent thiepine by transition metal complexation", J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1991, volume 113, 5059-5060. Benzothiepines have one fused benzene group and ''dibenzothiepines'' such as dosulepin and zotepine have two fused benzene groups. Damotepine is another thiepin derivative. See also * Thiazepines Thiazepines are ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cyclononatetraene
Cyclononatetraene is an organic compound with the formula C9H10. It was first prepared in 1969 by protonation of the corresponding aromatic anion (described below). It is unstable and isomerizes with a half-life of 50 minutes at room temperature to 3a,7a-dihydro-1''H-''indene via a thermal 6π disrotatory electrocyclic ring closing. Upon exposure to ultraviolet light, it undergoes a photochemical 8π electrocyclic ring closing to give bicyclo .1.0ona-2,4,6-triene. Cyclononatetraenyl anion Cyclononatetraenyl anion is a 10π aromatic system. Two isomers of the cyclononatetraenyl anion are known: the ''trans'',''cis'',''cis'',''cis'' isomer (" Pac-Man"-shaped) and the all-''cis'' isomer (a convex enneagon). The former is less stable and isomerizes to the latter upon warming from –40 °C to room temperature. The all-''cis'' isomer of C9H9− can be prepared by treatment of 9-chlorobicyclo .1.0ona-2,4,6-triene (1) with lithium or potassium metal. Despite the ring strain re ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
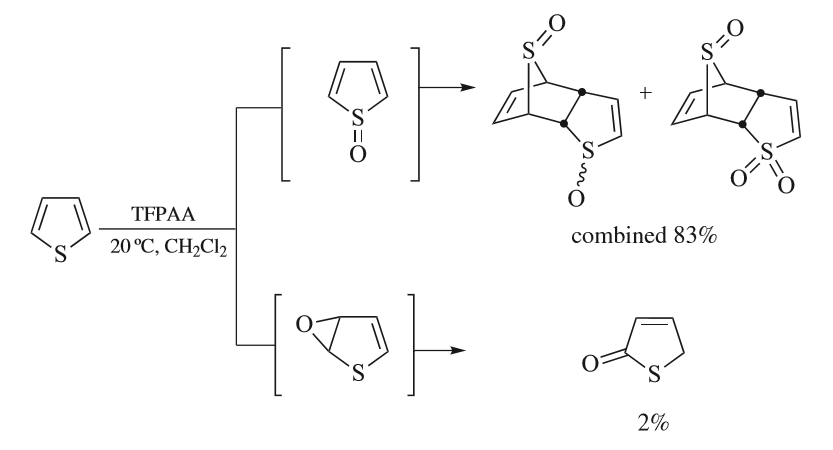
Thiophene
Thiophene is a heterocyclic compound with the formula C4H4S. Consisting of a planar five-membered ring, it is aromatic as indicated by its extensive substitution reactions. It is a colorless liquid with a benzene-like odor. In most of its reactions, it resembles benzene. Compounds analogous to thiophene include furan (C4H4O), selenophene (C4H4Se) and pyrrole (C4H4NH), which each vary by the heteroatom in the ring. Isolation and occurrence Thiophene was discovered as a contaminant in benzene. It was observed that isatin (an indole) forms a blue dye if it is mixed with sulfuric acid and crude benzene. The formation of the blue indophenin had long been believed to be a reaction of benzene itself. Viktor Meyer was able to isolate thiophene as the actual substance responsible for this reaction. Thiophene and especially its derivatives occur in petroleum, sometimes in concentrations up to 1–3%. The thiophenic content of oil and coal is removed via the hydrodesulfurization (HDS) ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sulfur Heterocycles
Sulfur (or sulphur in British English) is a chemical element with the Symbol (chemistry), symbol S and atomic number 16. It is abundance of the chemical elements, abundant, Polyvalency (chemistry), multivalent and nonmetallic. Under standard conditions for temperature and pressure, normal conditions, sulfur atoms form cyclic octatomic molecules with a chemical formula octasulfur, S8. Elemental sulfur is a bright yellow, crystalline solid at room temperature. Sulfur is the tenth most abundant element by mass in the universe and the fifth most on Earth. Though sometimes found in pure, native element minerals, native form, sulfur on Earth usually occurs as sulfide minerals, sulfide and sulfate minerals. Being abundant in native form, sulfur was known in ancient times, being mentioned for its uses in ancient India, ancient Greece, history of China#Ancient China, China, and ancient Egypt. Historically and in literature sulfur is also called brimstone, which means "burning stone". To ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Simple Aromatic Rings
Simple aromatic rings, also known as simple arenes or simple aromatics, are aromatic organic compounds that consist only of a conjugated planar ring system. Many simple aromatic rings have trivial names. They are usually found as substructures of more complex molecules ("substituted aromatics"). Typical simple aromatic compounds are benzene, indole, and pyridine. Simple aromatic rings can be heterocyclic if they contain non-carbon ring atoms, for example, oxygen, nitrogen, or sulfur. They can be monocyclic as in benzene, bicyclic as in naphthalene, or polycyclic as in anthracene. Simple monocyclic aromatic rings are usually five-membered rings like pyrrole or six-membered rings like pyridine. Fused/condensed aromatic rings consist of monocyclic rings that share their connecting bonds. Heterocyclic aromatic rings The nitrogen (N)-containing aromatic rings can be separated into basic aromatic rings that are easily protonated, and form aromatic cations and salts (e.g., pyridini ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |


.png)