|
Xia Dynasty
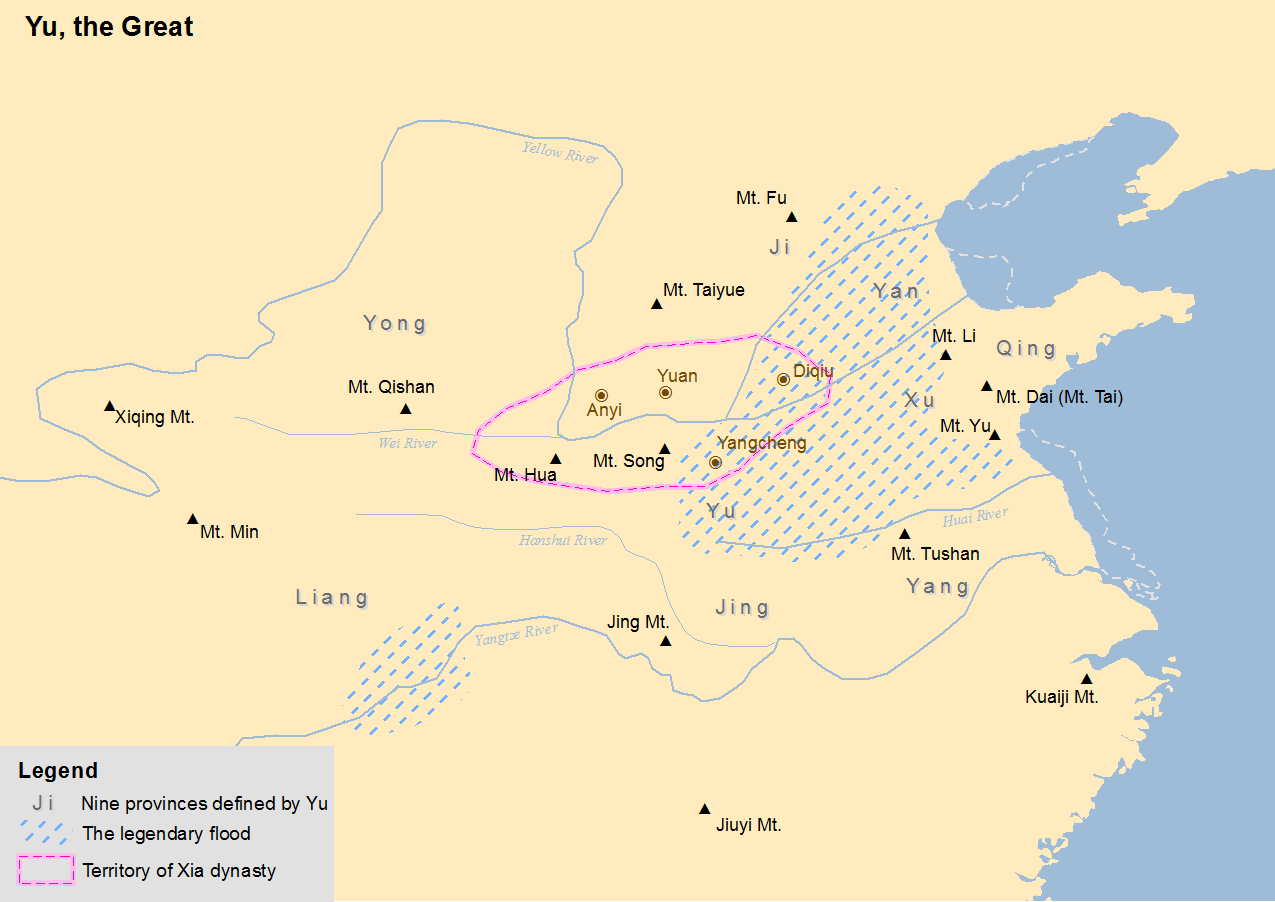
The Xia dynasty () is the first dynasty in traditional Chinese historiography. According to tradition, the Xia dynasty was established by the legendary Yu the Great, after Shun, the last of the Five Emperors, gave the throne to him. In traditional historiography, the Xia was later succeeded by the Shang dynasty. There are no contemporaneous records of the Xia, who are not mentioned in the oldest Chinese texts, since the earliest oracle bone inscriptions date from the late Shang period (13th century BC). The earliest mentions occur in the oldest chapters of the '' Book of Documents'', which report speeches from the early Western Zhou period and are accepted by most scholars as dating from that time. The speeches justify the Zhou conquest of the Shang as the passing of the Mandate of Heaven and liken it to the succession of the Xia by the Shang. That political philosophy was promoted by the Confucian school in the Eastern Zhou period. The succession of dynasties was incorpor ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Monarchy
A monarchy is a government#Forms, form of government in which a person, the monarch, is head of state for life or until abdication. The legitimacy (political)#monarchy, political legitimacy and authority of the monarch may vary from restricted and largely symbolic (constitutional monarchy), to fully autocracy, autocratic (absolute monarchy), and can expand across the domains of the Executive (government), executive, legislature, legislative, and judiciary, judicial. The Order of succession, succession of monarchs in many cases has been hereditary monarchy, hereditical, often building dynasty, dynastic periods. However, elective monarchy, elective and Self-proclaimed monarchy, self-proclaimed monarchies have also happened. Aristocracy (class), Aristocrats, though not inherent to monarchies, often serve as the pool of persons to draw the monarch from and fill the constituting institutions (e.g. Diet (assembly), diet and royal court, court), giving many monarchies oligarchy, ol ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
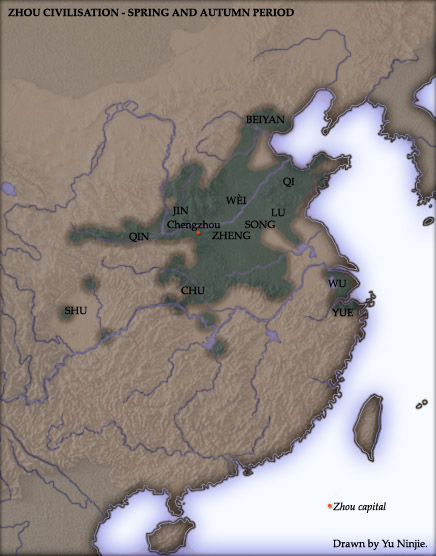
Eastern Zhou
The Eastern Zhou (; zh, c=, p=Dōngzhōu, w=Tung1-chou1, t= ; 771–256 BC) was a royal dynasty of China and the second half of the Zhou dynasty. It was divided into two periods: the Spring and Autumn and the Warring States. History In 770 BCE, the capital of the Zhou Kingdom was moved from Haojing (Chang'an County in Xi'an City) to Luoyi (known today as Luoyang, Henan Province). This brought about the beginning of the Eastern Zhou dynasty (as opposed to Western Zhou dynasty), so named due to Luoyi being situated to the east of Haojing. Over 25 kings reigned over the Eastern Zhou Dynasty, lasting 515 years in all. With the death of King You of Zhou, the last king of the Western Zhou Dynasty, ascended Crown Prince Yijiu was proclaimed the new king by the nobles from the states of Zheng, Lü, Qin and the Marquess of Shen. He was King Ping of Zhou. In the second year of his reign, he moved the capital east to Luoyi as Quanrong invaded Haojing, indicating the end of the W ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Yellow Emperor
The Yellow Emperor, also known as the Yellow Thearch or by his Chinese name Huangdi (), is a deity ('' shen'') in Chinese religion, one of the legendary Chinese sovereigns and culture heroes included among the mytho-historical Three Sovereigns and Five Emperors and cosmological Five Regions' Highest Deities (). Calculated by Jesuit missionaries on the basis of Chinese chronicles and later accepted by the twentieth-century promoters of a universal calendar starting with the Yellow Emperor, Huangdi's traditional reign dates are 2697–2597 or 2698–2598 BC. Huangdi's cult became prominent in the late Warring States and early Han dynasty, when he was portrayed as the originator of the centralized state, as a cosmic ruler, and as a patron of esoteric arts. A large number of texts – such as the '' Huangdi Neijing'', a medical classic, and the '' Huangdi Sijing'', a group of political treatises – were thus attributed to him. Having waned in influence during most of th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Han Chinese
The Han Chinese () or Han people (), are an East Asian ethnic group native to China. They constitute the world's largest ethnic group, making up about 18% of the global population and consisting of various subgroups speaking distinctive varieties of the Chinese language. The estimated 1.4 billion Han Chinese people, worldwide, are primarily concentrated in the People's Republic of China (including Mainland China, Hong Kong and Macau) where they make up about 92% of the total population. In the Republic of China (Taiwan), they make up about 97% of the population. People of Han Chinese descent also make up around 75% of the total population of Singapore. Originating from Northern China, the Han Chinese trace their cultural ancestry to the Huaxia, the confederation of agricultural tribes living along the Yellow River. This collective Neolithic confederation included agricultural tribes Hua and Xia, hence the name. They settled along the Central Plains around the middle ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Huaxia
''Huaxia'' (華夏, ) is a historical concept representing the Chinese nation, and came from the self-awareness of a common cultural ancestry by the various confederations of pre-Qin ethnic ancestors of Han people. Etymology The earliest extant authentic attestion of the concept ''Huáxià'' is in the historical narrative and commentary Zuo zhuan (finished around 300 BCE). In Zuo zhuan, Huaxia refers to the central states (中國 '' Zhōngguó'') in the Yellow River valley, dwelt by the Huaxia people, ethnically equivalent to Han Chinese in pre-imperial discourses. According to Confucianist Kong Yingda's "True Meaning of '' Chunqiu Zuo zhuan''", ''xià'' () "grand" signified the "greatness" () in the ceremonial etiquettes of the central states, while ''huá'' () "flower" or "blossom" was used in reference to the "beauty" () in the clothing that those states' denizens wore. History Origin Han historian Sima Qian asserts that Xia was the name of the state enfeoffed ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sima Qian
Sima Qian (; ; ) was a Chinese historian of the early Han dynasty (206AD220). He is considered the father of Chinese historiography for his ''Records of the Grand Historian'', a general history of China covering more than two thousand years beginning from the rise of the legendary Yellow Emperor and the formation of the first Chinese polity to the reigning sovereign of Sima Qian's time, Emperor Wu of Han. As the first universal history of the world as it was known to the ancient Chinese, the ''Records of the Grand Historian'' served as a model for official history-writing for subsequent Chinese dynasties and the Chinese cultural sphere (Korea, Vietnam, Japan) up until the 20th century. Sima Qian's father Sima Tan first conceived of the ambitious project of writing a complete history of China, but had completed only some preparatory sketches at the time of his death. After inheriting his father's position as court historian in the imperial court, he was determined to fulfill ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Classic Of History
The ''Book of Documents'' (''Shūjīng'', earlier ''Shu King'') or ''Classic of History'', also known as the ''Shangshu'' (“Venerated Documents”), is one of the Five Classics of ancient Chinese literature. It is a collection of rhetorical prose attributed to figures of ancient China, and served as the foundation of Chinese political philosophy for over 2,000 years. The ''Book of Documents'' was the subject of one of China's oldest literary controversies, between proponents of different versions of the text. A version was preserved from Qin Shi Huang's burning of books and burying of scholars by scholar Fu Sheng, in 29 sections (''pian'' 篇). This group of texts were referred to as "Modern Script" ''jinwen'' 今文, because written with the script in use at the beginning of the Western Han dyansty. According to Western Han dynasty documents, new textual material was discovered in the wall of Confucius' family estate in Qufu by his descendant Kong Anguo in the late ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nine Provinces Of China
The term Nine Provinces or Nine Regions (), is used in ancient Chinese histories to refer to territorial divisions or islands during the Xia and Shang dynasties and has now come to symbolically represent China. "Province" is the word used to translate '' zhou'' (州) – since before the Tang dynasty (618–907 CE), it was the largest Chinese territorial division. Although the current definition of the Nine Provinces can be dated to the Spring and Autumn and Warring States periods, it was not until the Eastern Han dynasty that the Nine Provinces were treated as actual administrative regions. Different interpretations of the Nine Provinces The ''Rongcheng Shi'' bamboo slips from the Chu state has the earliest interpretation of the Nine Provinces, but these early descriptions differ widely from the currently recognized Nine Provinces. The Nine Provinces, according to the ''Rongcheng Shi'', are Tu (涂), Jia (夾), Zhang (竞), Ju (莒), Ou (藕), Jing (荊), Yang (� ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Xia–Shang–Zhou Chronology Project
The Xia–Shang–Zhou Chronology Project () was a multi-disciplinary project commissioned by the People's Republic of China in 1996 to determine with accuracy the location and time frame of the Xia, Shang, and Zhou dynasties. The project was directed by professor Li Xueqin of Tsinghua University in Beijing, and involved around 200 experts. It used radiocarbon dating, archaeological dating methods, historical textual analysis, astronomy, and other methods to achieve greater temporal and geographic accuracy. Preliminary results were released in November 2000. However, several of the project's methods and conclusions have been disputed by other scholars. Background The traditional account of ancient China, represented by the ''Records of the Grand Historian'' written by Sima Qian in the Han dynasty, begins with the Three Sovereigns and Five Emperors, leading through a sequence of dynasties, the Xia, Shang and Zhou. Sima Qian felt able to give a year-by-year chronology bac ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
David Nivison
David Shepherd Nivison (January 17, 1923 – October 16, 2014) was an American Sinologist and scholar known for his publications on late imperial and ancient Chinese history, philology, and philosophy, and his 40 years as a professor at Stanford University. Nivison is known for his use of archaeoastronomy to accurately determine the date of the founding of the Zhou dynasty as 1045 BC instead of the traditional date of 1122 BC. Life and career David Shepherd Nivison was born on January 17, 1923, outside of Farmingdale, Maine. His great-uncle, Edwin Arlington Robinson, was a notable 19th-century American poet and a three-time recipient of the Pulitzer Prize. Nivison entered Harvard University in 1940, but, like many American men of his generation, his studies were interrupted by World War II. Nivison served in the United States Army Signal Corps as a Japanese translator, where he worked in a group organized by Edwin O. Reischauer. He returned to Harvard after the war's ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Conjunction (astronomy)
In astronomy, a conjunction occurs when two astronomical objects or spacecraft have either the same right ascension or the same ecliptic longitude, usually as observed from Earth. When two objects always appear close to the ecliptic—such as two planets, the Moon and a planet, or the Sun and a planet—this fact implies an apparent close approach between the objects as seen in the sky. A related word, '' appulse'', is the minimum apparent separation in the sky of two astronomical objects. Conjunctions involve either two objects in the Solar System or one object in the Solar System and a more distant object, such as a star. A conjunction is an apparent phenomenon caused by the observer's perspective: the two objects involved are not actually close to one another in space. Conjunctions between two bright objects close to the ecliptic, such as two bright planets, can be seen with the naked eye. The astronomical symbol for conjunction is (Unicode U+260C ☌). The conjunct ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Liu Xin (scholar)
Liu Xin (; c. 50 BCE – 23 CE), courtesy name Zijun (), was a Chinese astronomer, mathematician, historian, librarian and politician during the Western Han Dynasty (206 BCE – 9 CE) and Xin Dynasty (9 – 23 CE). He later changed his name to Liu Xiu () due to the naming taboo of Emperor Ai of Han. He was the son of Confucian scholar Liu Xiang (77 – 6 BCE) and an associate of other prominent thinkers such as the philosopher Huan Tan (c. 43 BCE – 28 CE). Liu founded the Old Text school of Confucianism. Early life Liu Xin was the son of Confucian scholar Liu Xiang (77 – 6 BCE). Liu was a distant relative of Liu Bang, the founder of the Han dynasty, and was thus a member of the ruling dynastic clan (the Liu family). Liu Xin's paternal grandfather ranked as a marquess. Librarian As a curator of the imperial library he was the first to establish a library classification system and the first book notation system. At this time the library catalog was writte ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |